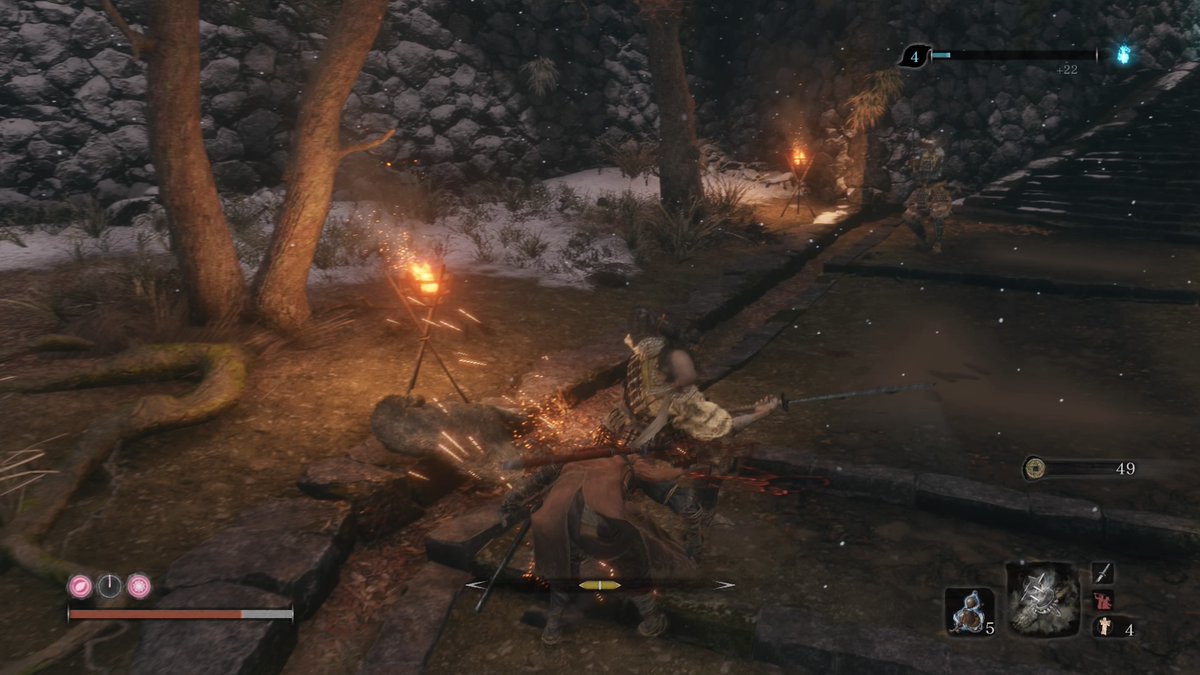
How do humanoid bosses in Sekiro remain predictable yet provide increasing challenge over the course of a boss fight? Let’s look at arguably one of the more difficult humanoid boss fights - Genichiro Ashina. #gamedesign #combatdesign 🧵 



PLAYSTYLE - The player can influence the predictability of the fight with an aggressive playstyle with a mix of attack pressure and parry mastery. Passive or evasive playstyle invokes Ashina to perform arguably harder and a wider array of attacks to deal with. 1/3
Ashina’s neutral attacks (non-defensive attacks) have tricky movement/timing characteristics and hit with more frequency than counter attacks. He also has an unique unblockable grab out of neutral. Ashina rarely performs these attacks when on the defensive in the early fight. 2/3
Suboptimal parrying disrupts his attack pattern which causes him to reset/perform attacks usually not seen with an aggressive playstyle. Also, mistimed parries against certain attacks prevents his follow-up that can be “easily” countered using a Mikiri Counter. 3/3
COUNTERS - Ashina ~99% of the time performs a counter action after blocking the player’s 2nd consecutive attack. When he has ~full health, he’ll either deflect and counter with a quick slash or evade back out of reach. 1/4
These two actions serve as a primer to encourage the player to be deliberate in different ways. The predictable tempo allows the player to count when the enemy will perform a counter. Each counter attack is varied in tempo to throw the player off from button mashing attack. 2/4
The quick slash is faster than the player’s first attack. The player can be aggressive and attack right after being deflected but there’s a moderate chance the player will get hit. This <40% chance is enough to make a player hesitate from button mashing attack. 3/4
When he first performs the evade, he’ll never follow up with an attack. This allows the player to OBSERVE the enemy's defensive options without any danger. He'll chain attacks from this evade after losing health. At this point, the evade becomes a “Tell” for the player. 4/4
ATTACK REUSE - Using the same attack in different situations is a smart way for designers to keep the fight fresh and the player on their toes without greatly increasing the player’s cognitive load. (It also smartly reduces development scope). 1/2
The unblockable thrust is used as a chain attack AND as a defensive counter. As Ashina gets lower on health, he’ll start to incorporate this attack as a block counter. This also increases how many counter attacks Ashina has after blocking. 2/2
50/50 - Once he loses some health, the leap now has 2 options to branch into: thrust or spin slash. Each of these moves are defended against by using the Jump or Mikiri Counter, respectively. This is an example of a COIN FLIP decision the player has to make by reading the enemy.
PROGRESSION - During the final phase, Ashina gains a far leaping slash that could be Mikiri countered. Ashina ALWAYS performs this far leap at the start of the final phase. This gives the player an opportunity to land a guaranteed hit while making the boss feel intimidating. 1/4
Additionally, he gains 2 NEW attacks that forces the player to learn how to defend against them. This is especially difficult since most players will probably learn by dying. With no checkpoints in between each phase, the player is forced to start from the beginning. 2/4
Parrying some phase 1 attacks now adds a BRANCHING attack that wasn’t there initially. When the player parries the final attack of the flurry, Ashina will now branch into an unblockable thrust where the player must evade or use the Mikiri Counter. 3/4
This linear difficulty ramping is a design technique to continue to give the player a sense of mastery while throwing them a curveball; however the unblockable thrust added here is still a move the player has dealt with in the past making it easier to digest under pressure. 4/4
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh