Hello from Hong Kong - the weather has turned colder as we head towards the winter, which is intensifying EUR weakness as colder weather adds to the energy crisis as well as seasonal spike of Covid & thus lockdowns/protests. Jerome Powell got the job & key for USD & rates ⏫⏫🔥 

Since his confirmation again, note that no matter the administration (Trump or Biden), the Fed continues on w/ the same person in charge w/ relatively dovish policy as real rates super negative.
But Jerome Powell is more free to rock the boat now & markets price HIGHER rates.
But Jerome Powell is more free to rock the boat now & markets price HIGHER rates.

Look at markets' implied expectations of interest rates. On Bloomberg, type MIPR GO (weird to care about rates after decades of ZIRP) but rates markets are on the move & after the vol this year, it's heading one direction - upward. JPO talked about corrosive impact of CPI, so? 

So this is basically team "transitory" moving towards doing something about CPI & markets listened. It has listened & questioned the Fed mantra of QE tapering divorced from interest rates lift off & started selling bonds, esp the short-end. Here we are. USD rates matter globally. 

If the price of cash is less TRASHY, basically increasingly less negative as expectations of rates go up to narrow the gap w/ inflation, then RISK assets pay attention. And it isn't just risky assets. Relative value w/ others such as EUR. Let's take a looksie. Btw, PMIs out today 

To understand the relationship between FX & rates market, we must think in relative value & the CHANGE of that relative value.
Here u see markets expecting higher RATES in the US but look at the Eurozone, higher but by LESS than USD. Why? Well, it goes back to macro & monetary.
Here u see markets expecting higher RATES in the US but look at the Eurozone, higher but by LESS than USD. Why? Well, it goes back to macro & monetary.
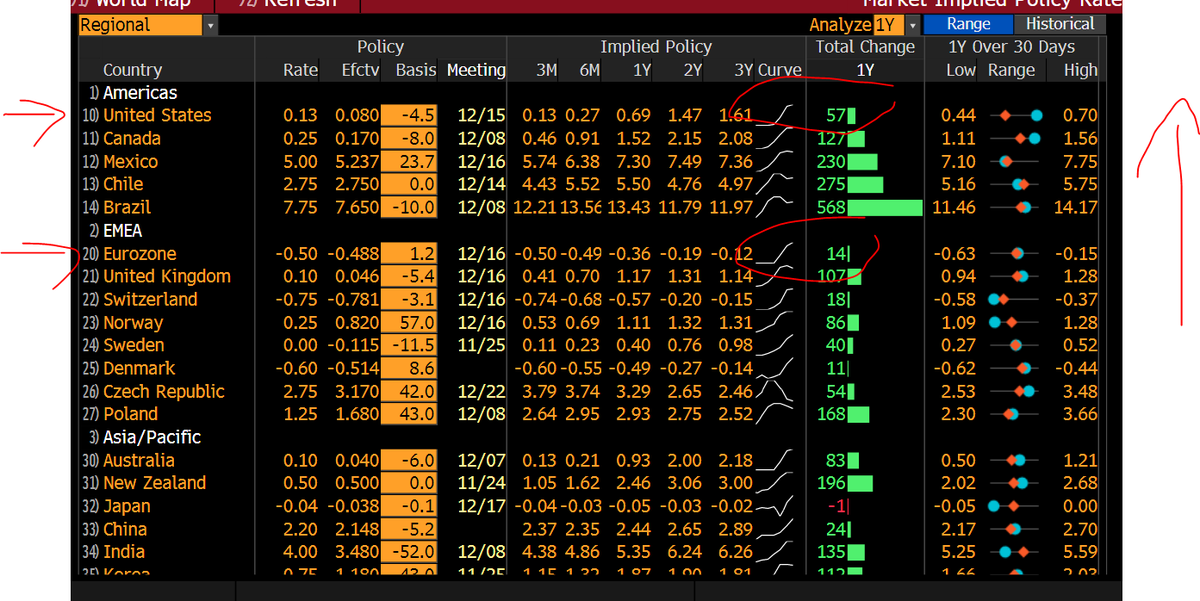
The price of the USD is its interest rates, which are going higher as expectations of a stronger economy + CPI = Fed tapering + higher interest rates in 22. What about the price of EUR? Well, higher but markets still sees NEGATIVE RATES. Why? PMIs were strong but starting to sag 

Why is it sagging? Covid-19 reaction function + energy crisis. Higher cases = now lockdowns in EU while in the US even w/ higher cases in the summer no lockdown. US & Europe differ in the energy crisis, one net exporter & the other importer. MOST KEY is monetary policy divergence 



Christine keeps saying that INFLATION IS TRANSITORY, as in even if it goes past the ECB 2% target, this lady isn't going to lift rates or reduce accommodation.
Look at CPI, hasn't been this high since 1996.
Jerome is saying differently. He's tapering & lately CPI is corrosive.
Look at CPI, hasn't been this high since 1996.
Jerome is saying differently. He's tapering & lately CPI is corrosive.
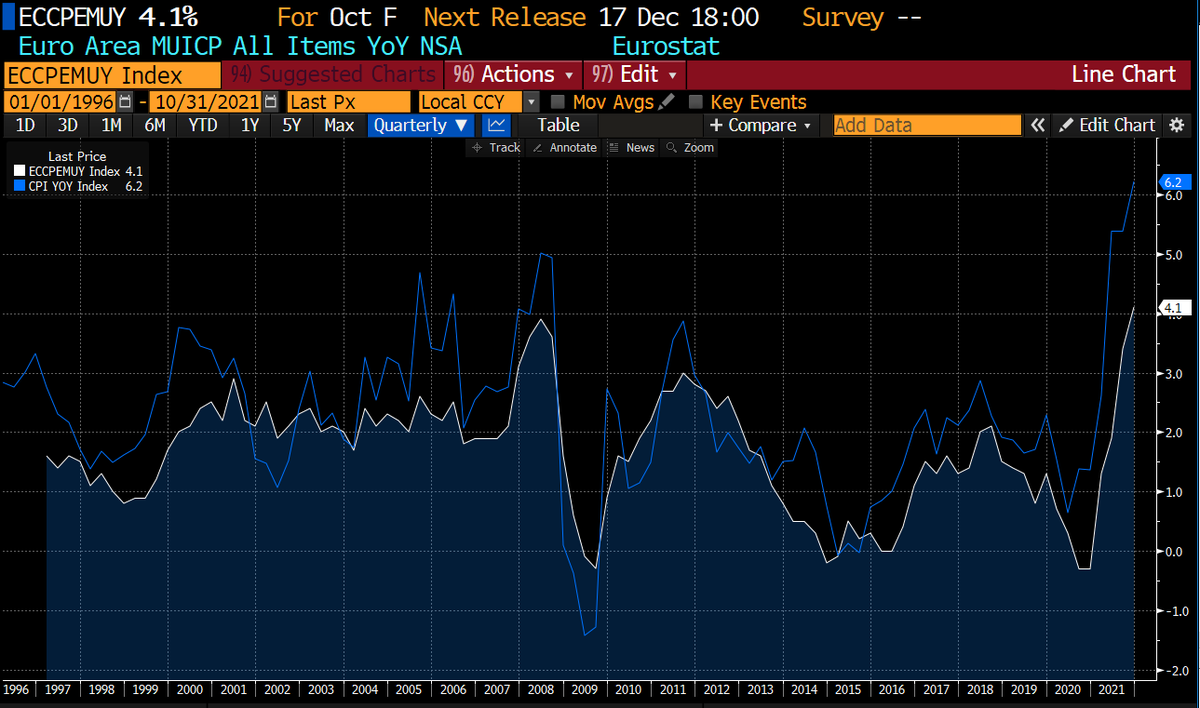
This chart is powerful right? How did we get here - inflation at all time since since the 1990s & central banks say negative interest rates still NEEDED.
Once you're NIRPED, hard to go PIRP. No matter what Draghi said, this isn't TEMPORARY.
And so, here we are. What about 2022?
Once you're NIRPED, hard to go PIRP. No matter what Draghi said, this isn't TEMPORARY.
And so, here we are. What about 2022?

I gotta go as this week is crazy busy given our Outlook coming out & I have to say I have had a lot of fun thinking about the Asia Pacific region locally, regionally and globally.
Learned a lot & frankly the exercise cements my passion to learn & important to sit back & read.👋🏻

Learned a lot & frankly the exercise cements my passion to learn & important to sit back & read.👋🏻


• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh