🧵 A thread on #StarHealth #starhealthipo
📽️Will post YouTube video tomorrow
You may skip initial tweets but do read last 7-8 tweets because that is where the key risks are and some of them are least discussed
Please like and retweet for better reach🙏
📽️Will post YouTube video tomorrow
You may skip initial tweets but do read last 7-8 tweets because that is where the key risks are and some of them are least discussed
Please like and retweet for better reach🙏
The good side: Why health insurance sector?
High Growth Industry
Huge Market Size Opportunity
Yet to catch up with worldwide average
Shift from public to private


High Growth Industry
Huge Market Size Opportunity
Yet to catch up with worldwide average
Shift from public to private


Good future opportunity size and growth prospects if India’s GDP can grow
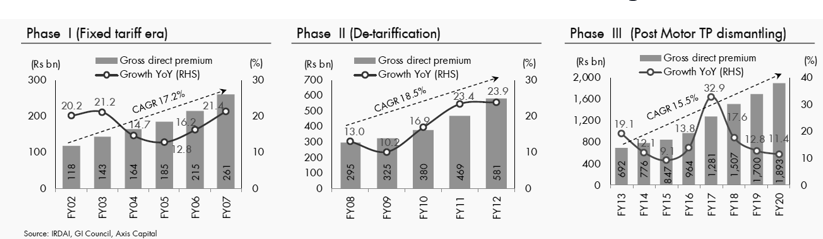
health insurance expected to grow at ~16% CAGR over FY20-30E with an assumption of ~53% penetration (penetration in USA at 91% as of CY17 ), 1% CAGR population growth of 1% CAGR and 6% medical inflation


health insurance expected to grow at ~16% CAGR over FY20-30E with an assumption of ~53% penetration (penetration in USA at 91% as of CY17 ), 1% CAGR population growth of 1% CAGR and 6% medical inflation



Decent industry dynamics with multiple listed players in general insurance space having reasonable premium and bottom-line growth and decent ROE 

So, given above, look at health insurance where #StarHealth operates. Health Insurance divided in 3 categories based on payor:
Retail: individuals and families
Group Health: For large corporate and SMEs for their employees.
Government Schemes: Introduced by the Govt for mass
Retail: individuals and families
Group Health: For large corporate and SMEs for their employees.
Government Schemes: Introduced by the Govt for mass
Health Insurance Industry Dynamics:
Unlike other segments, where PSU insures have lost market share, in retail health even private multi line insurers have ceded market share to SAHIs (standalone health - Star is leader in SAHI)
Unlike other segments, where PSU insures have lost market share, in retail health even private multi line insurers have ceded market share to SAHIs (standalone health - Star is leader in SAHI)

While retail is the focus, SAHIs grew significantly ahead. In retail, SAHIs grew at ~2x industry leading to market share gains (~47% in FY19 from ~24% in FY14)
SAHIs also have a superior product mix as share of retail is higher at ~76% vs. 27/29% for PSU and private insurers


SAHIs also have a superior product mix as share of retail is higher at ~76% vs. 27/29% for PSU and private insurers



Retail - most profitable and sticky. 20% CAGR over FY12-19 led by 10.8% CAGR on lives covered and 8.3% CAGR on premium per life
Retail claims ratio been lowest at 71-72% in last 2 years before Covid
Corporate - 50% of industry premium, low pricing power low profit

Retail claims ratio been lowest at 71-72% in last 2 years before Covid
Corporate - 50% of industry premium, low pricing power low profit


So, now, u know #StarHealth operates in lucrative sector general insurance and in most lucrative sub segment - retail
#StarHealth The Good Part
Largest private health insurer with market share of 15.8% in health insurance market & 31.3% retail health insurance market
#StarHealth The Good Part
Largest private health insurer with market share of 15.8% in health insurance market & 31.3% retail health insurance market

Retail health and group health, which accounted for 89.3% and 10.7%, respectively, of our total health GWP in Fiscal 2021
Distributes policies mainly through individual agents (CAGR of 27.3% from 0.29M in FY19 to 0.46 M in FY21), which accounted for 78.9% of our GWP in Fiscal 21

Distributes policies mainly through individual agents (CAGR of 27.3% from 0.29M in FY19 to 0.46 M in FY21), which accounted for 78.9% of our GWP in Fiscal 21


In Fiscal 2021,
Solvency ratio of 2.23x against IRDAI prescribed level of 1.5x
Renewals by GWP value for retail health business was ~97.9% & ~63.4% higher inward portability
31 claims complaints per 10,000 claims.
Lower claims ratios, which were 73% in retail health
Solvency ratio of 2.23x against IRDAI prescribed level of 1.5x
Renewals by GWP value for retail health business was ~97.9% & ~63.4% higher inward portability
31 claims complaints per 10,000 claims.
Lower claims ratios, which were 73% in retail health
Now The BAD #StarHealth
Risks:
Natural/Unnatural Calamity/Mass Health Infection Risk
Interest Rate Risk
Disruption Risk
Accounting Risk
Competitive and Pricing Risk
Regulatory Risk
Asset Management Risk
Brand Management Risk
Risk of not seeing the risk – Governance
Risks:
Natural/Unnatural Calamity/Mass Health Infection Risk
Interest Rate Risk
Disruption Risk
Accounting Risk
Competitive and Pricing Risk
Regulatory Risk
Asset Management Risk
Brand Management Risk
Risk of not seeing the risk – Governance
Risk 2: Asset Management Risk
Remember IL&FS Risk, aia koi saga nahi, jisko isne dasa nahi.
Had to make write offs on investments
Also, see a deterioration in asset credit rating quality, for higher returns before IPO????
Remember, insurance companies earn a lot through float


Remember IL&FS Risk, aia koi saga nahi, jisko isne dasa nahi.
Had to make write offs on investments
Also, see a deterioration in asset credit rating quality, for higher returns before IPO????
Remember, insurance companies earn a lot through float



Risk 3: regulatory Risk - no one talking about it important to note:
IRDAI has formed a committee on studying the feasibility of allowing life insurers to offer indemnity-based health policies. As of now, life insurers already offer benefit-based health insurance policies
IRDAI has formed a committee on studying the feasibility of allowing life insurers to offer indemnity-based health policies. As of now, life insurers already offer benefit-based health insurance policies
Life insurers in India have a wider reach (bigger agency channel); hence if IRDAI allows life insurers to sell indemnity-based products it can lead to expansion of the health insurance pool. However, will also lead to price competition will further intensify and will be
negative for non-life insurers. Globally, life insurers are allowed to offer both life and health insurance policies. Naturally, health policy is a better fit with life insurance policy and some product innovation could be done on this side by life insurers
Risk 5 - Accounting Risk: Against general perception of all losses due to Covid, there were few accounting treatments. Need better understanding of insurance accounting - Discontinuation of VQST and accounting method change for UPR 

Risk 6 - Interest Rate Cycle Risk ; Though currently at bottom, from a long term market cycle perspective, need to be tracked as AUM return would depend on this and higher interest rate cycles lead to higher profitability & higher ROE & so more chances of undercutting competition 

Risk 7- Intensive Competition: Combined ratio over the years has had high standard deviation which is party due to business stage and party cyclic 





Risk 8 - Disruption Risk - Company's may need to keep doing product innovation. you never know from where disruption comes. Some of sandbox experiments in new product side in attached image 

Risk 9: Risk of have not seen the risk. IPO companies have not lived their public life to say anything about corporate governance standards 

If you have read till here and still interested and want to know about IPO valuation, do keep a tab on our Youtube channel, we will talk about it in today's video
youtube.com/scientificinve…
Thanks for reading. Please like and retweet for better reach. Comments welcome 🙏🙏
youtube.com/scientificinve…
Thanks for reading. Please like and retweet for better reach. Comments welcome 🙏🙏
tomorrow video*
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh