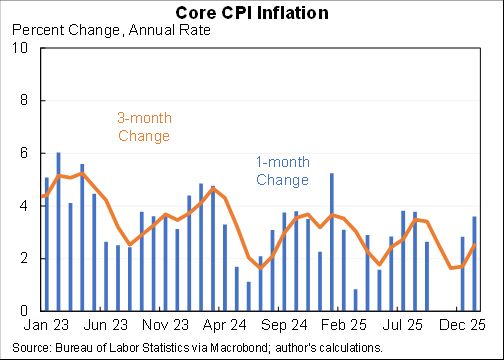
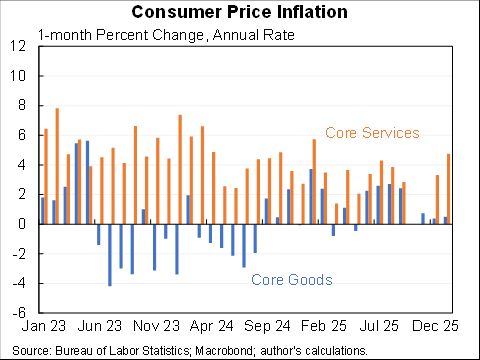
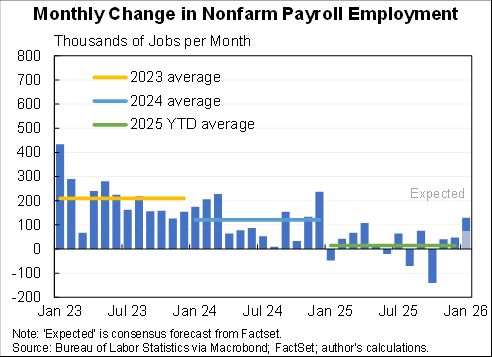
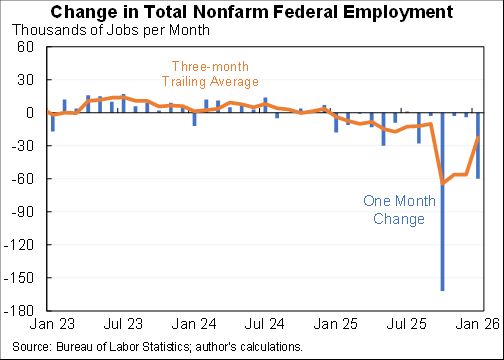
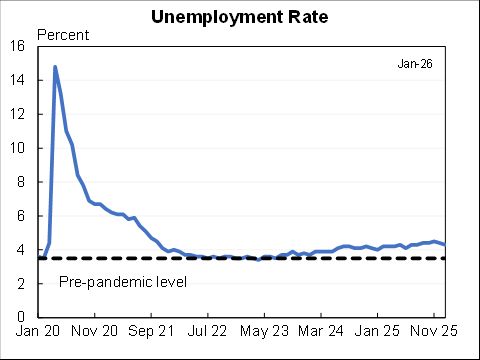
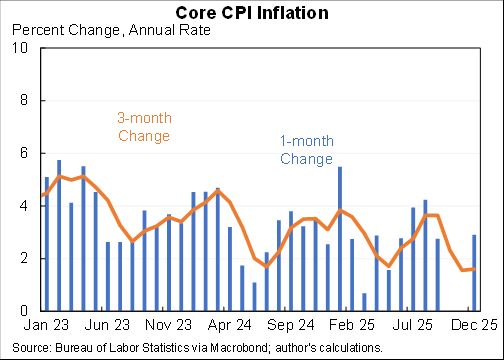
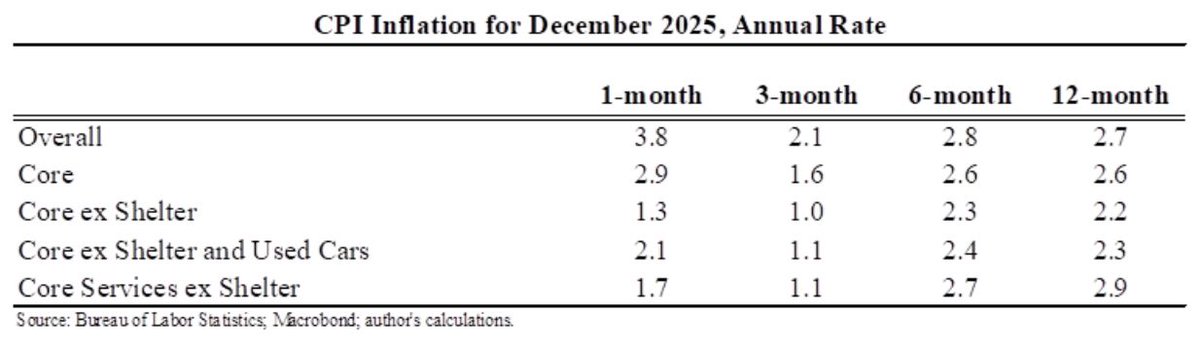
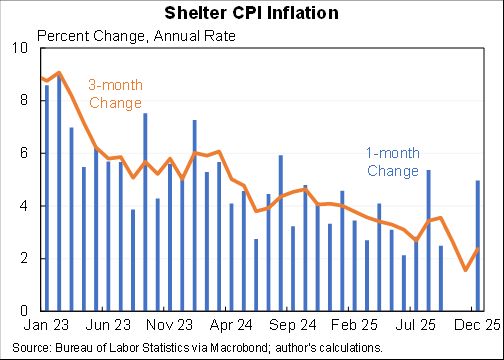
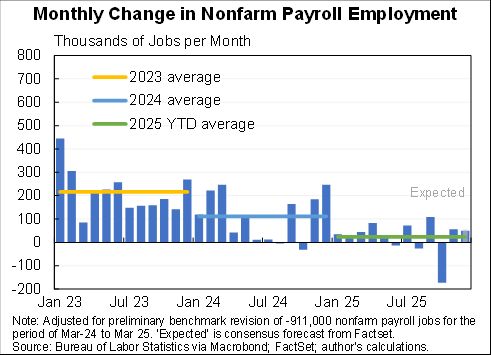
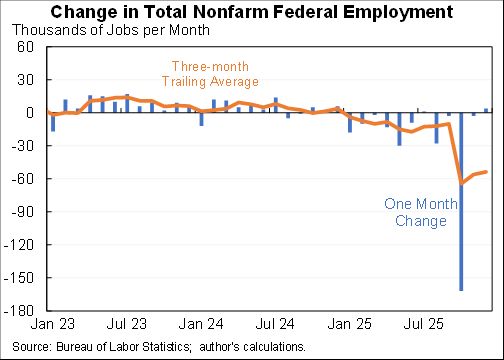
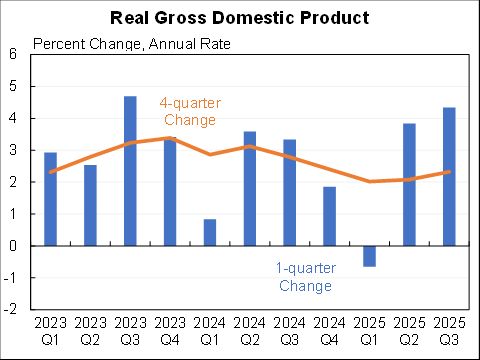
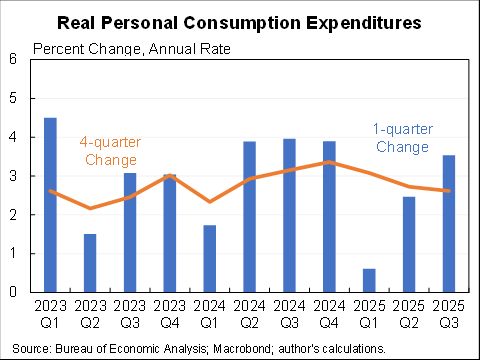
Wow, people reacted very differently to the rise in COVID in December than they did to previous waves.
Retail sales in December:
Nonstore retailers (mostly online): -8.7%
Food services and drinking places: -0.8%
Overall retail sales fell sharply, 1.9% overall.
Retail sales in December:
Nonstore retailers (mostly online): -8.7%
Food services and drinking places: -0.8%
Overall retail sales fell sharply, 1.9% overall.
The decline in retail sales might actually be a positive sign of a healthy normalization.
The economy has struggled to produce enough goods to match the voracious consumer appetite for them. If goods spending continues to normalize that would be, well, good.
The economy has struggled to produce enough goods to match the voracious consumer appetite for them. If goods spending continues to normalize that would be, well, good.

To be clear, the chart in the previous tweet was real retail sales. Nominal retail spending remains very high but in it is no longer buying massive amounts more stuff than it used to be.
(Retail sales is mostly goods but does include services like restaurants and bars.)
(Retail sales is mostly goods but does include services like restaurants and bars.)

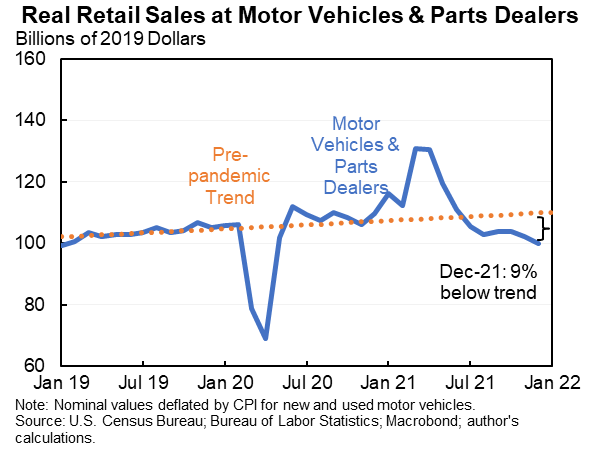
The biggest piece of retail sales is spending at motor vehicle and parts dealers (~20 percent of the total). It is up a lot in nominal terms but down in real terms. 


Sales at stores selling sporting goods, hobby, musical instruments and books are not nearly as important to the economy (~2% of the total) but they're much more fun and they're WAY up. 



People are basically spending a roughly normal amount at restaurants, give or take. But with prices up they're getting less for it in real terms. With this service part of retail sales lagging it suggests the goods part is a bit more above trend than I've shown. 



The December numbers plus downward revisions for November have led the bean counters to lower their forecasts for Q4 GDP growth to more like 6% instead of 7%. But that's still very strong. And if that growth is also happening in a more balanced, sustainable way that's good.
P.S. Omicron was just starting to wreak its havoc in December and people were slowly adjusting. I expect a lot more disruption to the January data. But also think that most analysts should mostly look through the January data which will (hopefully, fingers crossed) be anomalous.
P.P.S. Takeout counts as a purchase from "food service & drinking places." So these data don't tell us what happened to face-to-face behavior. But people weren't making a major shift from restaurant-prepared meals to home-prepared meals (w/ grocery store sales down in December).
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh