
Some slides from today's discussion on China at Kiel Institute for the World Economy.
The Chinese elite (top 5%) moved from being associated with the government to being composed mostly of businessmen and professionals.
The Chinese elite (top 5%) moved from being associated with the government to being composed mostly of businessmen and professionals.

Educational level of the elite increased substantially: from only 12% with university education in 1988 to 44% in 2013. 

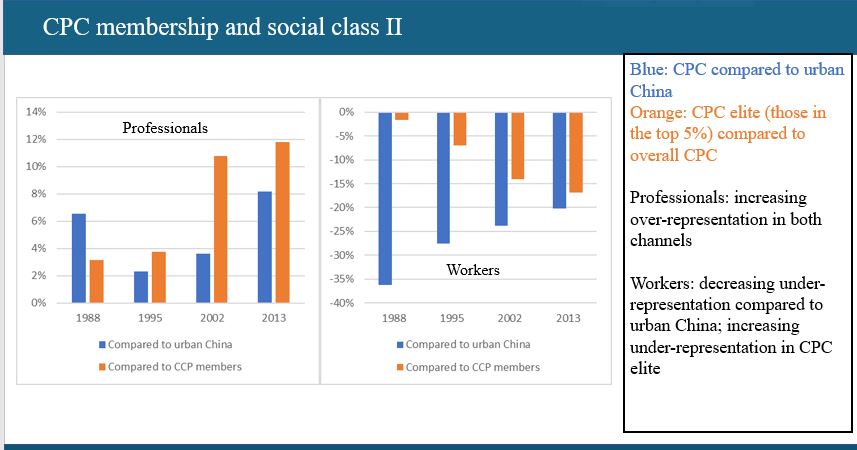
Professionals are over-represented in both CPC (compared to their share in the urban population) and in the elite. The composition of the richest members of CPC increasingly diverges from the composition of overall CPC. 
Based on the paper by Yang, Novokmet and Milanovic.
"From workers to capitalists in less than two generations: A study of Chinese urban top group transformation between 1988 and 2013"
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.111…
"From workers to capitalists in less than two generations: A study of Chinese urban top group transformation between 1988 and 2013"
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.111…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





