As the news that Kuwait may struggle to keep its oil output in the coming years, we like to explain some facts on "Base Declines". Kuwait is said to have 3.2mbpd capacity & produces 2.5mbpd in Oct 2021.
Kuwait is major, not minor for the market.
Thread
Kuwait is major, not minor for the market.
Thread
https://twitter.com/BurggrabenH/status/1468631349883977729?s=20
First, think of a conventional oil fields like a "normal distribution" or, after its mathematician, a "Gauss curve". As a field starts producing hydrocarbons, its production is stable or increases (with reservoir pressure & wells No) bf it enters in a "permanent decline".
2/...
2/...
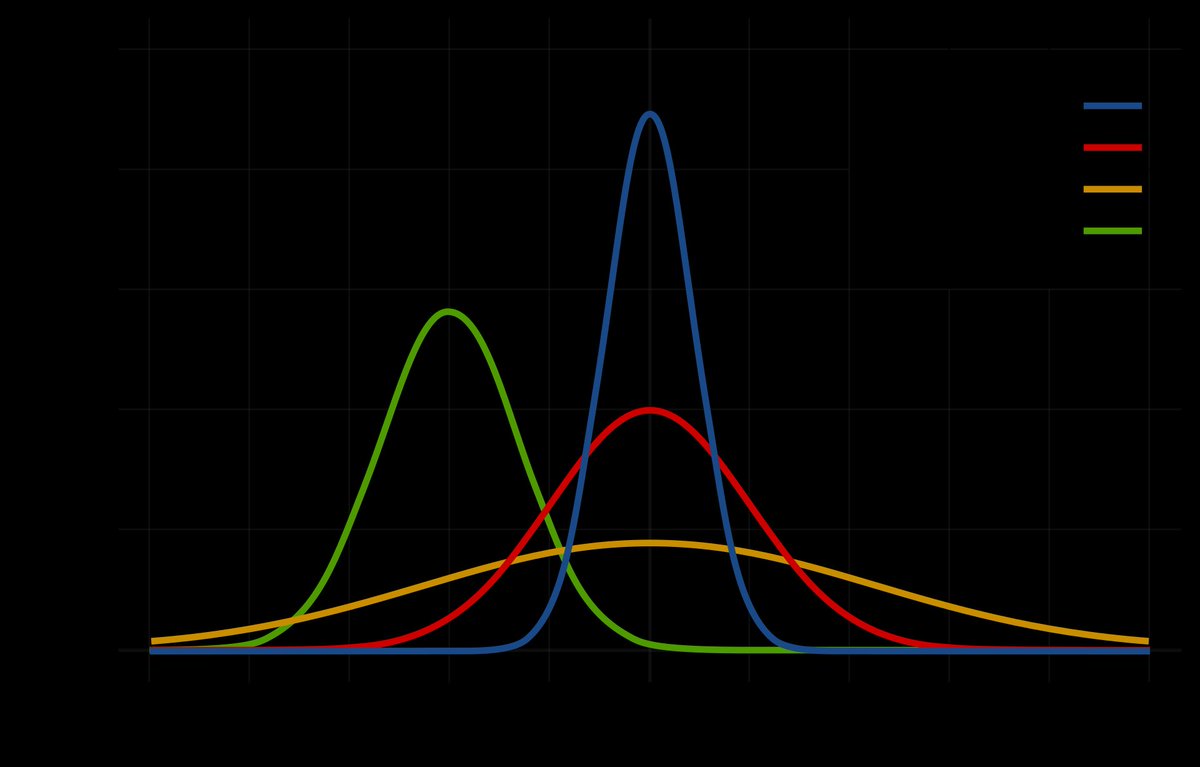
Take the Cantarell offshore field in Mexico, one of a few "giant" conventional oil fields ever to be discovered. Do you see the "Gauss" curve below? In May 2021, Cantarell was down to 90kbpd, a fraction of its 2mbpd peak production in 2004.
3/...
3/...

Now, let us do that for all 65,000 conventional oil fields in the world & we basically get - Gauss again!
Oil & gas is an extractive industry. If world production needs to be stable, annual reinvestment (replacement of production) is required or global supplies decline.
4/..
Oil & gas is an extractive industry. If world production needs to be stable, annual reinvestment (replacement of production) is required or global supplies decline.
4/..

More concretely, back in 2018 maturing fields around the globe declined at around 6% pa as reservoir pressure of oil fields globally decrease over time until the production rate eventually declines to a point at which it no longer produces profitable amounts.
5/...
5/...

In 2018, the IEA assumed 51 Mbpd of production to be in permenant decline. At 6% annual decline, operators need to replace 3.1 Mbpd with new projects EACH YEAR just to stay still. That is a lot of oil in an industry that is happy to find a new fields with 100mb size.
6/...
6/...

Again, in this decade the oil industry needs to replace one "North Sea" each year to keep production stable as ageing oil fields lost more than 3mbpd per year.
7/...
7/...

Is the industry re-investing enough? Of course not.
If anything, the industry continues to reduce investments due to Covid-19 & ongoing ESG demands ("Green Shift").
Worse, think about the signalling effect of SPR releases in that context to get lower prices!?
8/
If anything, the industry continues to reduce investments due to Covid-19 & ongoing ESG demands ("Green Shift").
Worse, think about the signalling effect of SPR releases in that context to get lower prices!?
8/

So if anything, the industry lost potentially up to 4mbpd of barrels in the past 18 months in addition to the impact of project delays or increased decline rates due to "over-production".
9/...
9/...

Again, under-investment is going to lead to unsustainable oil production in the near future as reserves deplete from a lack of replacement.
10/...
10/...

It gets worse, not only did the industry not invest enough, decline rates are likely to increase too, potentially from 6% to more like 8% or 9%.
11/...
11/...

And that is true for Non-OPEC or OPEC fields, as you can easily see from the below table.
12/12 (end; pls retweet)
12/12 (end; pls retweet)
https://twitter.com/BurggrabenH/status/1468612040898105346?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh