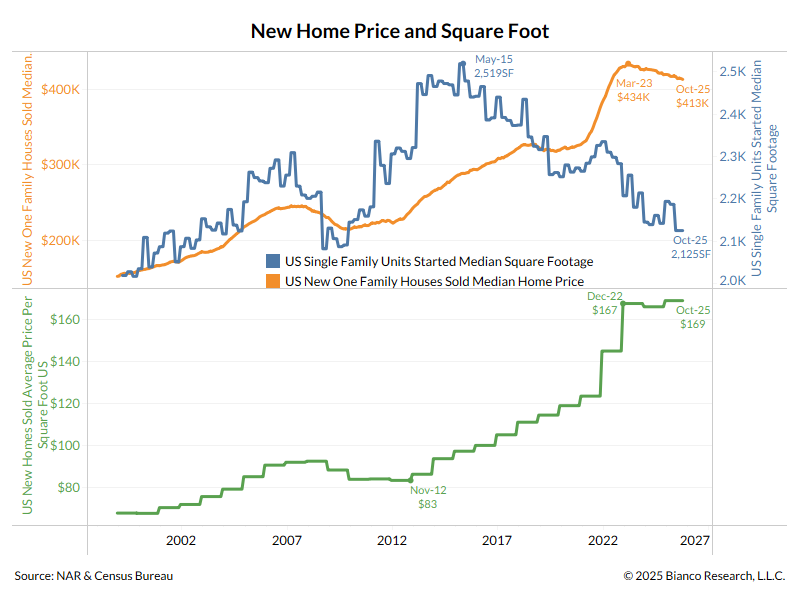
1/5
A thread to go over my interpretation of interest rates.
First this is what the market currently has priced in. 36% for the 5th hike in Feb 2023 is the highest ever.
First hike in March is now 86%. At this point any talk of no hike in March would move the market.
A thread to go over my interpretation of interest rates.
First this is what the market currently has priced in. 36% for the 5th hike in Feb 2023 is the highest ever.
First hike in March is now 86%. At this point any talk of no hike in March would move the market.

2/5
Earlier this morning Mike Wilson of Morgan Stanley was on Bloomberg TV. He is looking for 1.60% on 2-year yields at mid-year (from 0.945%).
Earlier this morning Mike Wilson of Morgan Stanley was on Bloomberg TV. He is looking for 1.60% on 2-year yields at mid-year (from 0.945%).

4/5
Why are 10yr ylds trending sideways as 2yr ylds relentlessly rise?
10yr ylds are a risk-off instrument, not an inflation pay. The fact that 10yr ylds are not rising in the face of inflation is a market signal that the Fed is going to hike too much and break something.
Why are 10yr ylds trending sideways as 2yr ylds relentlessly rise?
10yr ylds are a risk-off instrument, not an inflation pay. The fact that 10yr ylds are not rising in the face of inflation is a market signal that the Fed is going to hike too much and break something.

5/5
We will know when the Fed has “broken something” when/if the yield curve inverts.
It might not be obvious what broke the day the yield curve inverts, but the market will be signaling that something is indeed broken and it will be apparent in short order.
We will know when the Fed has “broken something” when/if the yield curve inverts.
It might not be obvious what broke the day the yield curve inverts, but the market will be signaling that something is indeed broken and it will be apparent in short order.
Bonus
Why will the Fed hike so much they will break something?
Inflation got away from them and is now intensely political. The economists can leave the FOMC board room. Hiking to address inflation is now the domain of politics and PR people worried about Fed optics.
Why will the Fed hike so much they will break something?
Inflation got away from them and is now intensely political. The economists can leave the FOMC board room. Hiking to address inflation is now the domain of politics and PR people worried about Fed optics.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh