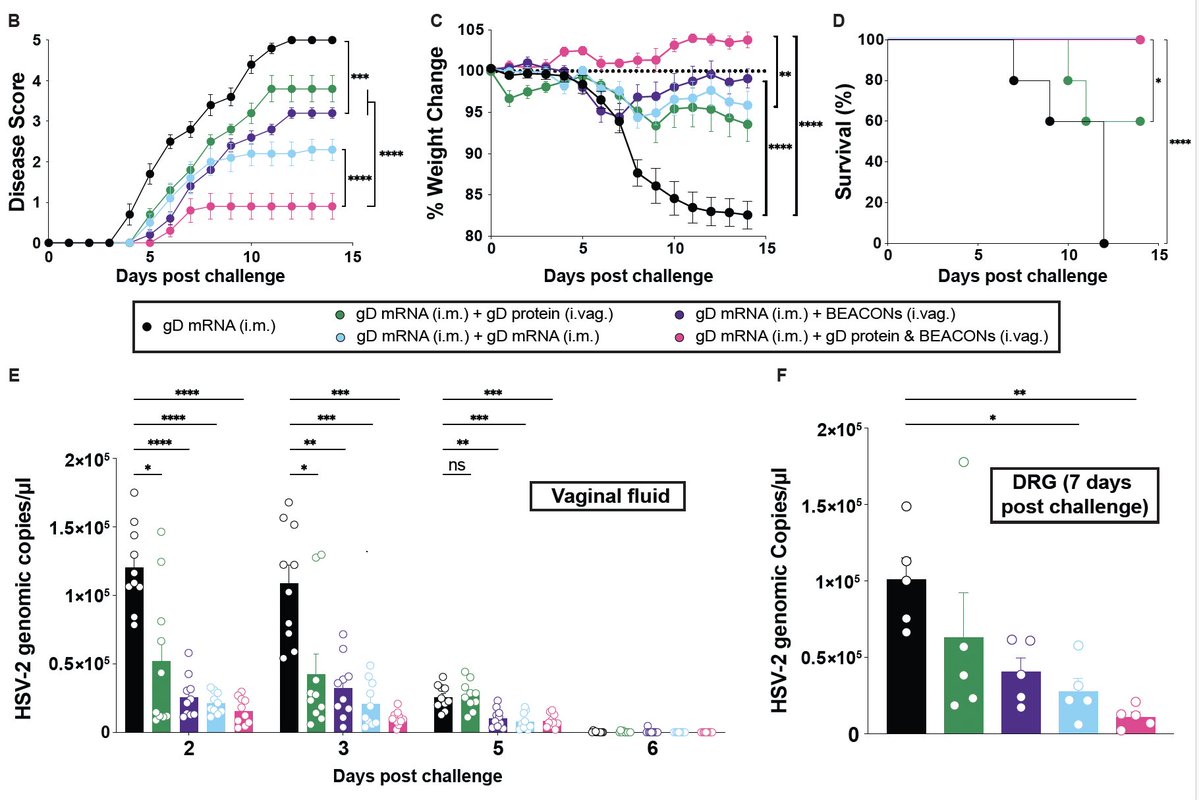
Our new study by @JieunOh9 @ericsongg @MiyuMoriyama et al shows that immune priming via intranasal route provides superior protection against heterologous respiratory virus challenge. The key is in inducing local secretory IgA with broader coverage. (1/)
science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
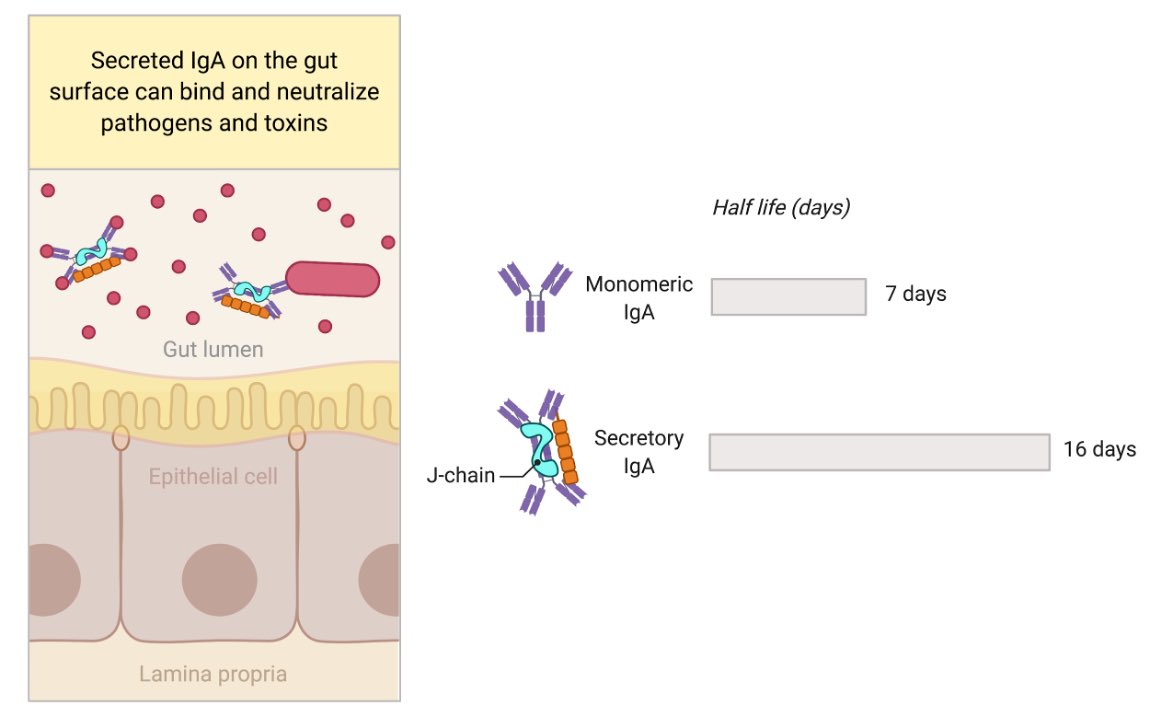
Mucosal surface epithelium expresses polymeric Ig receptor (pIgR), which transports dimeric IgA + J-chain secreted from plasma cells within the tissue, across to the luminal side. IgA dimer + J-Chain + part of pIgR is released as ‘secretory IgA’. Figure by @BioRender. (2/) 

The secretory IgA can bind viruses, bacteria, toxin in the lumen of intestine and neutralize them. Advantages of secretory IgA is the extended longevity as well as having 4 Fab instead of 2 Fab (monomeric IgA) to bind to the antigen. Secretory IgA is well studied in the gut. (3/) 
What about sIgA in the lung? Here, we show that only nasal, but not parenteral, priming induces secretory IgA in the lung. Similar circulating Abs are induced by both routes. Note we used ~30 PFU x1 for nasal and 4 million PFU x5 for i.p. priming. sIgA induction via👃🏼>>💉 (4/) 

When you look inside the lungs of nasal vs. parenteral primed mice 5 weeks later, nasal primed mice contain tons of plasma cells secreting IgA beneath the epithelium, and IgA is bathing the lumen of the lung 😲 (5/) 

These IgA secreting cells at 5 weeks post prime are mostly tissue-resident cells (meaning they sit within the lung and do not move around). (6/) 

What is the source of lung IgA? Is it circulating antibodies or locally produced? @JieunOh9 tested this by creating parabiotic mice. She found that most of the lung IgA is coming from the local tissue-resident IgA secreting cells. (7/) 

@Ericsongg analyzed the transcriptional profiles in lymph node and lung B cells. He found IgA secreting cells in the lung were mostly plasma cell, plasmablasts and memory B cells, & were CXCR3+, a chemokine receptor we found earlier for HSV memory B. (8/) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31189952/ 

Knocking out CXCR3 in B cells led to less IgA secreting cells in the lung, and less IgA secreted into the lung. Thus, B cell intrinsic CXCR3 is necessary for establishment of IgA secreting cells in the lung. (9/) 

A key finding in our study is that intranasal but not systemic immunization led to cross-protective immunity against heterologous influenza virus in the absence of T cells. Only intranasal priming led to the production of cross-reactive IgA in the lung secretion 👇🏽 (10/) 

As part of the effort to create universal flu vaccine, @florian_krammer’s group developed a recombinant neuraminidase (rNA) vaccine. Adjuvanted rNA vaccine provides robust protection to heterologous influenza viruses when nasally administered. (11/)
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25759506/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25759506/
With @Shirin_Strohm & @florian_krammer, we tested whether this rNA vaccine also rely on local IgA. In immunized mice, only nasal route induced IgA+ B-resident memory cells and protected against heterologous challenge in the absence of T cells. Via @MiyuMoriyama 💪🏼 (12/) 



These results indicate that nasal vaccines induce IgA and promote better cross-protective immunity against viral variants, and suggest its utility in combating COVID-19 variants of concern. A great write up by Bill Hathaway. (13/)
news.yale.edu/2021/12/10/nas…
news.yale.edu/2021/12/10/nas…
Highlighting all the authors that made this study possible, incl. Patrick Wong, Sophia Zhang, @RuoyiJiang @skleinstein. We started this work four years ago when @JieunOh9 was still a postdoc in the lab. Now she runs her own lab at @kaistpr 💪🏼 Thanks for reading till the end. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh