
We study antiviral immunity and viral disease pathogenesis. #COVID19 #longCOVID #vaccines @HHMINEWS @YaleIBIO @YaleMed @YaleCII
80 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App






 Females show higher mtROS levels and insufficient antioxidant levels, while males show mitochondrial lipid oxidative damage. While the reason for this is unclear, it may explain the sex differences in lymphocyte dysfunction we see in PAIS in general. (2/)
Females show higher mtROS levels and insufficient antioxidant levels, while males show mitochondrial lipid oxidative damage. While the reason for this is unclear, it may explain the sex differences in lymphocyte dysfunction we see in PAIS in general. (2/)







 Among research participants who reported acute SARS-CoV2 infection, 64,384 participants reported to have experienced Long COVID and 178,537 participants did not. Their analytical cohort consisted of 54,390 cases and 124,777 controls 👇🏼 (2/)
Among research participants who reported acute SARS-CoV2 infection, 64,384 participants reported to have experienced Long COVID and 178,537 participants did not. Their analytical cohort consisted of 54,390 cases and 124,777 controls 👇🏼 (2/) 








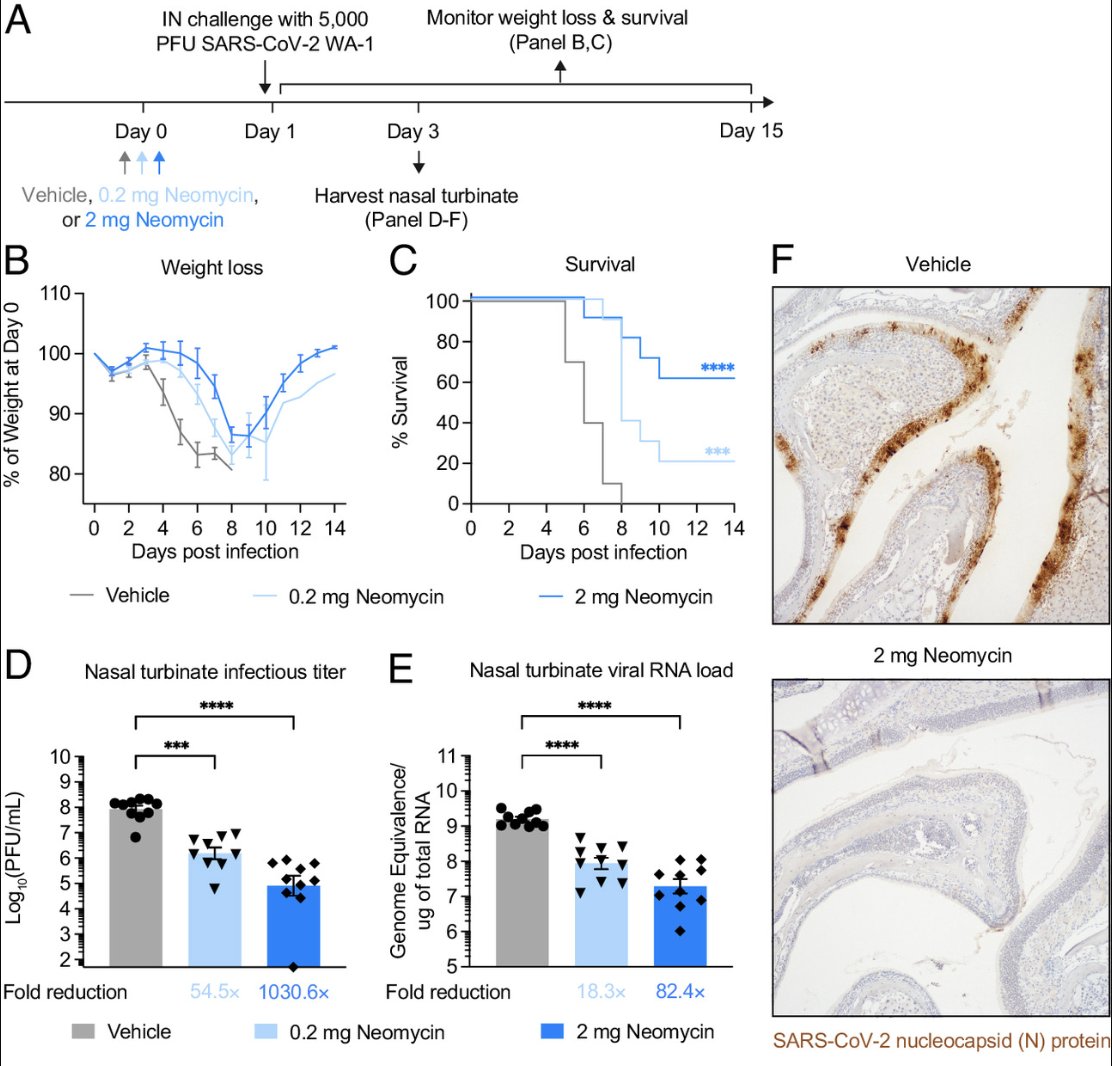


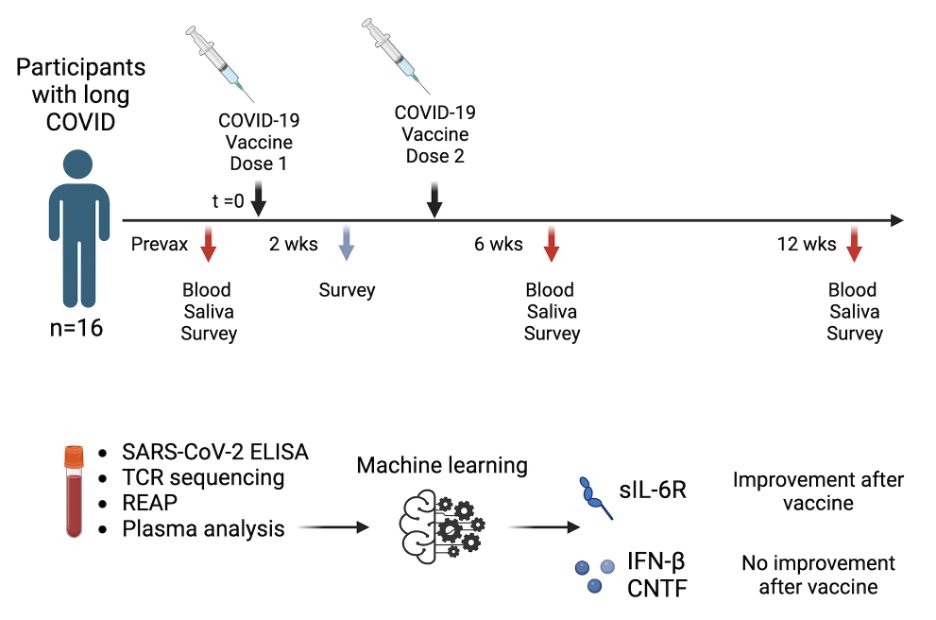
 This study was initiated in collaboration with @Survivor_Corps @dianaberrent based on their Facebook poll showing that 40% of respondents with self-reported Long COVID had mild to full symptom resolution after vaccination while 14% reported worsening of their symptoms. (2/)
This study was initiated in collaboration with @Survivor_Corps @dianaberrent based on their Facebook poll showing that 40% of respondents with self-reported Long COVID had mild to full symptom resolution after vaccination while 14% reported worsening of their symptoms. (2/)

