1/ Antiepileptic drugs: a constantly evolving frontier- like many other fields in #Neurology. It’s hard to know about every single medication in-depth. Here, I attempted to make AEDs simple, easy to understand and a handy layout of important facts to know about #AED #epilepsy.
2/ Let’s begin with understanding what is synapse and how it works, then only we can understand how the AEDs work. Look at the cartoon I created from references (acknowledged at the end) with help of an amazing app #Procreate. I’m a fan of @PeterMLawrence1 great art work !! 

3/ Looks chaotic?Let’s break it down. You got this!
There are 2 main types of synapses.
A)Excitatory synapse-neurotransmitter is Glutamate- receptors are AMPA and NMDA
B)Inhibitory synapse-neurotransmitter is GABA-receptor is GABAa binding site on ligand gated Cl- channel
There are 2 main types of synapses.
A)Excitatory synapse-neurotransmitter is Glutamate- receptors are AMPA and NMDA
B)Inhibitory synapse-neurotransmitter is GABA-receptor is GABAa binding site on ligand gated Cl- channel
4/ In addition, there are ion channels which cause depolarization or degranulation of transmitter vesicles.
A)Voltage gated Na+
B)Voltage gated K+ (KCNQ or Kv7)
C)alpha-1 subunit of Voltage gated T-type Ca++(low volt)
D)alpha-2-delta subunit of Voltage gated N-type Ca++(hi volt)
A)Voltage gated Na+
B)Voltage gated K+ (KCNQ or Kv7)
C)alpha-1 subunit of Voltage gated T-type Ca++(low volt)
D)alpha-2-delta subunit of Voltage gated N-type Ca++(hi volt)
5/ A few more things to know:
A) GABA amino-transferase - mitochondrial enzyme degrades GABA
B) GABA transporter-1 - reuptake of GABA
C) Carbonic anhydrase enzyme in mitochondria
D) CB1 pre-synaptic receptor - regulates degranulation of Glutamate and GABA (PMID 11316486)
A) GABA amino-transferase - mitochondrial enzyme degrades GABA
B) GABA transporter-1 - reuptake of GABA
C) Carbonic anhydrase enzyme in mitochondria
D) CB1 pre-synaptic receptor - regulates degranulation of Glutamate and GABA (PMID 11316486)
6/ Now since we got the basics, let’s see how to stop a seizure:
A) Enhancing GABA effect
B) Inhibiting Glutamate effect
C) Preventing neuronal depolarization (by stabilizing resting membrane action potential) and degranulation
D) You guessed it-there’s always some random things!
A) Enhancing GABA effect
B) Inhibiting Glutamate effect
C) Preventing neuronal depolarization (by stabilizing resting membrane action potential) and degranulation
D) You guessed it-there’s always some random things!
7/ Let’s explore each strategy 101:
A)Enhancing GABA effect by-
i] Prolonged/frequent/facilitated opening of Ligand gated Cl- channel to cause influx in Cl- causing hyperpolarization of post synaptic neuron
ii] Inhibiting GABA reuptake
iii] Inhibiting GABA degradation.
A)Enhancing GABA effect by-
i] Prolonged/frequent/facilitated opening of Ligand gated Cl- channel to cause influx in Cl- causing hyperpolarization of post synaptic neuron
ii] Inhibiting GABA reuptake
iii] Inhibiting GABA degradation.
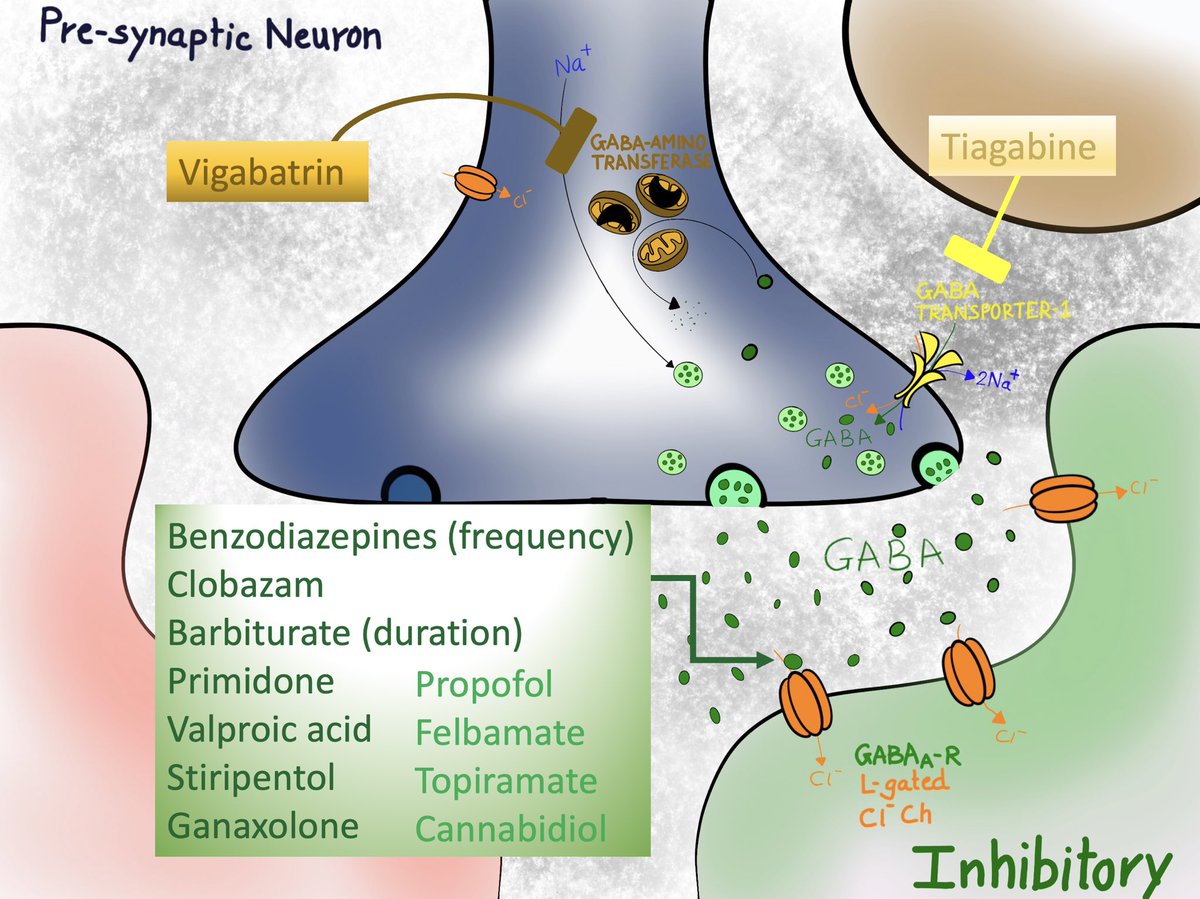
Ai] = bunch of examples as listed in the cartoon. Drugs in bold have principle mechanism of action at this receptor and the ones in light color, have variable effects.
Aii] GABA transporter-1 inhibitor = Tiagabine
Aiii] GABA amino-transferase inhibitor = Vigabatrin
Aii] GABA transporter-1 inhibitor = Tiagabine
Aiii] GABA amino-transferase inhibitor = Vigabatrin
8/
B) inhibiting Glutamate effect by-
i] Preventing release of Glutamate from vesicles by blocking SV2A receptor
ii] Blocking AMPA receptor mediated Na+ influx and depolarization of post synaptic neuron
iii] Blocking NMDA receptor mediated Na+ and Ca++ influx
B) inhibiting Glutamate effect by-
i] Preventing release of Glutamate from vesicles by blocking SV2A receptor
ii] Blocking AMPA receptor mediated Na+ influx and depolarization of post synaptic neuron
iii] Blocking NMDA receptor mediated Na+ and Ca++ influx
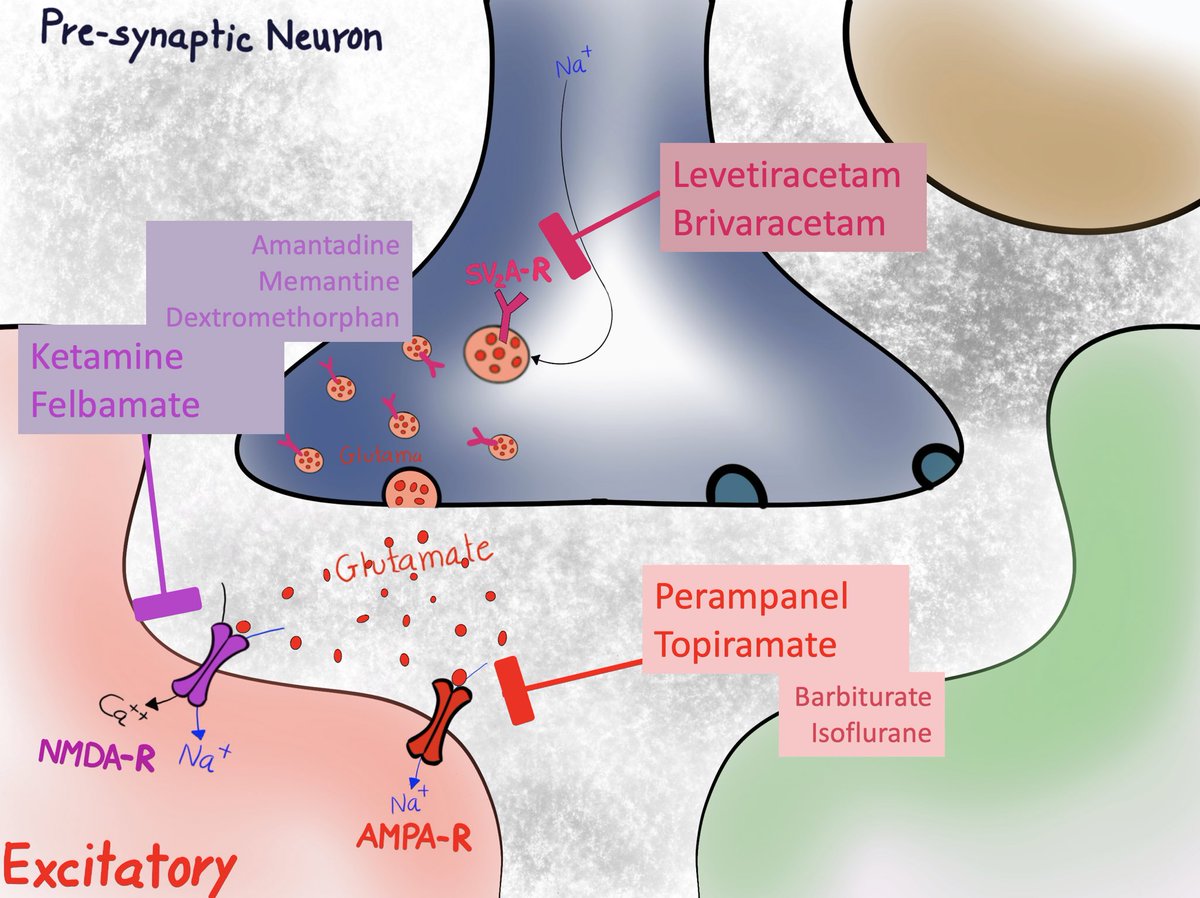
Bi] SV2A blockers = Levetiracetam, Brivaracetam
Bii] AMPA blockers =Perampanel, Topiramate; variable - Barbiturate, Isoflurane
Biii] NMDA blockers = Ketamine, Felbamate; less potent (not used for seizure) = Amantadine, Memantine, Dextromethorphan
Bii] AMPA blockers =Perampanel, Topiramate; variable - Barbiturate, Isoflurane
Biii] NMDA blockers = Ketamine, Felbamate; less potent (not used for seizure) = Amantadine, Memantine, Dextromethorphan
9/
C) Preventing neuronal depolarization and degranulation by ion channels-
i] VGNaC-pre-synaptic neuronal resting membrane
ii] VGKC-pre and excitatory post-synaptic
iii] VGCC T-type(low volt)-thalamo-cortical neuron stabilization
iv] VGCC N-type(hi volt)-prevent degranulation
C) Preventing neuronal depolarization and degranulation by ion channels-
i] VGNaC-pre-synaptic neuronal resting membrane
ii] VGKC-pre and excitatory post-synaptic
iii] VGCC T-type(low volt)-thalamo-cortical neuron stabilization
iv] VGCC N-type(hi volt)-prevent degranulation

Ci] Na+ channel blockers= too many!!
All block fast channels except Lacosamide (slow channel)
Cii] K+ channel blocker=Ezogabine
Ciii] T-type Ca++ channel=Ethosuximide, Valproic acid, Zonisamide
Civ] N-type Ca++ channel=Gabapentine, Pregabalin; variable=Topiramate, Lamotrigine
All block fast channels except Lacosamide (slow channel)
Cii] K+ channel blocker=Ezogabine
Ciii] T-type Ca++ channel=Ethosuximide, Valproic acid, Zonisamide
Civ] N-type Ca++ channel=Gabapentine, Pregabalin; variable=Topiramate, Lamotrigine
10/
D) Remember random things??
i] Mitochondrial Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor effective due to following:
-epileptic neurons have high CAse activity
-increase CO2 intracellularly-decrease neuronal excitability
-stabilizing pH
ii] CB1 receptor regulates degranulation.
D) Remember random things??
i] Mitochondrial Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor effective due to following:
-epileptic neurons have high CAse activity
-increase CO2 intracellularly-decrease neuronal excitability
-stabilizing pH
ii] CB1 receptor regulates degranulation.

Di] By various mechanisms, Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors prevent seizures= Acetazolamide, Sulthamine, secondary action=Topiramate, Zonisamide. In fact, they have been used since 1953. Acetazolamide has been used in Catamenial epilepsy.
Dii] CB1 receptor modulation=Cannabidiol
Dii] CB1 receptor modulation=Cannabidiol
11/ Exhausted? Phew…. You made it !!!
12/ Names of AED can be confusing. But if we understand mechanism by which they act, we can’t be fooled.
Let’s answer the question below.
Which of the following AEDs, do not bind on GABAa receptor?
Let’s answer the question below.
Which of the following AEDs, do not bind on GABAa receptor?
13/ You got the gist !!
Many AEDs have ‘gab’ in their names (strange, right? You’d think they’ll name drugs properly!!) but have nothing to do with GABA receptor on Cl- channel.
But wait !!
What about Baclofen?? Doesn’t it act on GABA too?
Many AEDs have ‘gab’ in their names (strange, right? You’d think they’ll name drugs properly!!) but have nothing to do with GABA receptor on Cl- channel.
But wait !!
What about Baclofen?? Doesn’t it act on GABA too?
14/ here’s the explanation;
Baclofen exerts it’s effect through GABAb, which is a G-protein coupled Metaboceptor, which is present pre and post synaptic, in CNS and PNS, acting on slow K+ and Ca++ channels. It lacks antiepileptic-property.
Cl- channel has GABAa receptor.
Baclofen exerts it’s effect through GABAb, which is a G-protein coupled Metaboceptor, which is present pre and post synaptic, in CNS and PNS, acting on slow K+ and Ca++ channels. It lacks antiepileptic-property.
Cl- channel has GABAa receptor.
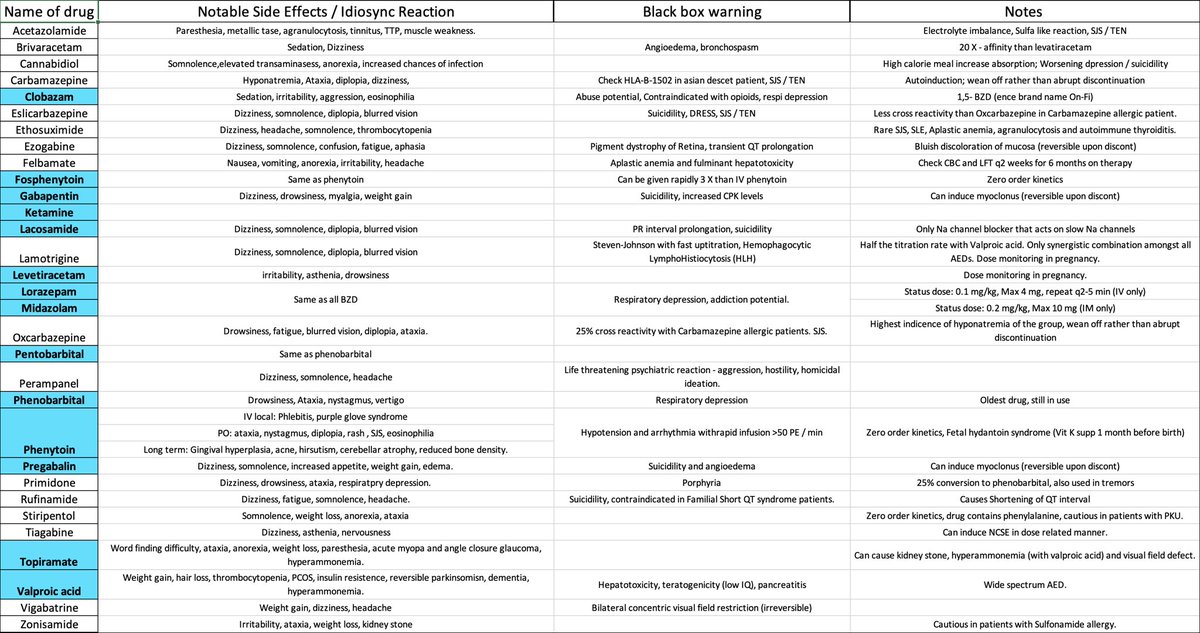
15/ I wanted to compile common side effects and warnings of AEDs, so I have made a spreadsheet.
Highlighted in blue are the drugs we use commonly in NeuroICU @EmoryNeuroCrit and the others are usually outpatient based, unless patient is already on it.
(I’m biased !!)
Highlighted in blue are the drugs we use commonly in NeuroICU @EmoryNeuroCrit and the others are usually outpatient based, unless patient is already on it.
(I’m biased !!)
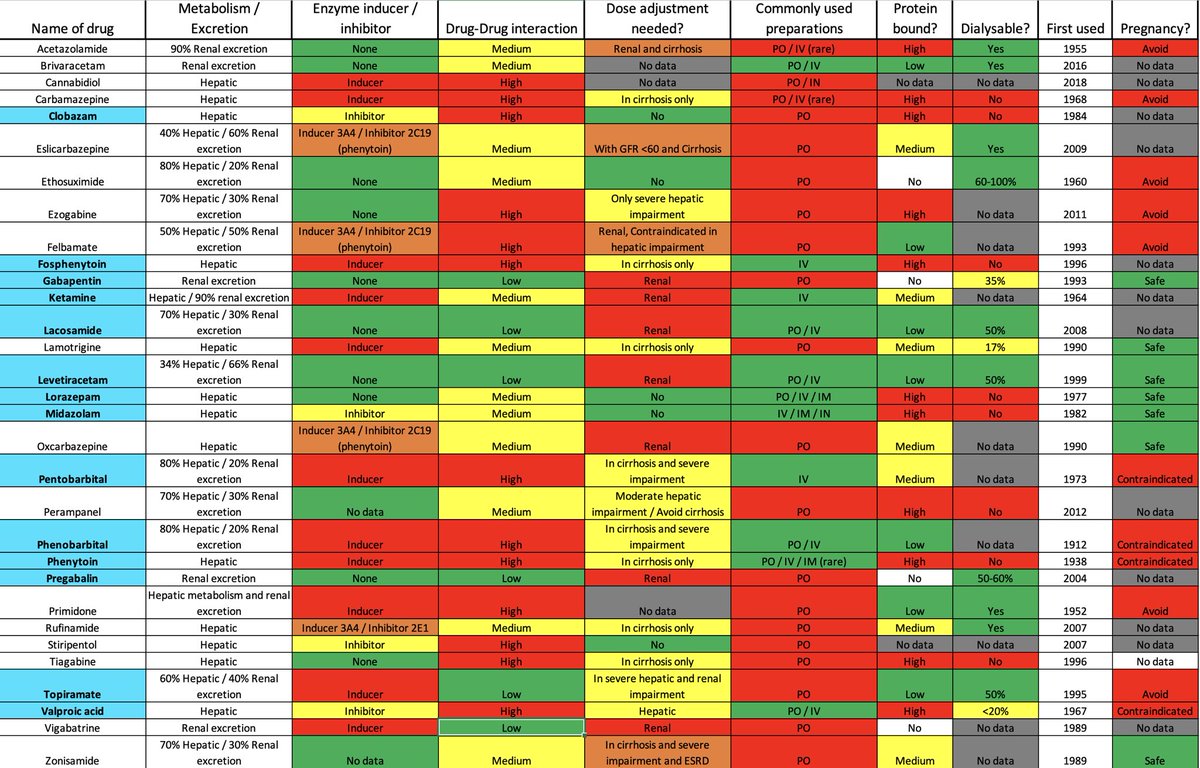
16/ Wait, there’s more:
Below, you’ll find common pharmacokinetic properties of AEDs. So next time, if you wonder- if this AED is dialysable OR do you need dose adjustment OR can you give it to pregnant patient?
Well, here’s a #OnePageSummary of everything you need to know.
Below, you’ll find common pharmacokinetic properties of AEDs. So next time, if you wonder- if this AED is dialysable OR do you need dose adjustment OR can you give it to pregnant patient?
Well, here’s a #OnePageSummary of everything you need to know.
17/ Ok, now we’re done, seriously!! Not kidding….
18/ Here are some reference that I used to make this.
PMID: 22635167, 31303443
@ContinuumAAN CONTINUUM (MINNEAP MINN) 2019;25(2, EPILEPSY):508–536.
The cartoon is inspired from DOI 10.1007/s40263-016-0384-x
Sketches entirely drafted @Procreate - check this out !
PMID: 22635167, 31303443
@ContinuumAAN CONTINUUM (MINNEAP MINN) 2019;25(2, EPILEPSY):508–536.
The cartoon is inspired from DOI 10.1007/s40263-016-0384-x
Sketches entirely drafted @Procreate - check this out !
19/ I’m always open to suggestions / corrections , so if any, please let me know. I’ll be happy to put addendum.
@DeeptiZutshiMD @RebeccaFasanoMD @drhibahaider @SrinivasMeghana @CajalButterfly @feras_akbik @Capt_Ammonia @caseyalbin @DeniseFChen
@DeeptiZutshiMD @RebeccaFasanoMD @drhibahaider @SrinivasMeghana @CajalButterfly @feras_akbik @Capt_Ammonia @caseyalbin @DeniseFChen
20/ Thank you for your patience. This was a long post.
Thanks to #DavidPearce for efforts to build #canvas database. I’m happy to be able to contribute to it. Looking forward to uploading this literate and a few more in video format soon.
Thanks to #DavidPearce for efforts to build #canvas database. I’m happy to be able to contribute to it. Looking forward to uploading this literate and a few more in video format soon.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh










