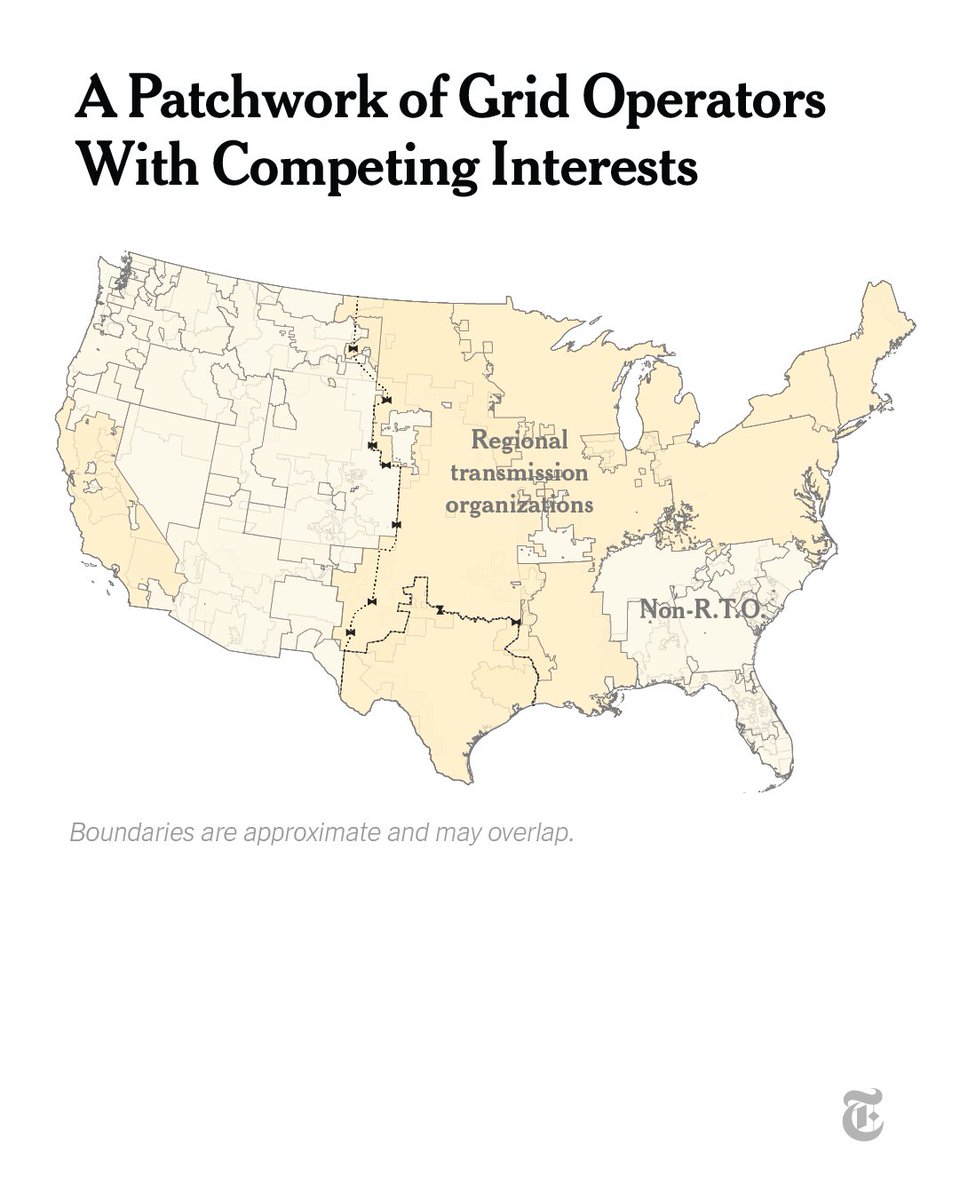
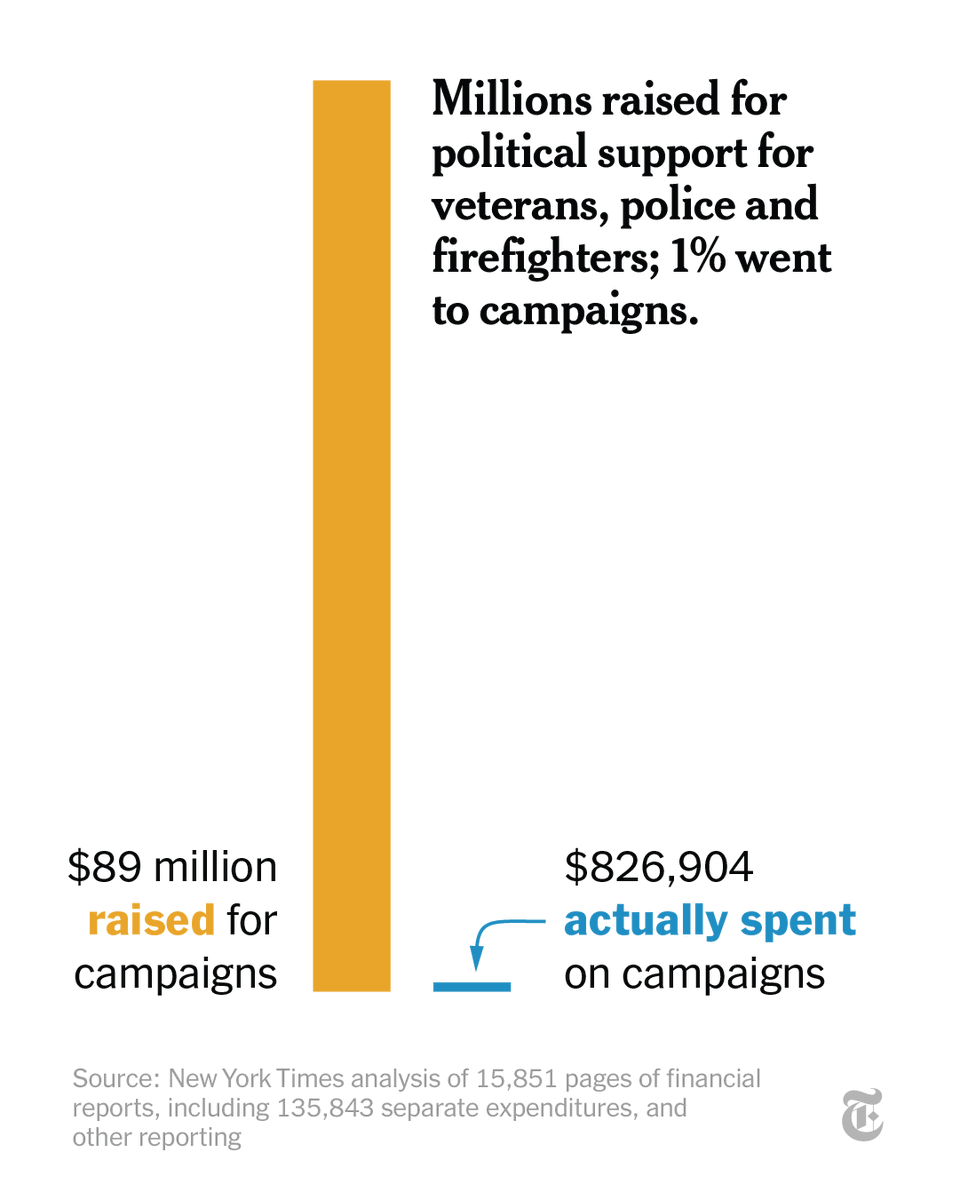
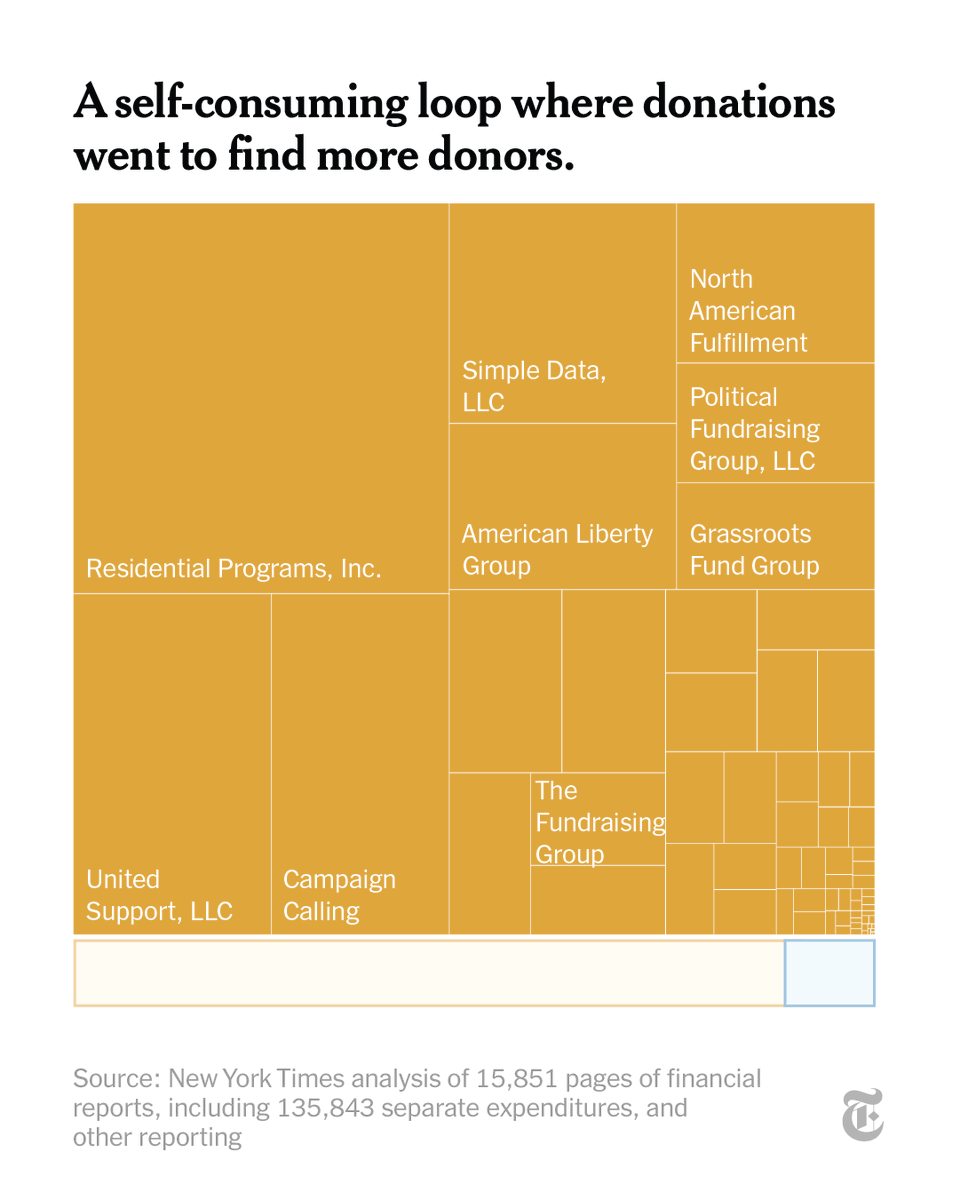
Have you ever wondered how a book becomes a book? From vats of ink to 800-pound rolls of paper, we went behind the scenes to reveal how exactly a book is made. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2
To illustrate the journey, we followed the creation of Marlon James’s “Moon Witch, Spider King,” a fantastical epic that draws on African mythology. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2
The book jacket is printed first:
The cover for “Moon Witch, Spider King” is unusually complicated. Most covers are printed using black, cyan, magenta and yellow ink, but two additional colors were used for this one: Day-Glo green and a special blue. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2
The cover for “Moon Witch, Spider King” is unusually complicated. Most covers are printed using black, cyan, magenta and yellow ink, but two additional colors were used for this one: Day-Glo green and a special blue. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2

Proofs of the cover are made to inspect the colors, and then the print run begins. After the covers are printed and laminated, they are put on a truck and driven to a plant that will print the book and package them all together. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2 



Next is the press:
“Moon Witch, Spider King” was printed by Lakeside Book Company, one of the largest printing companies in the U.S. The facility where it was printed runs 24 hours a day, seven days a week; it turns out millions of books each week. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2
“Moon Witch, Spider King” was printed by Lakeside Book Company, one of the largest printing companies in the U.S. The facility where it was printed runs 24 hours a day, seven days a week; it turns out millions of books each week. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2

On printing day, plates of text are installed. Giant rolls of paper, about 800 pounds each, are spliced and spooled. The book is printed 32 pages at a time, and every few hours, the plates must be swapped out so the next 32 pages can be printed. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2 
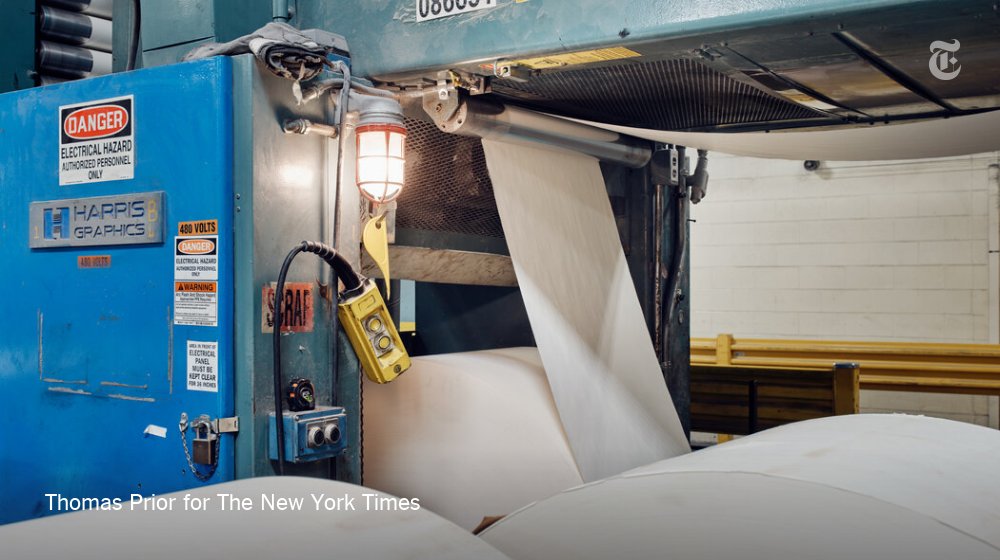



At the end of the printing press, the 32-page sections are automatically cut and folded. The printed sections are then bundled together to keep them in place until they are bound. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2
Next is the binding:
At a bindery, printed pages are loaded into a gathering machine. That machine will put the pages together in order, arranging them as a complete piece for the first time. Then, each book is trimmed and glued together. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2
At a bindery, printed pages are loaded into a gathering machine. That machine will put the pages together in order, arranging them as a complete piece for the first time. Then, each book is trimmed and glued together. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2

Next, the books head to a machine called the backer, which readies them for the cardboard cover to be attached, then to a case-in machine to apply the casing, then to a jacket wrapper machine that wraps the book with the printed and cut book jackets. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2
After all of that, copies are ready. “There is still something miraculous about a book, about seeing it,” Marlon James said. nyti.ms/3p2FPE2 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh