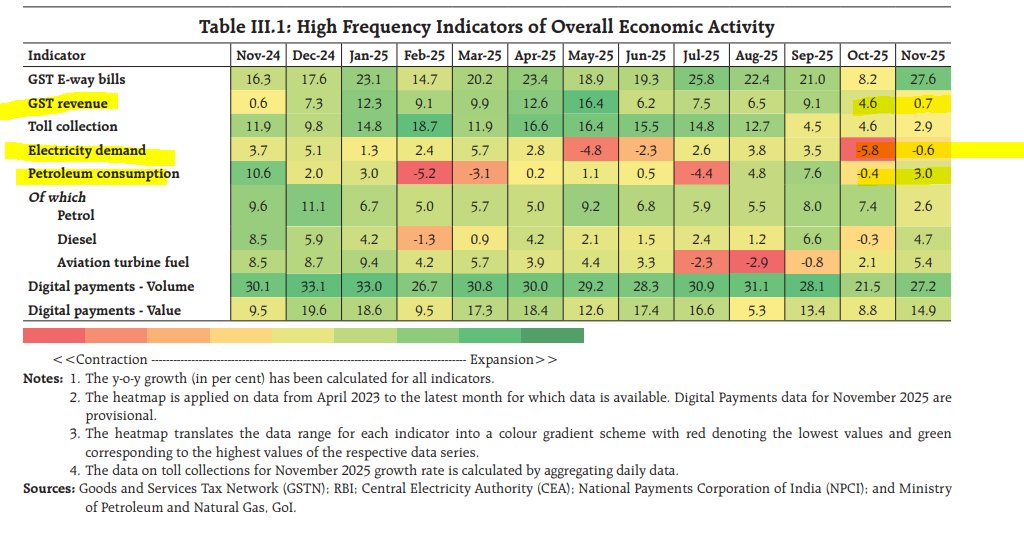
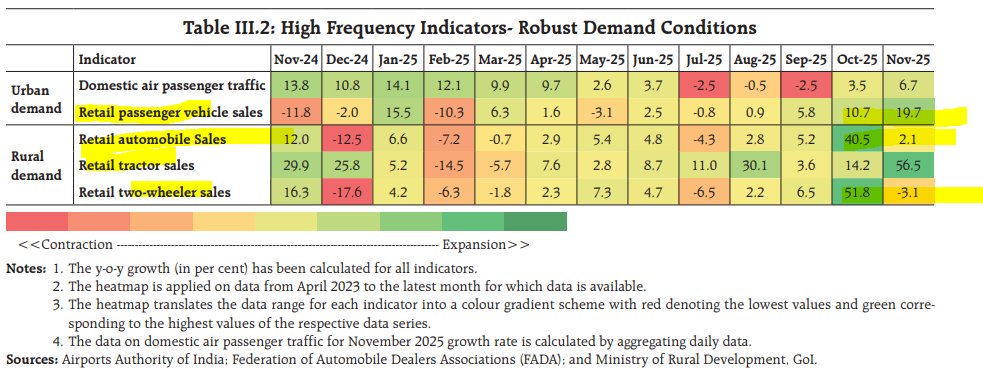
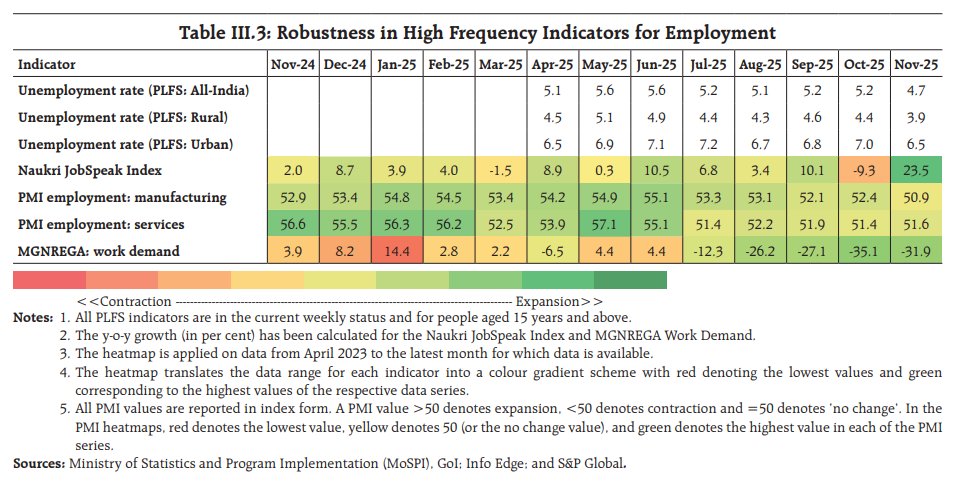
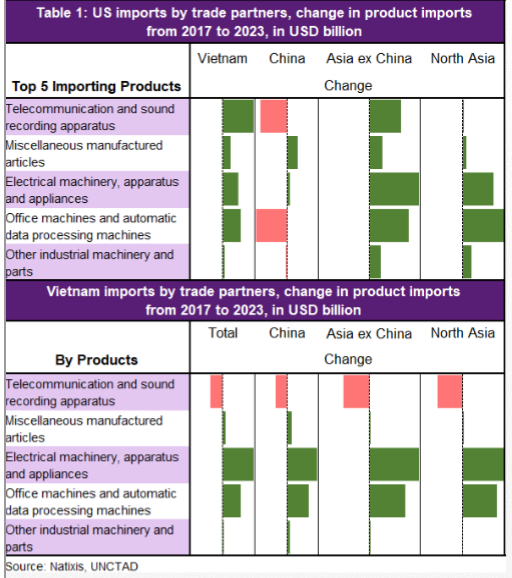
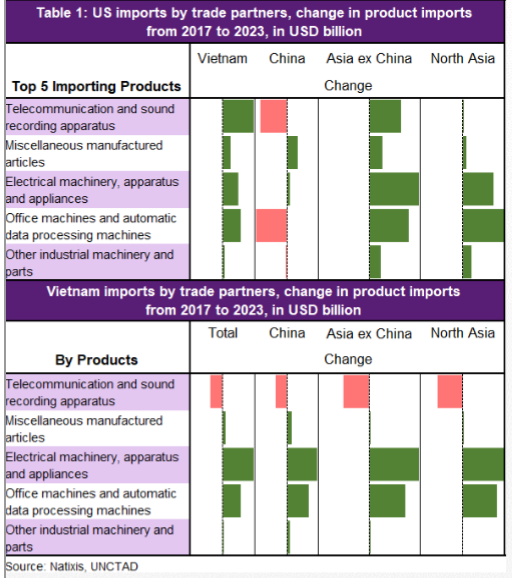
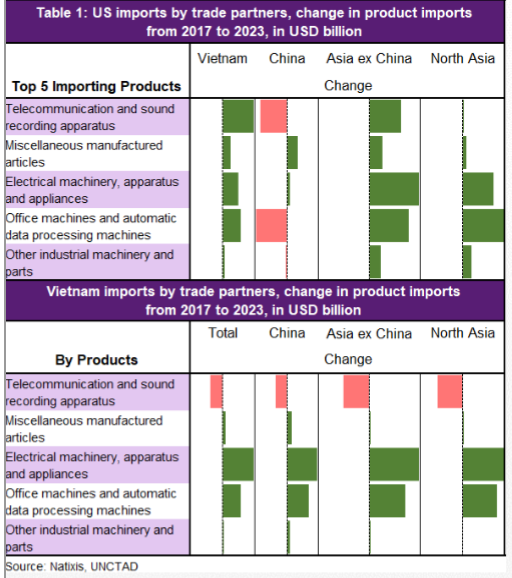
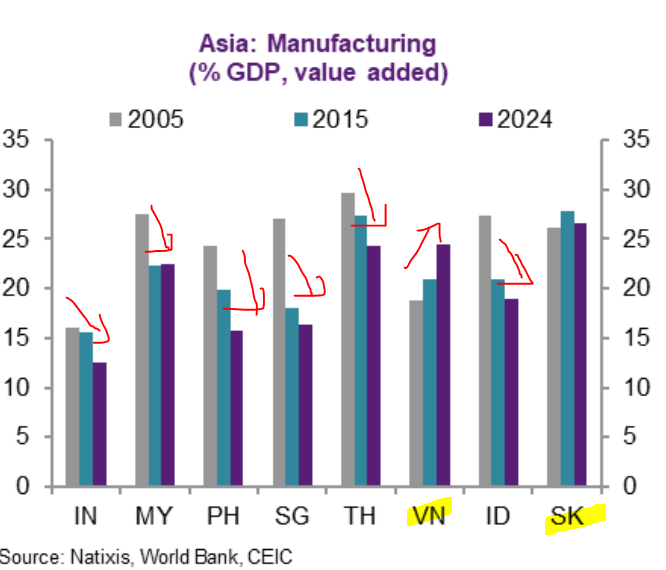
Ok, this is my last thread of 2021 & I'll talk about something that is MOST valuable in global exports - semiconductor - or chips, that powers the modern world. This is also very topical as we use it in our daily lives & at the center of politics & geopolitics given its shortages
https://twitter.com/SenWarren/status/1476327168833581056
In case you are wondering why we should know more about this most valuable global export item (worth about USD1trn & more valuable than oil), then we must not forget that in order for me to tweet this, we need chips. If we use the body analogy, chips = brain & oil is like blood.
Let's start with definition:
a) Semiconductor or in UN classification is known as cathode values & tubes & USD949bn was traded in global exports
b) It's a manufactured good & an INTERMEDIATE
c) U don't see it in the final product but products like CARS & laptops & mobiles need it
a) Semiconductor or in UN classification is known as cathode values & tubes & USD949bn was traded in global exports
b) It's a manufactured good & an INTERMEDIATE
c) U don't see it in the final product but products like CARS & laptops & mobiles need it

So the most valuable item in global trade is something you DON'T SEE as it is an intermediate product. You only see the final products such as cars/laptops/etc.
Chips are one of the US top exports (airplanes, oil, chips). China is a net importer of chips. Has a deficit of chips.
Chips are one of the US top exports (airplanes, oil, chips). China is a net importer of chips. Has a deficit of chips.

Meaning, money flows from China (USD350b) to chip exporters (North Asian countries like Taiwan (TSMC), South Korea (Samsung) & the US (Intel, Global Foundry). Let's talk about chips & its supply chain & why this is the US China trade-war & key to our national security (CHIPS ACT)
Chips were invented in the US & the US has 47% market share, Korea has 20% and Japan 10%, Europe 10%, & Taiwan 7%. China 5%.Now u may ask, well, why is the US fretting over chips if it DOMINATES. Because wants to retain the lead & this 47% includes design & manufacturing is less. 

Before you say, "I'm so proud to be an American" and bask in your glory (well, I am rather proud), let's look at the value added by activity or supply chain of chips. And this is where the Biden administration (Trump before it) & Senator Warren are having issues: MANUFACTURING. 

Let's put it a different way: American semiconductor firms are doing the R&D intensive part of the supply chain & they have OFFSHORED most of the manufacturing to Asia in various places in various segments of the supply chain, from Taiwan to Malaysia & Vietnam. India wants in too 

Note that the US still remains MOST OF THE VALUE CHAIN but increasingly LESS. Consumes 25% of global semiconductor while China 24%, so the same. Europe about 20%.
So where's the beef? The issue is that we DON'T manufacture most of it in the US so have little control over supply.
So where's the beef? The issue is that we DON'T manufacture most of it in the US so have little control over supply.
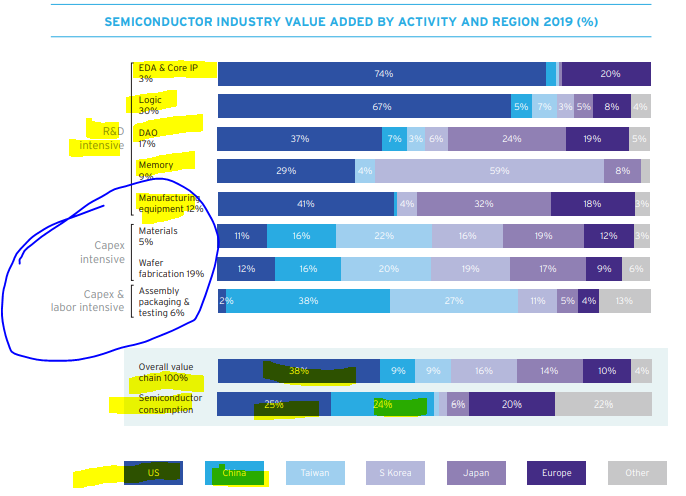
I won't go into the R&D part of the US supply chain & go straight into the heart of the matter & why I quote Senator Warren's tweet, which I think is simplistic but sets the tone of the hour.
The USA lead in R&D but LAG in manufacturing. Who leads? Taiwan! Specially, TSMC.
The USA lead in R&D but LAG in manufacturing. Who leads? Taiwan! Specially, TSMC.

To understand this chart, you need to understand a bit about chips but let me, a non engineer explain what this means: Foundries are where chips are manufactured. Manu of chips are capital intensive & very high tech. Basically u want smaller & faster chips & TW dominate < 10nm. 

This chart shows u by region (basically we only have a few firms here so this is where Senator Warren goes off about too much concentration but the consolidation is necessary as it's EXPENSIVE to build a foundry).
TW & SK lead or TSMC & Samsung.
US has Intel + Global Foundry.
TW & SK lead or TSMC & Samsung.
US has Intel + Global Foundry.
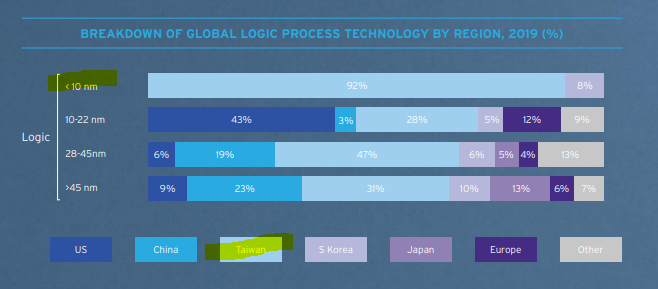
TSMC is ahead and DOMINATES <10nm & the US lags in this point. If u read the March 2021 US National Security Commission on AI paper, then it's all about the LACK OF MANUFACTURING in ADVANCED CHIPS that's a huge liability.
TMSC manus 54% of global chips.
nscai.gov/wp-content/upl…
TMSC manus 54% of global chips.
nscai.gov/wp-content/upl…

Btw, the former CEO of Google is a key author of this report that calls for more support of US manufacturing of chips because it is the support from other governments that has allowed them to thrive.
Anyway, key pts are: we are good at R&D & bad at manu
nscai.gov/wp-content/upl…
Anyway, key pts are: we are good at R&D & bad at manu
nscai.gov/wp-content/upl…
Okay, let me wrap this up on why it matters to you, first, u use semiconductor as it is an input into electronics (the brain). U want a faster brain that is not too heavy right to help u with ur whatever tasks. Anyway, below is where the usage of chips is as a share of total. So? 

Well, u know the SUPPLY of chips demand on INVESTMENT & it's capital intensive (at least 10bn for a decent foundry) & takes about 2 years. Plus we got Covid-19 related disruptions like Southeast Asia shutting down in Q3 2021.
Demand is HIGH & even acutely higher because Covid!
Demand is HIGH & even acutely higher because Covid!
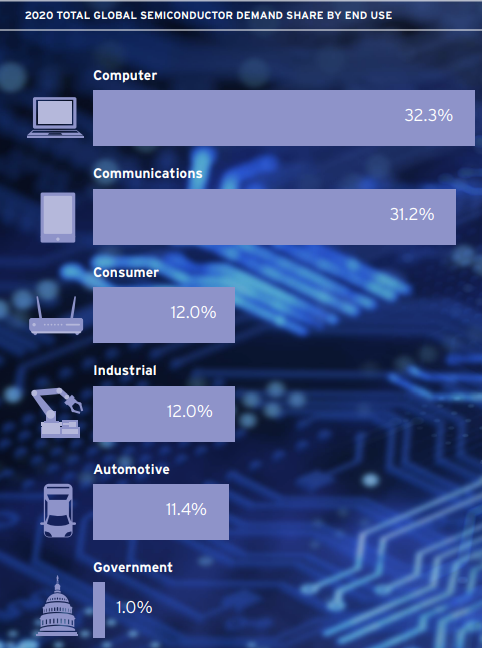
Note that I'm saying the following: we got supply that is relatively INELASTIC in the short-term for chips because of capacity constraints & time lag in investment & the fact we depend on TSMC for <10nm size. Second, operations were hit (remember my ASEAN note?) 3rd, demand high 

Ok, so what happens now? First, the US will try to retain its lead. The Biden Administration has the CHIPS Act that has 52bn passed by the Senate waiting for the House to pass that gives incentives. Btw, @intel is basically the last American manu at the size that can compete. So?
Given that there is so much emphasis on getting US manu up to speed, one an reckon that more support will be lobbied by American firms, and specifically 2 left that manufacture & specially Intel to get it to the competitive level or the US won't have any (if can't compete, exit).
The US isn't the only country. EU has a similar strategy but the US has more to lose & what the supply shock crisis shows that we have too much concentration risk to East Asia & in some sector Southeast Asia for manufacturing in general & that means more diversification needed.
Arizona has emerged as a place where Intel is adding additional foundry (basically connecting to its existing). But TSMC is not silly. It is smart. It knows where the game is headed & building there too. So is Samsung.
In fact, TSMC also looking into the EU given policy shift.
In fact, TSMC also looking into the EU given policy shift.
Note that American firms such as Intel have a global footprint. Specifically, it has investment in Vietnam and just added USD7bn to Malaysia.
India just passed 10bn bill to attract semiconductor (it wants in too on the supply chain). Diversification will include ASEAN + India.
India just passed 10bn bill to attract semiconductor (it wants in too on the supply chain). Diversification will include ASEAN + India.
Hope I got u excited about semiconductor & know a bit more about the product that U DON'T SEE BUT SHAPE YOUR LIFE, CPI, INTEREST RATES, DOMESTIC POLITICS, GEOPOLITICS & geeky & cool at the same time.
And yes, I think the US SHOULD support the sector, both R&D & manufacturing.🙏
And yes, I think the US SHOULD support the sector, both R&D & manufacturing.🙏
I have more too add but my threads always end up so long & let me end it by giving you the sources I used for this rant:
*Book: amazon.com/Fabless-Transf…
*The BBC video on semiconductor: bbc.com/reel/embed/p09…
*Policy paper: semiconductors.org/wp-content/upl…
*nscai.gov/wp-content/upl…
HNY!
*Book: amazon.com/Fabless-Transf…
*The BBC video on semiconductor: bbc.com/reel/embed/p09…
*Policy paper: semiconductors.org/wp-content/upl…
*nscai.gov/wp-content/upl…
HNY!
Have a happy new year! This was my way of saying thank u for being with me on Twitter Land. No matter how good/bad life is, key in my opinion is to focus on learning & processing what we learned to understand more about our world & each other!
See u in 2022!
💃@Trinhnomics
See u in 2022!
💃@Trinhnomics
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh