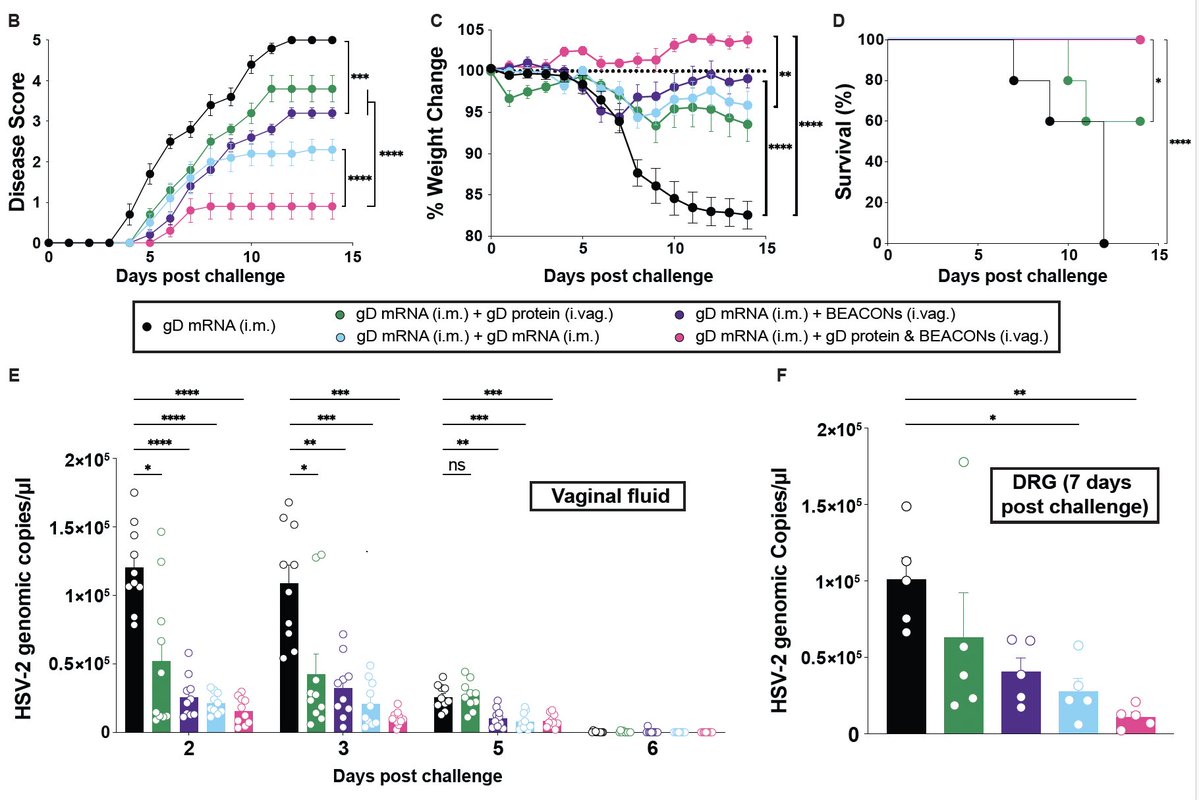
Vaccines that reduce infection & disease are needed to combat the pandemic. Here, @tianyangmao @BenIsraelow et al. describe our new mucosal booster strategy, Prime and Spike, to induce such immunity via nasal delivery of unadjuvanted spike vaccine 🧵 (1/)
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
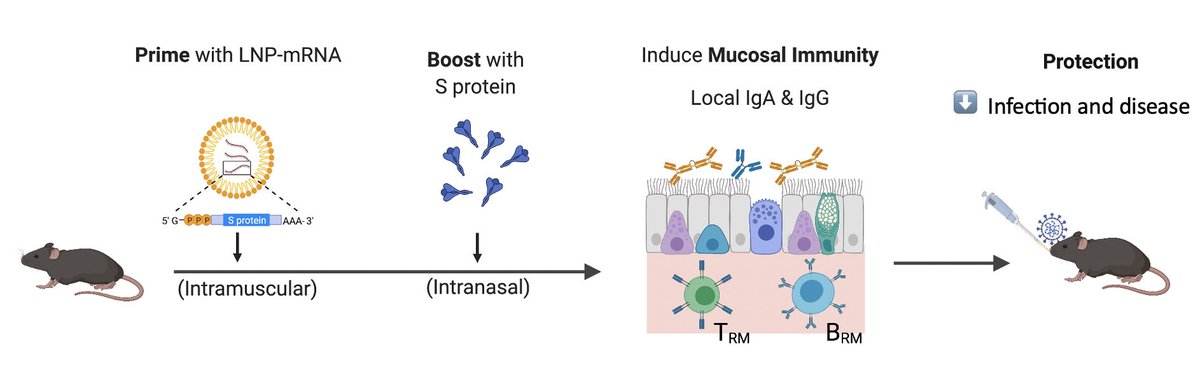
Current COVID vaccines are given intramuscularly. This induces robust circulating antibodies and systemic T & B cell responses that block viral spread and disease. However, to better block infection, immunity has to be established at mucosal surfaces. (2/)
annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/an…
annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/an…

To elicit mucosal immunity from scratch, live attenuated vaccines are often necessary, due to the need to introduce sufficient antigen and innate immune signals needed for priming via mucosal surfaces. Live vaccines are not safe for immunocompromised. (3/)
nature.com/articles/s4157…
nature.com/articles/s4157…

Adjuvanted inactivated vaccines have had safety concerns, as shown for the the intranasal flu vaccine significantly increasing the risk for Bell's palsy. (4/)
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
How do we overcome these problems? Intranasal inert antigens are not immunogenic, but adding adjuvant is unsafe. The answer lies in taking advantage of the existing adaptive immunity and use it as natural adjuvant to boost immunity. Hack the immune system. (5/)
To do this, @tianyangmao @BenIsraelow tested variety of boosting agents and found that simple purified spike protein (in stabilized prefusion confirmation) was able to boost ⬆️ nasal, lung and serum IgA/IgG & resident memory B & ASC following an IM Pfizer mRNA prime (blue). (6/) 
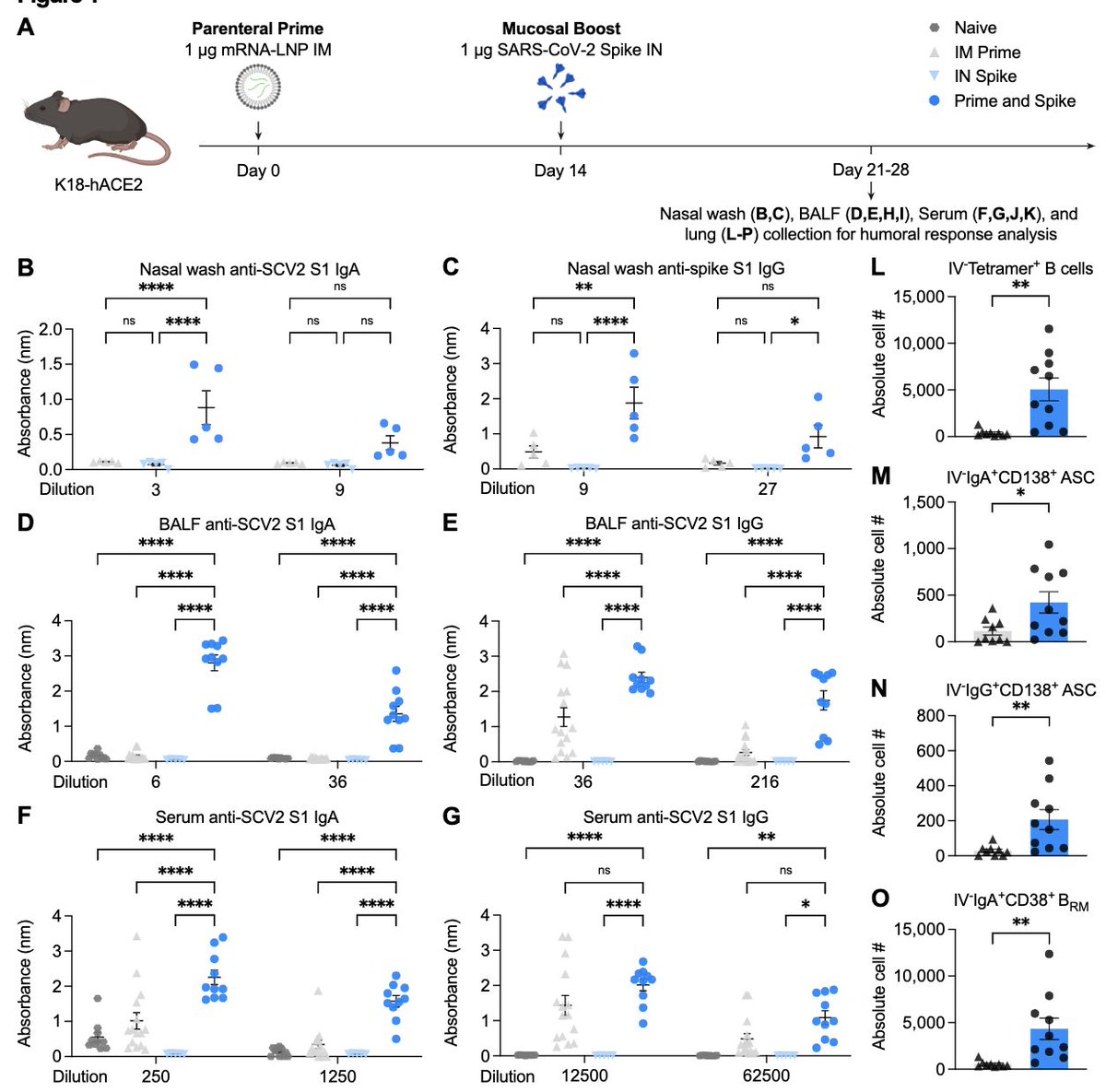
Further, in every respiratory compartment, lung parenchyma, lung lumen, nasal cavity, Prime and Spike led to increased CD4 tissue-resident memory (TRM) and spike-specific CD8 TRM (blue). Note that IN Spike without Prime (gray) does not induce Ab or T cells (7/) 

This strategy is versatile, and instead of using a recombinant protein, we show that spike mRNA encapsulated in immune-silent nanoparticle called Poly(amine-co-ester)s (PACE) developed by @wmsaltzman lab (PACE-Spike) IN was also capable of inducing TRM, BRM and mucosal Abs. (8/) 

So how well does Prime and Spike work compared to Prime alone? To mimic waning immunity, we gave very low dose of mRNA IM to prime the mice, then boosted nasally with Spike. 42 days later, they challenged mice with a lethal dose of SARS-CoV-2. (9/) 
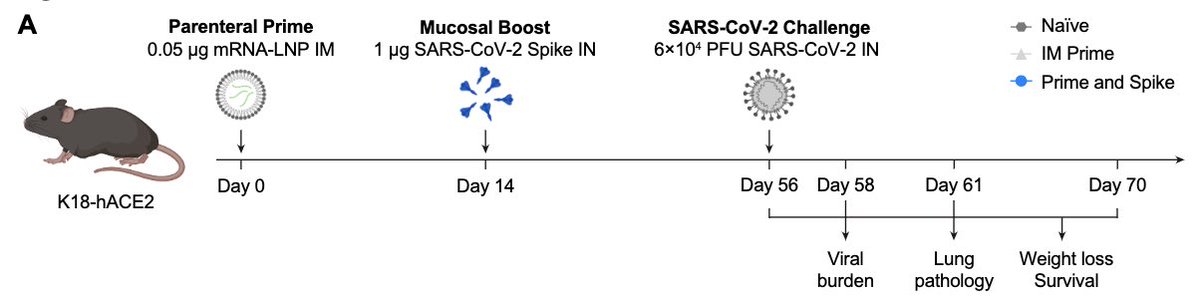
Prime (mRNA IM) and Spike (protein IN)(blue) protected all mice from disease and death. Moreover, Prime and Spike reduced both nasal and lung viral load. Prime alone (gray) was not able to protect mice from infection, disease or death. (10/) 

Similarly, Prime (mRNA IM) and PACE-Spike (mRNA in PACE IN) (green) also protected mice from death and disease, when challenged 42 days post boost. (11/) 

@tianyangmao @BenIsraelow took it one step further. Can Prime and SpikeX (a heterologous Spike) generate cross-reactive immunity against SpikeX? They set up Prime (mRNA IM) boost (mRNA IM) vs. Prime (mRNA IM) and Spike (protein IN) groups and compared. (12/) 

Remarkably, when SARS-CoV-1 spike was used as booster IN (red), mice developed lots of TRM (reactive to both CoV-1 and CoV-2) as well as boosted mucosal and systemic IgA and IgG against both CoV-1 and CoV-2 without suffering original antigenic sin. (13/) 

This study shows that unadjuvanted recombinant spike or PACE-mRNA-spike can be used to safely boost mucosal immunity in hosts primed with conventional mRNA vaccine to reduce infection and prevent disease. A heterologous spike boost can induce variant-specific T and Ab. (14/) 

Because Prime and Spike also establishes tissue-resident memory T and B cells, this strategy is likely to confer long-lasting and cross-reactive memory that can be quickly restimulated to prevent viral spread. (15/) 

The intranasal spike protein booster will also be much easier to administer (via nasal spray), quite stable (just protein) and is much more likely to be accepted by people who are hesitant of mRNA or those with needle phobia. (16/) 

This work was led by two brilliant colleagues, @tianyangmao and @BenIsraelow, along with @wmsaltzman and his lab members, and @marioph13 @rjhomer57 🔬(17/) 

This is the first step in making this a reality. After this proof of concept in mice, this strategy needs to be tested for safety and efficacy in larger animals and in clinical trials. Similar strategies can be used to combat other mucosal viral pathogens in the future. (End)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh