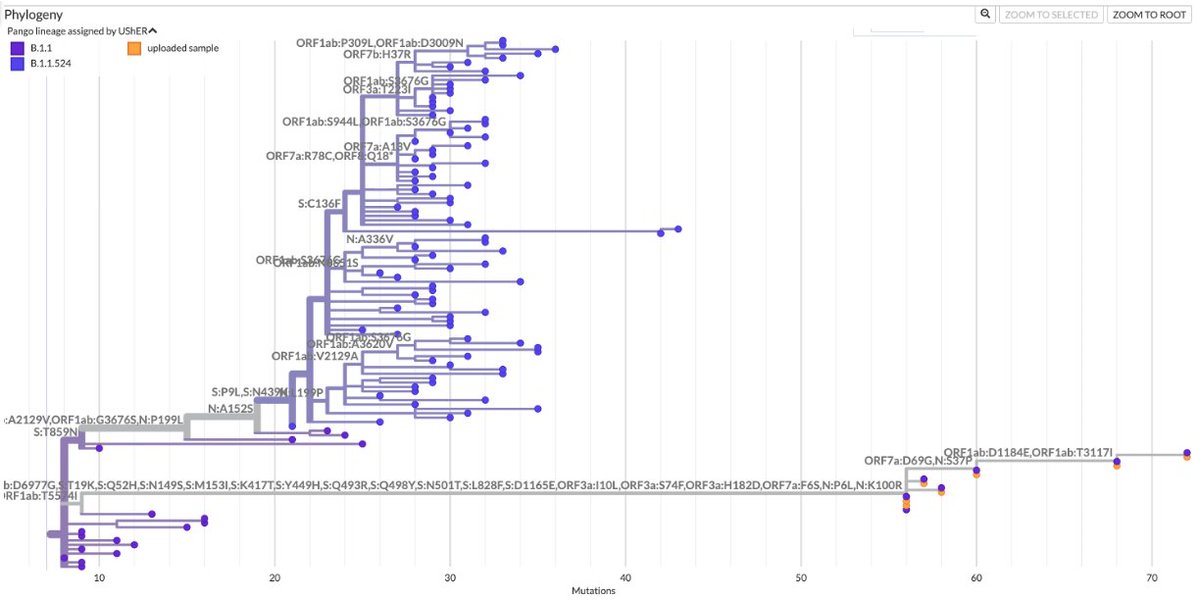
No one seems to know what BA.2 means for the world. I'm not aware of any studies on it, but I hope they come out soon. It seems apparent BA.2 will become dominant everywhere before long—as it already has in Denmark.
🧵 of graphs comparing BA.1 & BA.2 in various countries
1/16
🧵 of graphs comparing BA.1 & BA.2 in various countries
1/16
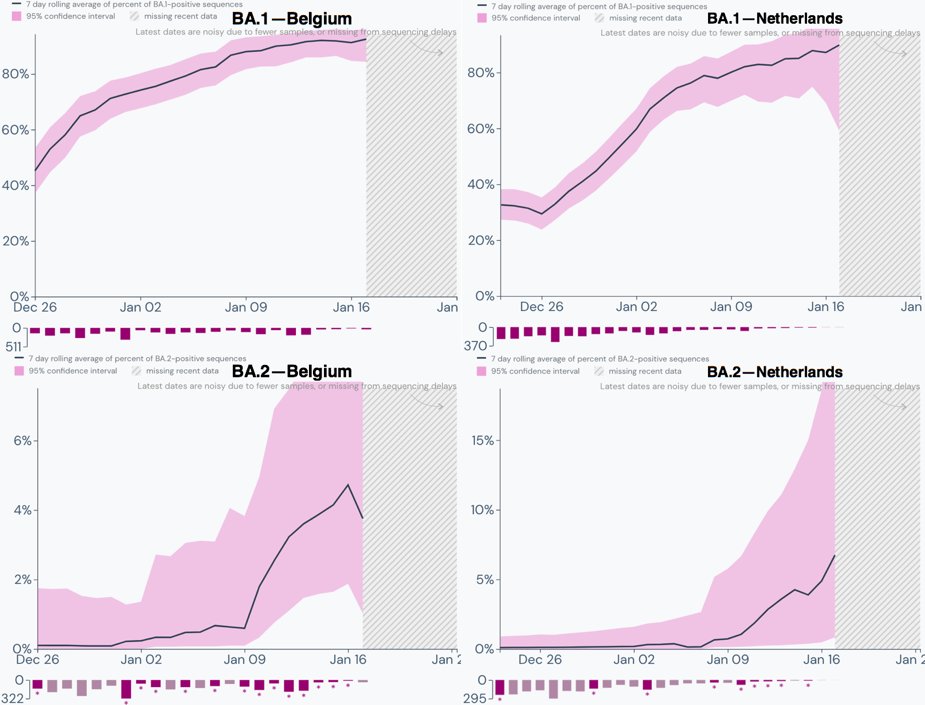
Of all the countries with decent genetic surveillance, Denmark has the highest proportion of BA.2. 2/16 

According to the Outbreak numbers compiled using @GISAID data, January 12 was when BA.2 surpassed 50% of all cases in Denmark, with 480/955 cases. 3/16 

A similar conclusion was reached by @JosetteSchoenma, who's assiduously tracked BA.2 prevalence in Denmark (and elsewhere) and was pointing out its significance before anyone else.
https://twitter.com/JosetteSchoenma/status/14841902954535813144/16
The fact that Denmark has the highest level of Covid cases per 100,000 of any country in the world and the highest percentage of BA.2 of any country with decent sequencing data is probably not a coincidence. 5/16 

The UK BA.2 numbers are far lower than in Denmark at the moment but are clearly on an exponentially increasing trajectory. It's only a matter of time before BA.2 becomes dominant there. 6/16 

According to @OliasDave, BA.2 is doubling every 4 days (as a percentage of all cases) in the UK, meaning it could become dominant there in about three weeks. 7/16
https://twitter.com/OliasDave/status/1485048710623076355
Genetic surveillance outside of Denmark & the UK is far less comprehensive. The graphs therefore noisier & the trends less consistent. Still exponential increase in the proportion of BA.2 seems universal. Sweden and Norway are in the 10-15% range & exhibit similar trends. 8/16 

Germany's data is pretty sparse after January 7, but there are hints of an early exponential increase in BA.2 there. 10/16 

Finally, there have only been 47 sequences of BA.2 detected in the US, 17 of them in Arizona. But there can hardly be any doubt we'll see large increases in BA.2 prevalence throughout the US in the coming weeks. 11/16 

Some have claimed that BA.2 is no different than BA.1 and nothing to worry about. It could turn out that way, but it seems far from certain. BA.2 has 70 mutations significantly more than the 53 of BA.1. 12/16
https://twitter.com/Unusual_Times/status/1485165200932319244
BA.1 and BA.2 share a set of mutations, but their mutations differ a great deal as well, both spike and non-spike. outbreak.info/compare-lineag… 13/16 


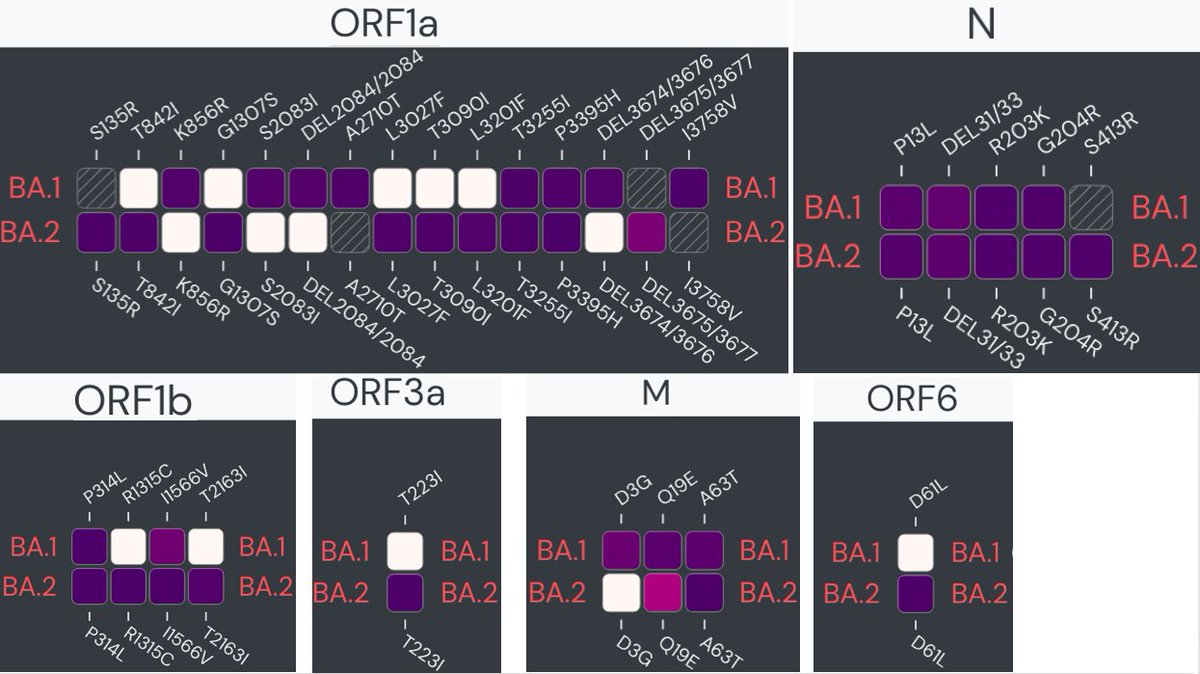
One Denmark report said there was "no evidence" of increased severity from BA.2. This may turn out to be right, but it reminds me of the early declarations that there was "no evidence" Alpha or Delta were more severe. Evidence takes time to accumulate. 14/16
We can hope BA.2 won't seriously change things for the worse, but to assume it is nothing to worry about seems extremely unwise. Similar assumptions have not worked out well for us in this pandemic.
Interesting tidbit from @bicidiario here. 15/16
Interesting tidbit from @bicidiario here. 15/16
https://twitter.com/bicidiario/status/1483757273424007169
See this great thread by @PeacockFlu for more info on BA.2. 16/16
https://twitter.com/PeacockFlu/status/1483768659420094464
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh