Basic Linux 🐧Commands📜 For Text Manipulation
A thread🧵
Hello everyone👋, Today I'll be doing a quick, easy to follow thread🧵 on basic Linux commands for text manipulation.
#infosec #cybersecurity #Linux
A thread🧵
Hello everyone👋, Today I'll be doing a quick, easy to follow thread🧵 on basic Linux commands for text manipulation.
#infosec #cybersecurity #Linux

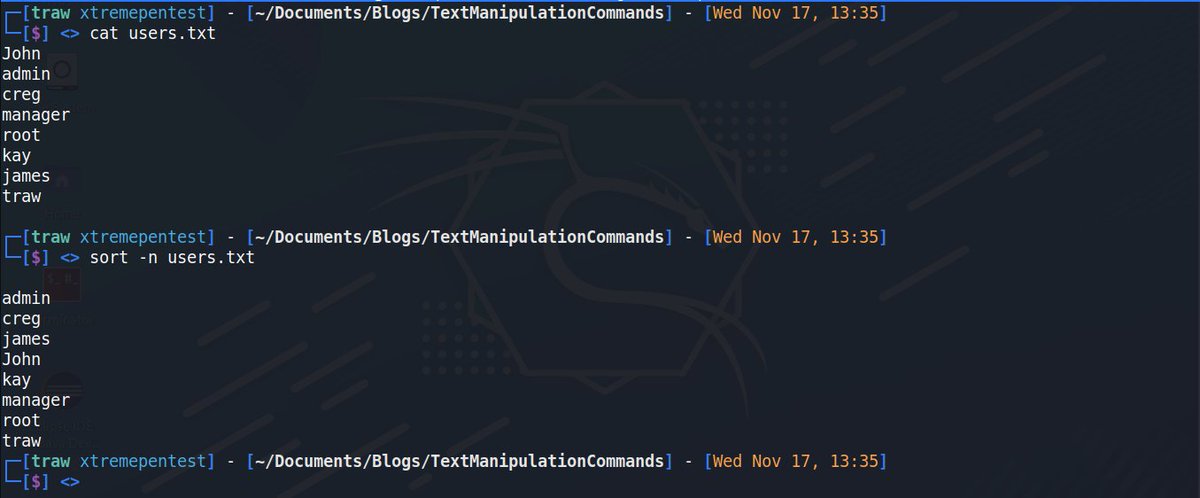
2. Cat🐧
The cat command is used concatenate files and print their contents on the standard output. In other words it's just used to display the contents of a file.
The cat command is used concatenate files and print their contents on the standard output. In other words it's just used to display the contents of a file.

3. Paste🐧
The paste command is similar to the cat command, it merges lines together in a file and make it a one huge single line.
The paste command is similar to the cat command, it merges lines together in a file and make it a one huge single line.

4. Head🐧
This command is used to display the first part of a file. Let's say we have a very long file and you just wanted to see the first couple of lines in this text file.
This command is used to display the first part of a file. Let's say we have a very long file and you just wanted to see the first couple of lines in this text file.
Well, this is when the head command comes into play, by default the head command will show you the first 10 lines in a file. 

You can also modify the line count to whatever you want, for example let's say I wanted to see the first -3 lines instead. From the picture below the -n stands for the number of lines we want to display. 

5. Tail🐧
Similar to the head command, the tail command lets you see the last 10 lines of a file by default. But you can always change it as well and specify the number of lines you want to display. Here I have chose to display the last 3 lines.
Similar to the head command, the tail command lets you see the last 10 lines of a file by default. But you can always change it as well and specify the number of lines you want to display. Here I have chose to display the last 3 lines.

7. Tac🐧
Similar to the cat command, the tac command concatenate and print files contents in reverse order. You can tell from the name that this command is the reverse version of the popular cat command.
Similar to the cat command, the tac command concatenate and print files contents in reverse order. You can tell from the name that this command is the reverse version of the popular cat command.

9. tr (Translate)🐧
The tr (translate) command allows you to translate a set of characters into another set of characters. It's also used to squeeze or delete characters from standard input and display the result to standard output.
The tr (translate) command allows you to translate a set of characters into another set of characters. It's also used to squeeze or delete characters from standard input and display the result to standard output.

On above screenshot we converted all the a -> A, b -> B and c -> C . Note that the number of characters on the first set should be equal to the number of characters on the second set. Let's try another example of translating characters. 

The tr command also supports the intimidating 😄regular expressions. Let's try an example of translating all lower case characters to uppercase characters using regex. 

10. Uniq (Unique)🐧
The uniq (unique) command is another useful tool for parsing text. It's used to omit/remove duplicates from a file, hence the name uniq.
The uniq (unique) command is another useful tool for parsing text. It's used to omit/remove duplicates from a file, hence the name uniq.

11. wc🐧
Word Count(wc) is used to print newline, word, and byte counts for each file. It display the number of lines, number of words and number of bytes, respectively.
Word Count(wc) is used to print newline, word, and byte counts for each file. It display the number of lines, number of words and number of bytes, respectively.

You can also explicitly specify what you want to display but using the l-, -w, or -c options which will displays number of lines, words, characters(bytes) respectively
let's try out to display the number of lines. Few free to also experiment with other options.
let's try out to display the number of lines. Few free to also experiment with other options.

12. nl🐧
Another command you can use to check the count of lines on a file is the nl (number lines) command.
Another command you can use to check the count of lines on a file is the nl (number lines) command.

13. grep🐧
The grep command is one of the most common text processing command you will use. It allows you to search files for characters that match a certain pattern.
The grep command is one of the most common text processing command you will use. It allows you to search files for characters that match a certain pattern.
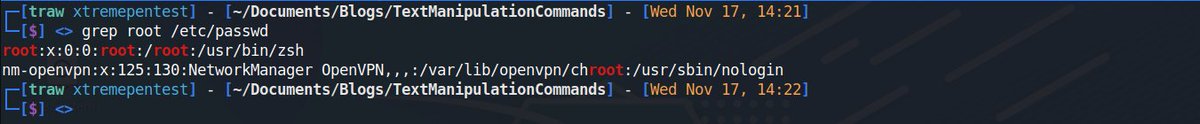
Grep has a lot of useful switches which I will not discuss😇, but you can also check grep man pages if you want to know more about this handy utility.
14. diff🐧
The diff command simply compares two text sources/text files and outputs their differences. It compares the files line by line to find the differences.
The diff command simply compares two text sources/text files and outputs their differences. It compares the files line by line to find the differences.

15. Cut🐧
The cut command can be used to remove/extract bytes, characters, and fields from files. Various parameters are used to specify what part or parts of the file are to be removed or displayed.
The cut command can be used to remove/extract bytes, characters, and fields from files. Various parameters are used to specify what part or parts of the file are to be removed or displayed.
That's it for today's thread! Thank💌 you for reading📚If you liked the thread and found it useful, give me a follow (@xtremepentest) for future Linux, Networking and Security content!. Be sure to also add some commands for text manipulation, would love to know them as well.😇
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh