🎯10 most useful string methods in Java
String is an object that represents sequence of char values. Strings are immutable in Java.There are two ways to create string in Java
1 - By String literal
2 - By new keyword
1 - By String literal
2 - By new keyword

📌Note: String literal create no new object if it exists already in the string constant pool (SCP) which is a special place for all strings in heap memory. Create string of same object using new keyword.This will create new object outside the string pool if it already exist in it
1 - indexOf() use to find characters and substrings in a string. It returns the index of first occurrence from left of the passed string or character
syntax - public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
str - substring to be search
fromIndex - search begin from this index
syntax - public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
str - substring to be search
fromIndex - search begin from this index

2 - toCharArray() used to form a character array of a string
syntax - public char[] toCharArray()
▶️Example : check if string is palindrome of not
syntax - public char[] toCharArray()
▶️Example : check if string is palindrome of not

3 - charAt() Used to find the character at particular index
syntax - public char charAt(int index)
▶️ Example : count no. of spaces in the string
syntax - public char charAt(int index)
▶️ Example : count no. of spaces in the string

4 - concat() Used to concatenate two strings
syntax - public String concat(String str)
▶️ Example : concatenate last name and firstname
syntax - public String concat(String str)
▶️ Example : concatenate last name and firstname

5 - replace() Used for replacing characters and substrings in a string
syntax - public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
▶️ Example : remove all white spaces from the string
syntax - public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
▶️ Example : remove all white spaces from the string

6 - substring() Used to extract a portion of a string from original string
syntax - public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
▶️Example : print first 3 character of a string
syntax - public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
▶️Example : print first 3 character of a string

7 - split() Used to breaks a given string around matches of the given regular expression.After splitting against the given regular expression, this method returns a char array
syntax - public String[] split(String regex, int limit)
limit : number of strings return after split
syntax - public String[] split(String regex, int limit)
limit : number of strings return after split

8 - compareTo() It compares the given string with the current string lexicographically. It returns a positive number, negative number, or 0
if s1 > s2, returns +ve number
if s1 < s2, returns -ve number
if s1 == s2, returns 0
syntax : public int compareTo(String anotherString)
if s1 > s2, returns +ve number
if s1 < s2, returns -ve number
if s1 == s2, returns 0
syntax : public int compareTo(String anotherString)

9 - strip() To eliminate all trailing and leading whitespaces from the given string
syntax - public String strip()
▶️ Example
syntax - public String strip()
▶️ Example

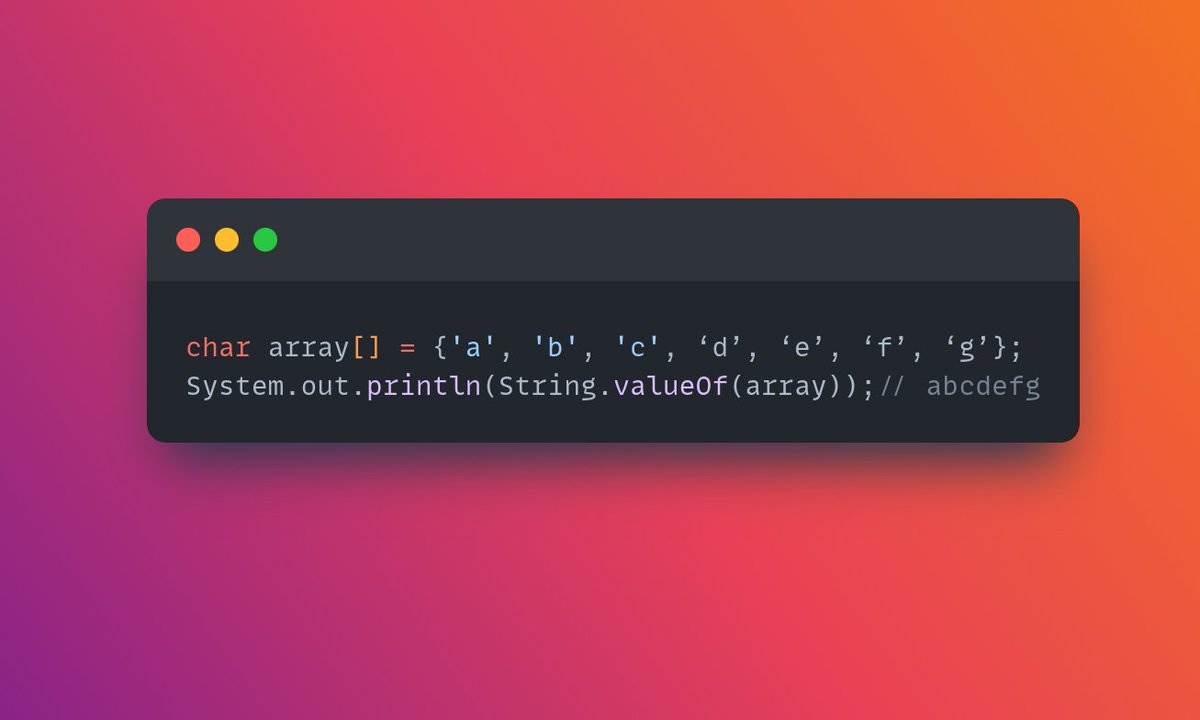
10 - valueOf() Used to return string representation of passed argument
syntax - public static String valueOf(char[] data)
Note : valueOf() has many overloaded variants that aid in the conversion of almost any primitive form to string
syntax - public static String valueOf(char[] data)
Note : valueOf() has many overloaded variants that aid in the conversion of almost any primitive form to string
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






