COVID-19: Causes unprecedented autoimmunity
Several studies have shown indicators and markers of autoimmunity (immune response attacking body's own health cells or tissues) present with and after COVID-19 infection. 🧵1/
Several studies have shown indicators and markers of autoimmunity (immune response attacking body's own health cells or tissues) present with and after COVID-19 infection. 🧵1/
One study found that CD8+ T-cells expressing killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are increased in the blood and inflamed tissues of patients with a variety of autoimmune diseases, including COVID-19 ( science.org/doi/10.1126/sc… ). 2/
They found elevated levels of KIR+CD8+ T-cells but not CD4+ regulatory T-cells in COVID-19 patients which correlated with disease severity, vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels) and were associated with autoimmune-related complications. 3/
Their results indicate that these regulatory CD8+ T-cells act uniquely to suppress pathogenic T-cells in autoimmune and infectious diseases. When they destroyed these cells in virus infected mice, it led to autoimmunity post-infection. 4/
Another study looked at 147 hospitalized COVID-19 patients and found autoantibodies in 50% of patients but less than 15% of healthy controls ( nature.com/articles/s4146… ). Autoantibodies mistakenly target and react with a person's own tissues or organs. 5/
They hypothesize that prolonged inability to eradicate and clear the virus expands the adaptive immune response to target non-structural viral proteins, some of which might physically interact or cross-react with components of the body. 6/
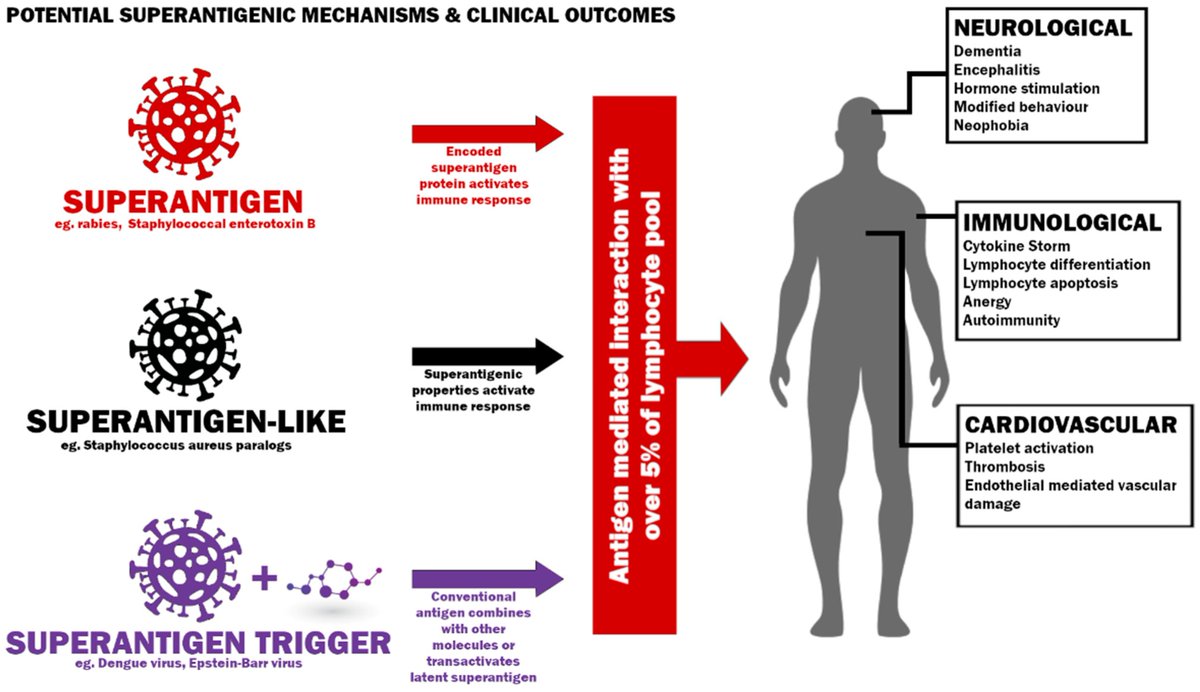
A new publication from @fitterhappierAJ discusses superantigens and COVID-19 ( mdpi.com/2076-0817/11/4… ). It has been suggested that the COVID-19 virus contains at least one superantigen-like pattern that is unique and not found in any other SARS or endemic coronaviruses. 7/
Why is this an issue? Superantigens can send the immune system into overdrive since multiple immune cells already trained for other pathogens might think it looks similar enough and activate. Normally a very small fraction of T-cells will be stimulated during an infection. 8/
A superantigen can stimulate up to 30% of naive T-cells which can also lead to a number of issues including anergy (T-cells become unresponsive), inflammation, cytotoxicity (kill cells), deletion of T-cells, and autoimmunity. 9/
"SARS-CoV-2 causes many of the biological and clinical consequences of a superantigen, and we believe in the context of reinfection and waning immunity,..." 10/
"... it is important to better understand the impact of a widely circulating, airborne pathogen that may be a superantigen, superantigen-like or trigger a superantigenic host response." 11/
Superantigens have differing effects on immature and mature CD4 and CD8 T-cells (see figure). They can deplete immature T-cells but hyperstimulate mature cells. 12/
They can also cause differentiation of naive T-cells and stimulation of CD8 memory cells from bystander activation which can also lead to T-cell death. 13/ 
The possibility of deletion of antiviral memory warrants investigation given the thymus loses its ability to produce new naive T-cells as we age and could compromise the ability for the immune system to clear pathogens. 14/
COVID-19 has been found to persist in the body for months after infection therefore chronic exposure to superantigen could continually stimulate T-cells, keeping them in a perpetual state between anergy and hyperstimulation. 15/
This could also manifest in an observed naive T-cell depletion and could explain the low quantities found in some Long COVID patients. 16/
The evidence of autoimmunity with COVID-19 keeps mounting. Studies have found immunological dysfunction following even mild to moderate infection, including depletion of naive T-cells and B-cells in individuals with Long COVID. 17/
Another study found the depletion of naive T-cells and higher levels of T-cell death (apoptosis) in COVID-19 infection than HIV. 18/
"Some countries seem willing to tolerate high levels of infection provided their healthcare systems can cope... If SARS-CoV-2 contains a superantigen, superantigen-like protein or triggers a superantigenic host response, this strategy may prove a grave error." 19/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh