Willie Powell and my new @PIIE blog on the latest employment numbers--and looking back at 2021 and the COVID recession and its aftermath.
Short version: very rapid progress, still not all the way there, uncertainty looking forward.
A 🧵.
piie.com/blogs/realtime…
Short version: very rapid progress, still not all the way there, uncertainty looking forward.
A 🧵.
piie.com/blogs/realtime…
The economy added 6.4 million jobs in 2021, a 4.5 percent increase in jobs. that makes 2021 the seventh fastest year for job creation since the aftermath of World War II. 

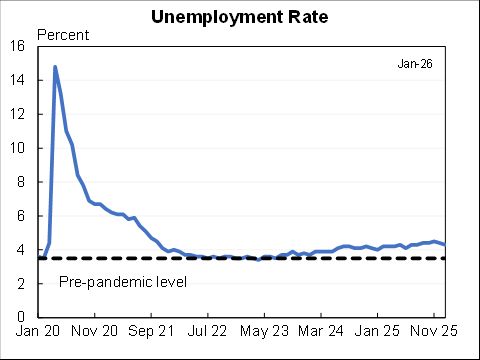
The unemployment rose very rapidly in March & April 2020 but then it has fallen rapidly ever since. Cumulatively the unemployment rate was 6.5 point-years above it's pre-recession value. That is about typical for postwar recessions and much better than the financial crisis. 

The unemployment rate is falling much faster than forecast. Now is well below what the Survey of Professional Forecasters expected in every forecast they have made since the pandemic hit. BUT, labor force participation would likely be worse than what they would have forecasted. 

Employment rates are still down relative to pre-pandemic for most age-sex groups. A larger fraction of men than women have stopped working with larger employment declines for the prime-age population than for younger people (whose employment has gone up) or retirement age. 

Overall employment is 2.7 million workers short of what CBO forecast prior to the pandemic while jobs (based on surveying employers) are 4.4 million short. This indicates that there is still work to do. FIN. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh