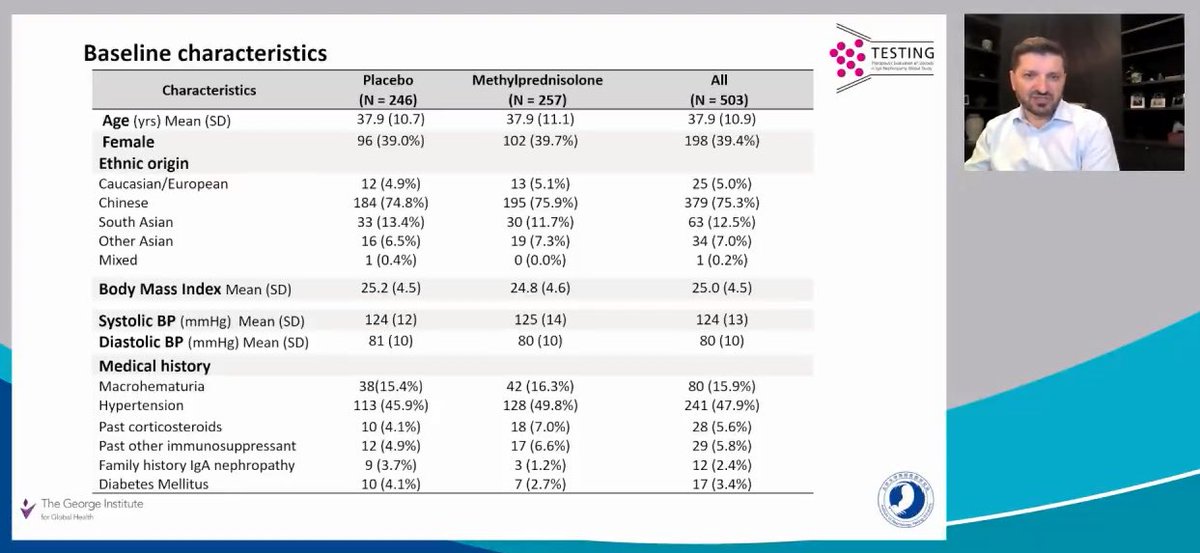
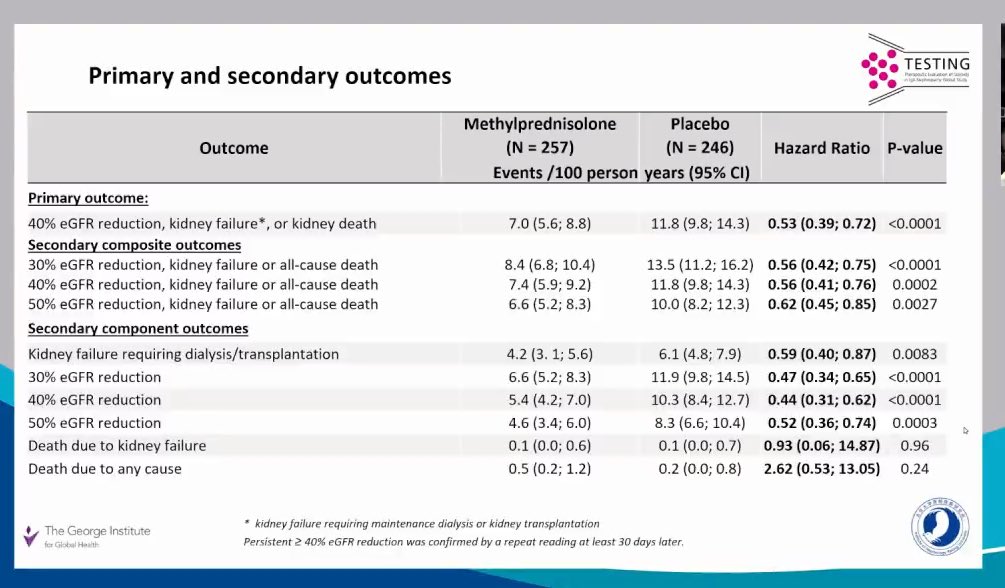
Workup for detection of Monoclonal Immunoglobulin (MIg) in patients with Monoclonal Gammopathy of Renal Significance (MGRS)
(Talk by Dr. Frank Bridoux at the Kidney Week)
#Onconephrology #MGRS
(Talk by Dr. Frank Bridoux at the Kidney Week)
#Onconephrology #MGRS
Workup for detection of Monoclonal Immunoglobulin
1. Find the circulating monoclonal Ig:
-SPEP & UPEP to quantify the Monoclonal (M) spike
-Serum & Urine Immunofixation to identify the monoclonal Ig & also to monitor response to Rx
1. Find the circulating monoclonal Ig:
-SPEP & UPEP to quantify the Monoclonal (M) spike
-Serum & Urine Immunofixation to identify the monoclonal Ig & also to monitor response to Rx
2. Serum Free Light Chain Assay to identify free light chains & to monitor hematological response to Rx in Light Chain-associated kidney disorders
There are 2 different LC assays: Binding site & N-Latex assay
-Use same assay to follow LC levels
There are 2 different LC assays: Binding site & N-Latex assay
-Use same assay to follow LC levels

3. If the Clone cannot be detected in serum or urine by SPEP/IF, UPEP/IF, sFLC assay then do Immunoblot Analysis of the serum & urine as it can detect small amounts of monoclonal immunoglobulins i.e. it is more sensitive 

4. Mass Spectrometry Assays are very sensitive in detecting monoclonal light chains & MS assay may replace Immunofixation
-MS assays also distinguish b/w therapeutic antibodies (which may be picked on Immunofixation: False +) from endogenous M-proteins
-MS assays also distinguish b/w therapeutic antibodies (which may be picked on Immunofixation: False +) from endogenous M-proteins

5. Determine the nature of the detected clone
Bone Marrow Aspiration/Biopsy:
-Immunohistochemistry & Flow cytometry to analyze lymphocyte & plasma cell markers
-FISH panel for cytogenetic abnormalities
-Molecular Biology to look for mutations
Bone Marrow Aspiration/Biopsy:
-Immunohistochemistry & Flow cytometry to analyze lymphocyte & plasma cell markers
-FISH panel for cytogenetic abnormalities
-Molecular Biology to look for mutations

6. If Clone is detected on Bone Marrow aspirate/biopsy & nature of the clone has been determined then determine tumor burden: CRAB criteria/CT/PET/MRI
7. If Clone is not detected on Bone marrow aspirate/biopsy:
-Flow cytometry of blood lymphocytes to detect small circulating clone
-Whole body imaging to detect localized plasmacytoma/low grade B-cell lymphoma
-Flow cytometry of blood lymphocytes to detect small circulating clone
-Whole body imaging to detect localized plasmacytoma/low grade B-cell lymphoma
8. There are newer techniques that can be used for detection of small clones in patients with MGRS
-Next generation flow cytometry
-RNA-based Immunoglobulin Repertoire Sequencing (RACE RepSeq)
End/

-Next generation flow cytometry
-RNA-based Immunoglobulin Repertoire Sequencing (RACE RepSeq)
End/


• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh