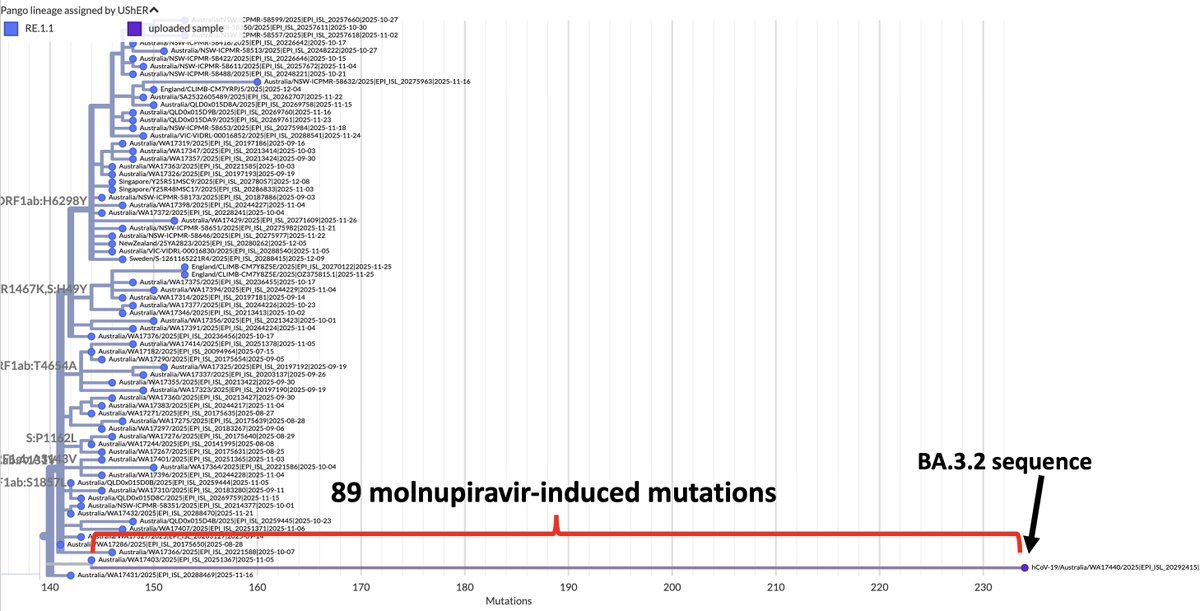
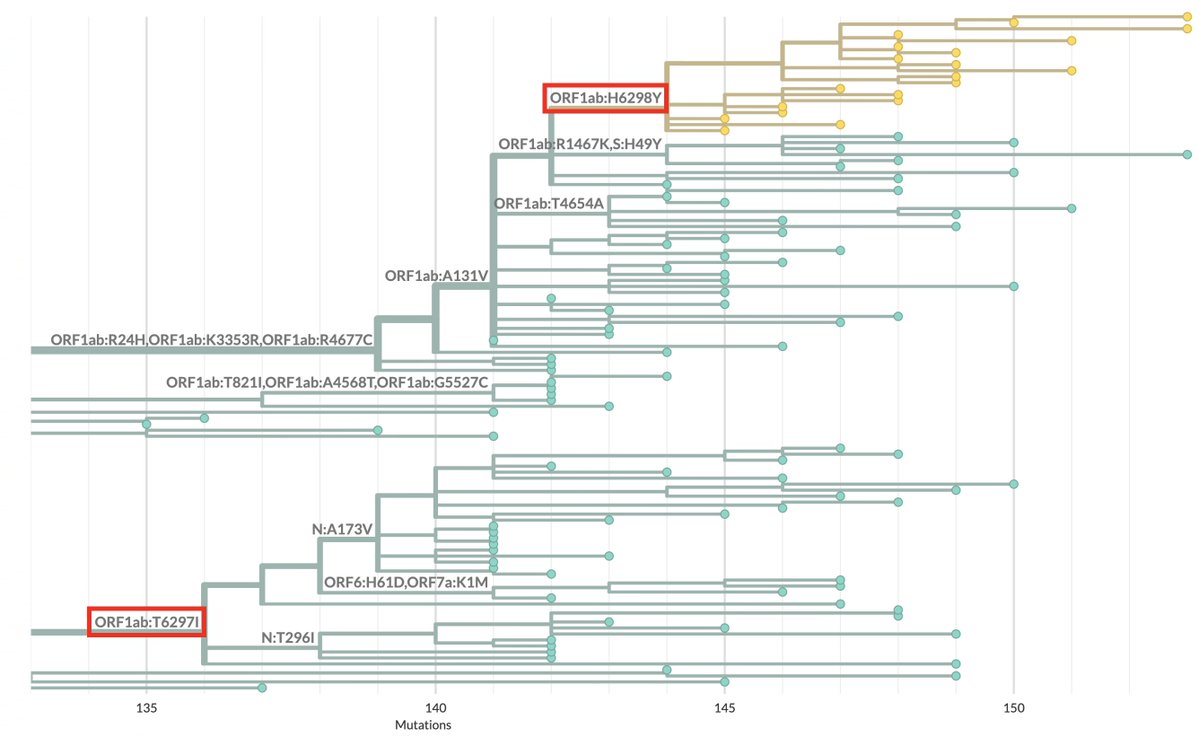
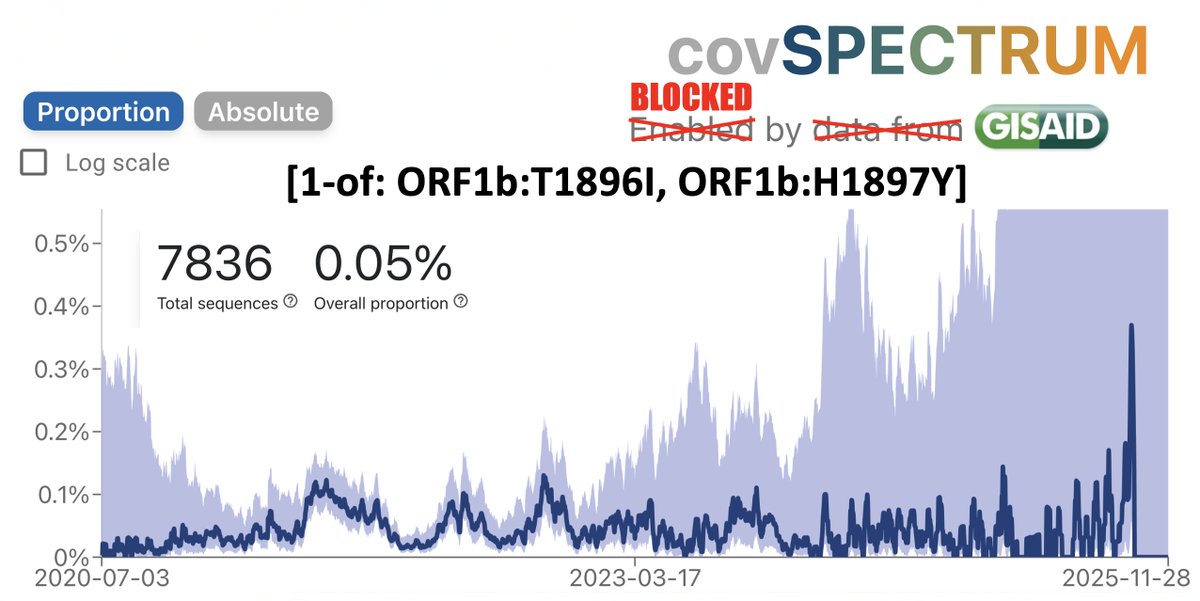
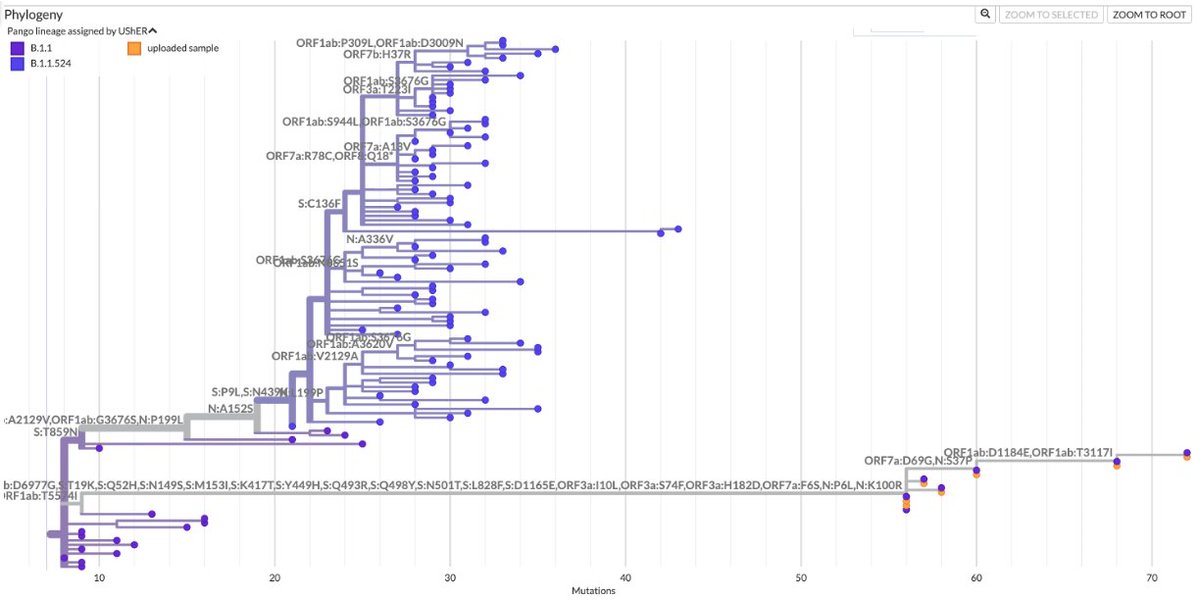
A thread of BA.2 updates.
BA.2 continues to do its thing in Denmark. The two most recent days of sequencing (January 20 & 21) recorded 74.2% BA.2 (285 of 384 cases). 1/9
BA.2 continues to do its thing in Denmark. The two most recent days of sequencing (January 20 & 21) recorded 74.2% BA.2 (285 of 384 cases). 1/9

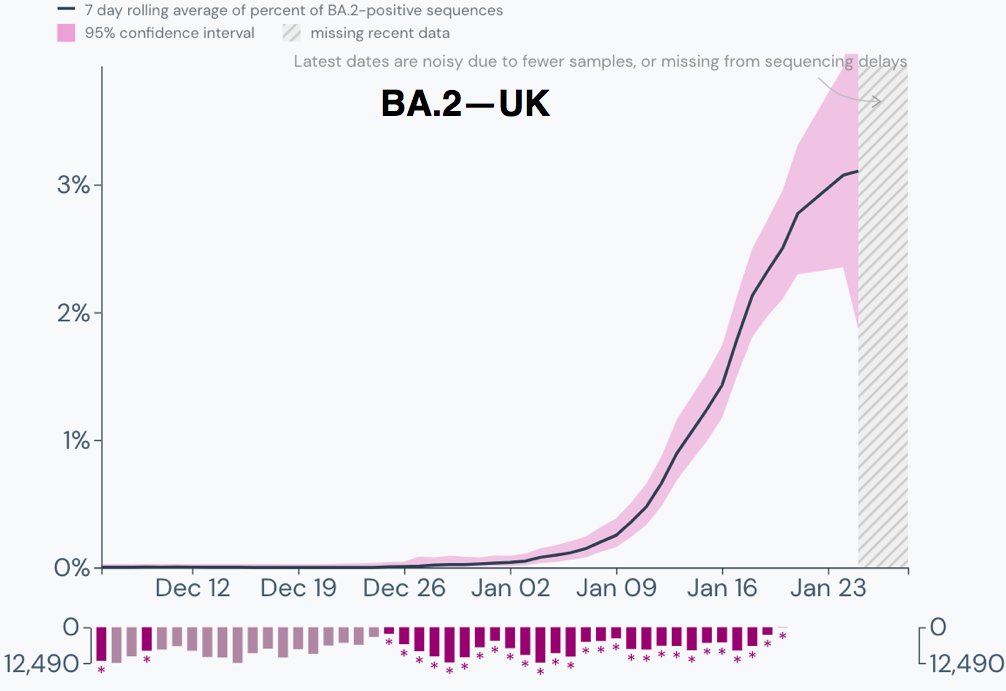
The exponential increase in the proportion of BA.2 cases continues in the UK.
The apparent slowdown in growth in the past several days is entirely due to 0 of 8 sequences being BA.2 over the past four days & should therefore be ignored. 2/9
The apparent slowdown in growth in the past several days is entirely due to 0 of 8 sequences being BA.2 over the past four days & should therefore be ignored. 2/9
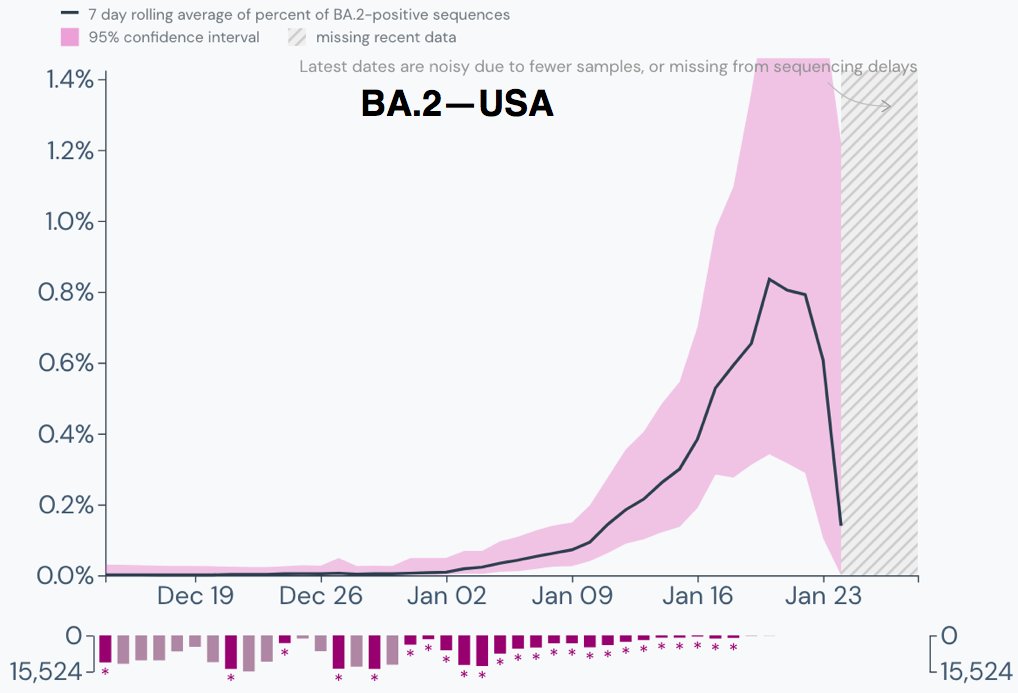
Similar exponential increase in the percentage of BA.2 cases in the US.
Again, the illusory plunge over the last five days is entirely due to a very small number of sequences and should be ignored. 3/9
Again, the illusory plunge over the last five days is entirely due to a very small number of sequences and should be ignored. 3/9
My home state of Indiana had recorded zero BA.2 cases before last night's update, when six cases were recorded in the most recent week of sequencing, indicating a substantial percentage of BA.2. Major caveat: sample size very small. 4/9 

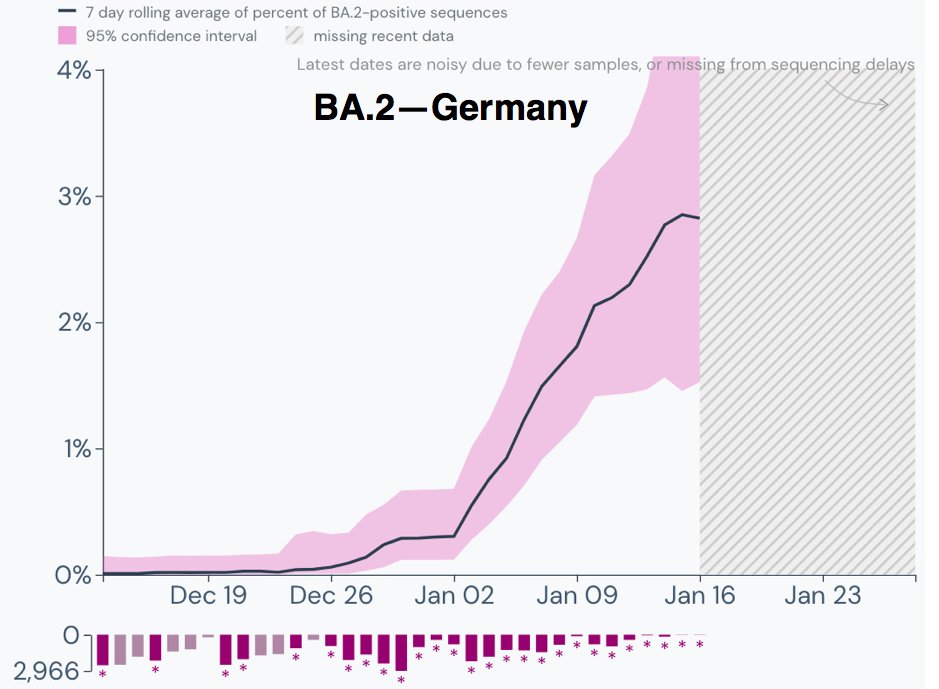
Germany's BA.2 path is similar to what Denmark's was early on. A recent report found that 30% of cases in Berlin were BA.2, so as has been the case elsewhere, large cities with lots of international travelers are leading the way. 5/9 
Japan finally has enough BA.2 to provide a decent indication of it's path. Surprise!—it's upward.
(Once again, the tiny sample sizes in recent days mean the illusory plunge at the end should be ignored.) 6/9
(Once again, the tiny sample sizes in recent days mean the illusory plunge at the end should be ignored.) 6/9

Not much sequencing in Portugal, but in the most recent day of sequencing, which was two weeks ago, all eight cases sequenced were BA.2. 7/9 

Spain, like Portugal, has poor genetic surveillance, but is seeing a similarly steep rise in BA.2.
Small sample size makes this a pretty unreliable estimate, however. 8/9
Small sample size makes this a pretty unreliable estimate, however. 8/9

Most of the other countries whose graphs I posted in a previous BA.2 update have seen little change. Not much has changed in Sweden, but I'll include it here since it has among the highest level of BA.2 among countries with decent sequencing. 9/9 

I was rushed when putting together this thread and made a mistake in the number of BA.2 cases recorded in Indiana. There have actually been 12 BA.2 sequences in the most recent 8 days of sequencing, not 6. This gives Indiana the highest percentage of BA.2 of any US state. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh