CoronaVac is an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine approved for use in 48 countries. In collaboration with the Ministry of Health in Dominican Republic, we tested whether CoronaVac (2x) + Pfizer booster induces neutralizing Abs to Delta and Omicron. (1/)
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
We analyzed plasma samples from 101 participants in Dominican Republic (DR) who received the BNT162b2 booster >4 weeks after the 2x of CoronaVac. We compared them to samples from people at Yale who received 2x of BNT162b2.
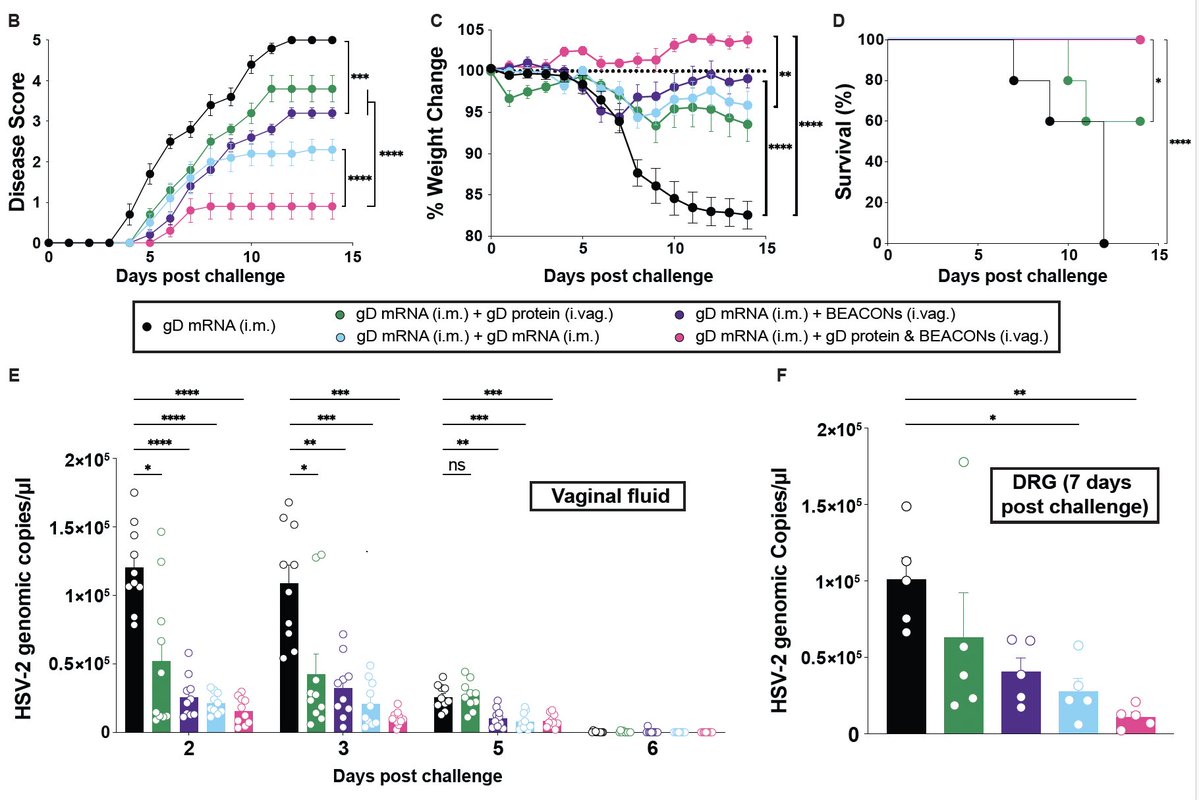
⬆️ ⬆️ Ab induced by heterologous prime & boost.(2/)
⬆️ ⬆️ Ab induced by heterologous prime & boost.(2/)

Next, @carolilucas & @ValterVSM analyzed NAb against ancestral vs. Delta variant. CoronaVac 2x followed by Pfizer mRNA vax booster robustly elevated NAb against both virus types, level similar to 2x Pfizer vaccine. (3/) 

Just focusing on Pfizer 2x, omicron had the highest escape from neutralization compared to other VOCs (using authentic virus isolates), reducing the NAb PRNT50 levels by 11.9x compared to ancestral virus. Similar data have already been reported by others. (4/) 

In CoronaVac fully vaccinated (2x) people, there was NO detectable neutralization against the infectious Omicron virus. Antibodies were assayed at mean days from second Coronavac shot of 113 days (with SD 33 days). (5/) 

However, after the Pfizer mRNA booster, CoronaVac recipients elicited detectable levels of neutralization against omicron. Note that PRNT50 is reduced by 7.3x against Omicron compared to the ancestral virus. (6/) 

How does prior infection modify neutralization against Omicron? In the mRNA vaccine recipients (28 days after second dose), prior infection provided advantages in cross protection against VOCs, including Omicron. (7/) 

Unfortunately, in the CoronaVac 2x recipients boosted with Pfizer mRNA vax, prior infection made no difference to the neutralization capacity against Omicron. (8/) 

Immunologically, this difference is interesting. Prior infection only synergies with the mRNA vax to elevate broadly neutralizing Ab but not with inactivated vax. This may relate to the persistent GC responses in mRNA vax reported by @TheBcellArtist. (9/)
nature.com/articles/s4158…
nature.com/articles/s4158…
In terms of public health, CoronaVac 2x is insufficient to neutralize Omicron. Even with CoronaVac 2x plus Pfizer booster, NAb is only 1.4x higher than 2x mRNA alone. Thus, CoronaVac recipients may need 2 additional booster doses to reach levels needed against Omicron. (10/) 

Lots of amazing folks from Dominican Republic and Yale contributed to this work. Special thank you to @SVermund for orchestrating this collaboration, and Drs. Eddy Perez-Then and Marija Miric for their leadership in DR. Always fantastic @carolilucas @ValterVSM 👏🏼 👏🏼 (end) 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh