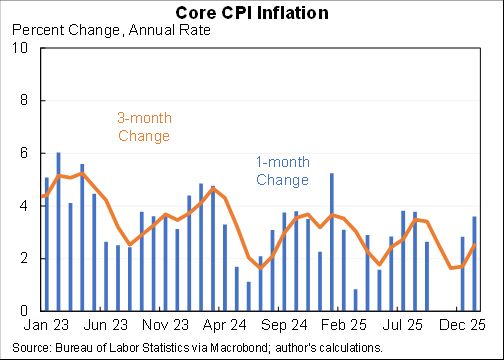
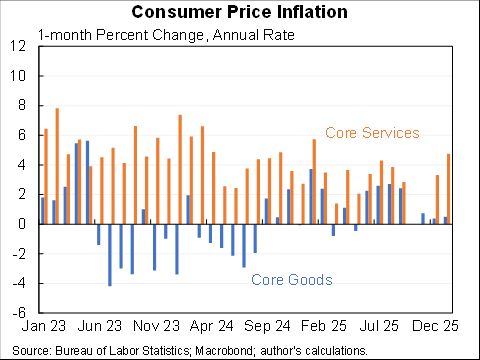
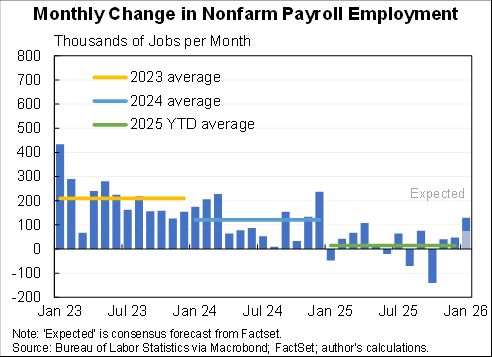
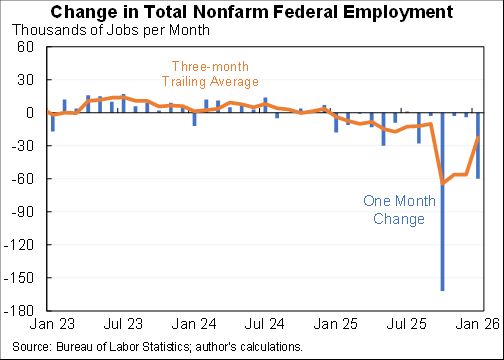
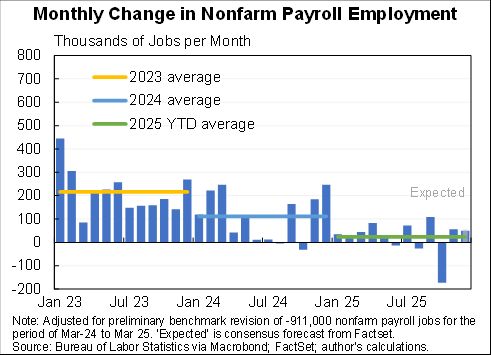
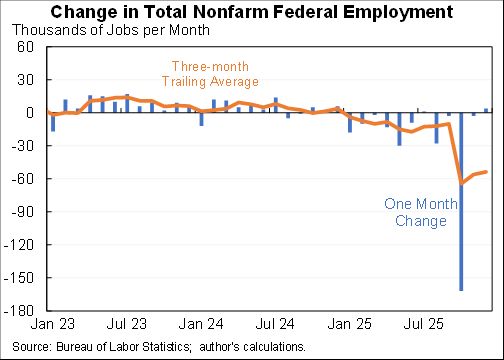
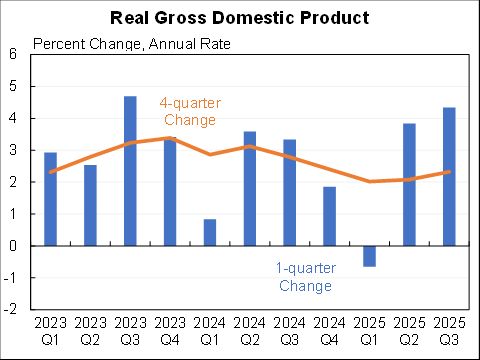
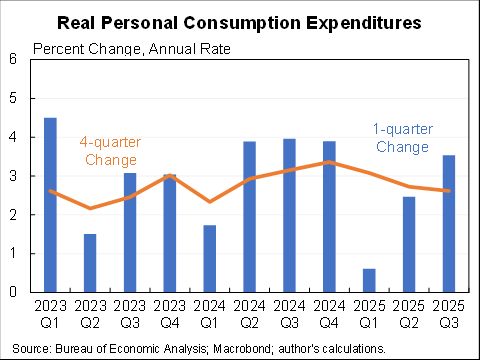
Willie Powell & my blog on today's (confusing) jobs numbers. We put the last year in context. Contrary to widespread belief, job growth has been near expectations--as surprisingly strong labor demand offsets surprisingly weak labor supply. A 🧵 piie.com/blogs/realtime…
To understand what was expected we use the median forecast from the Survey of Professional Forecasters. Other forecasts were similar. Overall, has slightly outpaced. Here is avg monthly jobs for 2021:
Nov 2020 forecast: 432K/month
May 2021 forecast: 562K/month
Actual: 555K/month
Nov 2020 forecast: 432K/month
May 2021 forecast: 562K/month
Actual: 555K/month

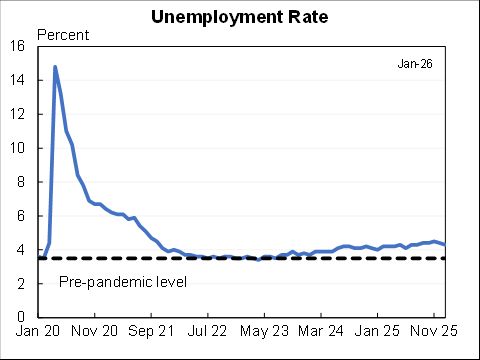
Similar story for unemployment. Back in May (the first forecast that incorporated the American Rescue Plan) the SPF expected the UR to be about 4.9% in Nov, instead it was 4.2%.
(Note, they don’t forecast labor force participation but likely would be worse than expected.)
(Note, they don’t forecast labor force participation but likely would be worse than expected.)
But not everything has played out as expected, there have been two big surprises: a decline in labor supply and an increase in labor demand. They've roughly offset each other for employment but both have led to higher nominal wages. 

(Technical note: we think of labor supply/demand as functions of *real* wages. I'm showing nominal due to a combo of wage illusion and expectation of transitory inflation. Both assumptions becoming increasingly untenable.)
Willie and I decompose the 1.5 pp decline in LFPR since COVID hit and find it is roughly one-third due to population aging, one-fifth due to ongoing weakness, and nearly half is "other." That "other" is both men and women, working age and retirement age. 



At the same time there were 0.6 unemployed per job opening, a very tight labor market by that metric. 

Different labor market indicators sending different signals. EPOP is still relatively slack, UR more balanced, & U/V and quits very tight. Which is right? The latter two have a lot of merit and worth taking seriously as Willie & I discussed before piie.com/blogs/realtime… 

The net result of this is nominal wages well above trend, something unusual if all you looked at is unemployment. Overall, those gains are being eaten by inflation—except for lower-wage workers who are seeing real gains, albeit at a slower pace than before COVID. 



Overall, the economy is 5 million jobs short of where it was expected to be prior to COVID. The gap is closing but fiscal and monetary policy should still be accommodative—as they are very likely to be. FIN. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh