Starting on 22 December, European gas prices experienced - shall we say - a bit of a "rug pull". Within 10 days they crashed by 60%. Is the gas crisis over?
Thread
1/n
Thread
1/n
TTF (EU equ. of US price Henry Hub) crashed from a record $59/MMBtu down to $23/MMBtu within 10 days. Today, the price is back at $29 (left axis; $168/boe) or >7x (!) the price US consumers pay for their heating bill.
So no, the crisis is hardly "over". It gets worse.
2/n
So no, the crisis is hardly "over". It gets worse.
2/n

Why did TTF (or it's UK equ. NBP) come crashing down in late December? Chiefly b/c Europe had an unusually warm weather patch. Warm weather meant less gas withdrawals.
3/n
3/n
High EU prices earlier in Dec H1 also meant a wide-open EU-Asia LNG arbitrage for US exports.
The new headline: "LNG flotilla" is heading to Europe. Narrative: Crisis solved. Well, not really. The "flotilla" couldn't move the EU gas market "dial".
4/n
The new headline: "LNG flotilla" is heading to Europe. Narrative: Crisis solved. Well, not really. The "flotilla" couldn't move the EU gas market "dial".
4/n
https://twitter.com/BurggrabenH/status/1476679031496060930?s=20
Less gas withdrawals & more LNG importing was the recipe which crashed TTF from its "demand destruction levels". But did net EU injections of 3.5TWh for 2.5 days made a diffence?
5/n
5/n

Of course NOT. Overall EU gas storage fill is now at 55% (chart below) or where it was on 29 December 2021. The "flotilla" fixed 2-3 days of gas shortages, warmer weather another 4-5 days. Meanwhile, the EU remains 30 days "short gas", subject to weather!
6/n
6/n

Meanwhile, lower TTF prices stopped LNG shipments from the US into Europe. This is b/c the price arbitrage for shipments to Europe (as opposed to Asia) is now closed again. What hasn't changed however is Europe's need for more gas, urgently so.
7/n
7/n
https://twitter.com/OKalleklev/status/1477941481080074247?s=20
Worse, high TTF prices forced some industrial output to be shut-in. After all, high commodity prices are supposed to do exactly that - reduce marginal consumption.
And now? Below seasonal consumption is roaring back up (chart: EU gas withdrawals (blue line) vs 8y-avg)
8/n
And now? Below seasonal consumption is roaring back up (chart: EU gas withdrawals (blue line) vs 8y-avg)
8/n

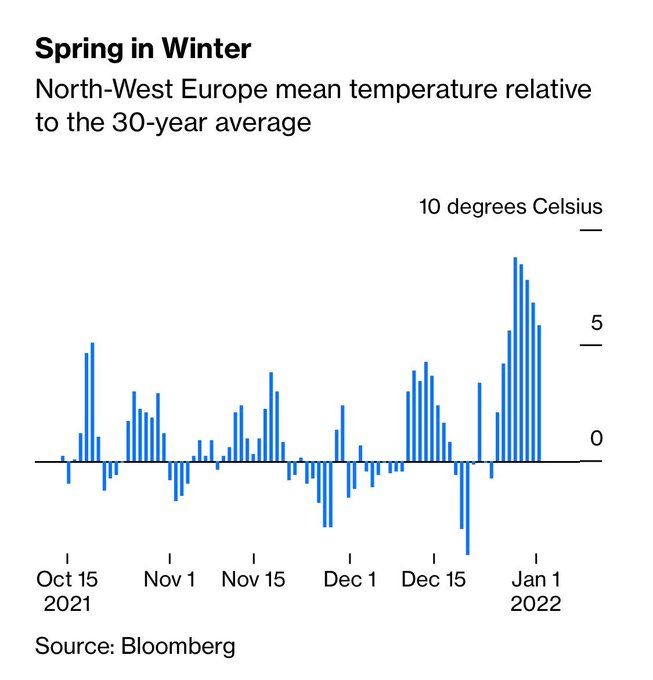
Consumption was already at record levels when compared to past 8y (as shown in chart above) as EU needs more gas for everything, but certainly for electricity generation. With a below-average cold temperature outlook (chart for 18 days; North-West EU), that will not change.
9/n
9/n

For more background on why Europe is in short supply of gas (the #hydrocarbon that provides power & heat) check this past thread. Upfront, the EU has structural supply issues, the alleviation of which need policy changes.
10/n @OlafScholz @vonderleyen
10/n @OlafScholz @vonderleyen
https://twitter.com/BurggrabenH/status/1463568920158289934?s=20
The Forward market however does not count on such policy changes. Instead it prices in a tighter EU gas market for years to come, as we illustrate below...
11/n
11/n
https://twitter.com/BurggrabenH/status/1478387749786955776?s=20
Finally, if somebody acuses you, @biancoresearch, that you are "clueless" or "if only media bothered to look at the numbers, it would have found out that #GAZPROM deliveries to EU are stable as a rock" - be careful b/c research is not their strength.
12/n @JavierBlas
12/n @JavierBlas

To be clear, the EU gas crisis has many reasons. But of course, Gazprom is one reason. It delivered 38% LESS gas into the CEE pipeline system when compared to 2019 levels (pre-Covid consumption). That is 600TWh of gas missing (net of S2M)!
How did he say, clueless!
13/13
How did he say, clueless!
13/13

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh