Here is a summary of my second lecture for The Norwegian Society for the Conservation of Nature on the topic of green growth. Question of the day: Is decoupling happening?
THREAD
THREAD
The best way to answer this question is to read the systematic review of the literature conducted by Helmut Haberl and fifteen colleagues in 2020.
iopscience.iop.org/article/10.108…
iopscience.iop.org/article/10.108…

The first finding of that review is that most studies focus on greenhouse gas emissions and energy use, leaving out all other environmental pressures. Also: only 8% of all decoupling studies use consumption-based indicators. 

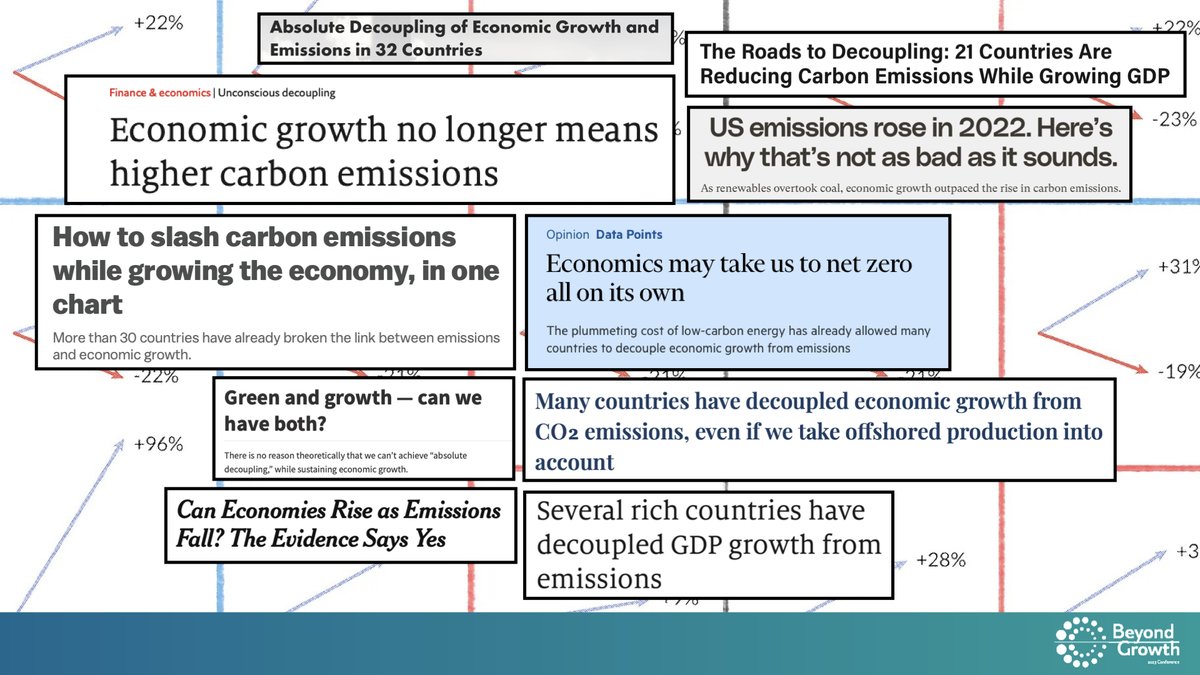
Main result of the study: absolute decoupling is more the exception than the rule. And when it happens, it's very very tiny. 

So basically, they agree with the conclusions of Decoupling Debunked, published exactly one year before.
eeb.org/library/decoup…
eeb.org/library/decoup…

Here is another study that is worth looking at, especially because it's the one most cited by green growth optimists.
For more on this study: unevenearth.org/2021/04/is-gre…
For more on this study: unevenearth.org/2021/04/is-gre…

To understand how small, compare what the UK has managed to decouple compare to what it needs to decouple. When talking about decoupling, size matters. 

If you want to watch the whole lecture, here it is:
END THREAD/
END THREAD/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh