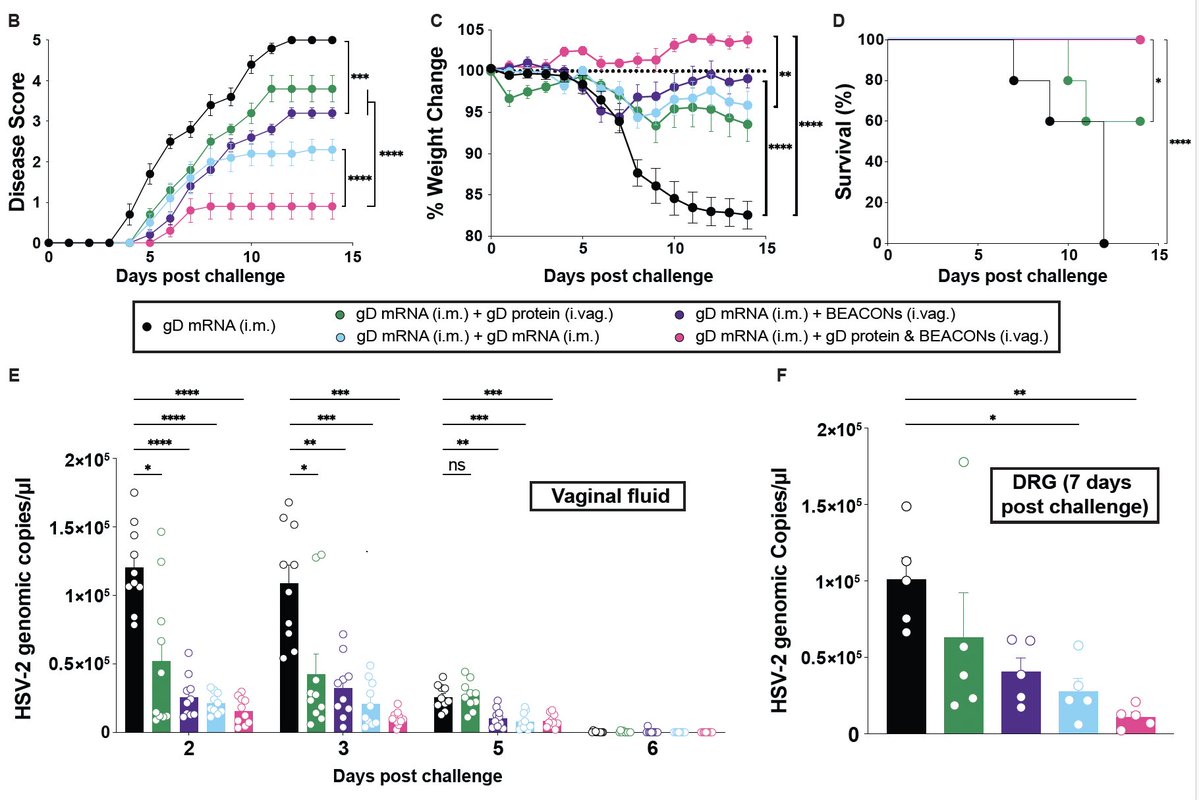
“COVID toes” are swollen discolored toes (and fingers) that were seen in areas with high incidence of COVID-19, but the cause is unknown. This new study by @JeffGehlhausen et al shows lack of association between covid toes and SARS-CoV-2 infection. 🧵(1/)
pnas.org/content/119/9/…
pnas.org/content/119/9/…
We enrolled 23 pandemic chilblains (PC) patients. While there is an association with community COVID cases (blue line) and PC (red bars), only 2 PC patients had evidence of infection by PCR or antibodies. We wondered if people may have missed the time window for testing +ve. (2/) 



PCR testing was difficult to access at the time of initial wave (2020). Thus, we employed two distinct measures of antibodies - ELISA and @serimmune SERA assays - against SARS-CoV-2 S, RBD and N. Only 2 of the 23 patients (who were also PCR +ve) had consistent antiviral Abs. (3/) 

However, Ab responses wane over time. So we next tested TCR repertoire of the PC patients using @AdaptiveBiotech’s immunoSEQ T-MAP COVID platform. This assay is more sensitive than Ab assay. It picked up one additional patient, PC #10, as testing pos for antiviral T cells. (4/) 

Using an orthogonal approach, we conducted a T cell stimulation assays of PBMCs utilizing a pool of S-protein peptides. This analysis also picked up patient #10 as being positive for T cells against S (consistent with immunoSEQ data). Thus patient #10, 12 and 16 are positive.(5/) 

Spike antigen in the toe has been detected by some and suggested as a cause of PC.When we used anti-S Ab for immunohistochemistry (IHC), we saw nice signals for spike in the PC skin (left). However, the same Ab also stained pre-pandemic tissues (right) -> Ab non-specific. (6/) 

In fact, we tested a few commercially available antibodies to the S and N and found cross-reactivity to human tissues from the prepandemic era. This is why we need multiple different approaches to ensure what we see in IHC is real. (7/) 

So only 3 of 23 pandemic chilblains patients were found to be COVID positive by PCR/Ab/T tests. What accounts for the rest of the patients’ skin lesions? We tested autoantibodies to human exoproteome with REAP with @Aaronmring team and found no increase in PC over control. (8/) 

So what can explain pandemic chilblains? Strong mucosal innate immune responses (interferons) that eliminated virus at exposure but caused delayed onset skin inflammation? Seronegative abortive infections by cross-protective T-cells that somehow led to delayed skin rash? (9/)
While we do not understand the ultimate driver of pandemic chilblain, our data show that it happens in most without detectable signs of infection & immunity. A heroic work of @JeffGehlhausen with others from @yalederm @AdrianoAguzzi @Aaronmring @InciYildirim11 @SaadOmer3 🙏🏼 (end) 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh