The #Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, situated in the border area of northwest China and the hinterland of the Eurasian Continent, occupies an area of 1.6649 million sq km, accounting for one sixth of Chinese territory. It has a land border of 5,700 km bounded by 8 countries.↘️ 
It was an important section of the ancient Silk Road. Since ancient times,#Xinjiang has been inhabited by many ethnic groups believing in a number of religions. Since the Western Han Dynasty (206BC-24AD),it has been an inseparable part of the unitary multi-ethnic Chinese nation↘️ 

According to statistics, in the year 2020 #Xinjiang had a population of 25.8523 million, including 14.9322 million people of other ethnic groups than the Han, China's majority ethnic group.↘️ 

There are 56 ethnic groups in #Xinjiang , mainly the Uyghur, Han, Kazak, Hui, Mongolian, Kirgiz, Xibe, Tajik, Ozbek, Manchu, Daur, Tatar and Russian. It is one of China's five autonomous regions for ethnic minorities.↘️ 

In ancient history, many tribes and ethnic groups lived in #Xinjiang . The ethnic origins of the residents of XJ began to be clearly recorded in the Han Dynasty (206BC-220AD), the main ones being the Sai (Sak), Rouzhi (or Yueh-chih), Wusun (Usun), Qiang, Xiongnu (Hun) and Han. ↘️ 

The Sai(塞)as a nomadic tribe used to roam about the area from the Ili and Chuhe river basins in the east to the Sir (Syrdarya) River valley in the west. Under pressure from the Rouzhi, they moved to the north bank of the Sir River, and southward to scatter in the Pamirs.↘️ 

The Rouzhi(月氏)roamed the vast region between the Gansu Corridor and the Tarim Basin during the Warring States Period (475 B.C.-221 B.C.) and flourished during the Qin (秦 221B.C.-206 B.C.) and Han dynasties.↘️ 
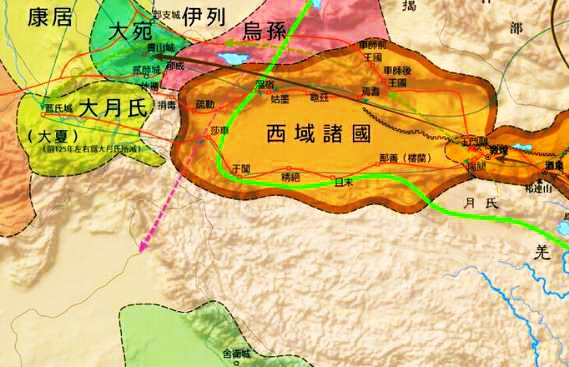
Attacked by the Xiongnu(匈奴)around 176 BC, they were forced to move to the Ili River basin, from which they dislodged the Sai.
The Wusun(乌孙 )first lived in the Gansu Corridor. In the late Qin and early Han period, ↘️
The Wusun(乌孙 )first lived in the Gansu Corridor. In the late Qin and early Han period, ↘️

attacked by the Rouzhi they yielded their allegiance to the Xiongnu. Supported by the Xiongnu, the Wusun attacked the Rouzhi, and drove them out of the Ili River basin.↘️ 

The Qiang(羌)originally lived along the middle and upper reaches of the Yellow River. During the Spring and Autumn (770 B.C.-476 B.C.) and Warring States periods, some of the Qiang migrated westward across the Gansu Corridor and the Qilian-Kunlun mountain ranges,↘️ 

leaving their footprints in #Xinjiang . The Xiongnu entered Xinjiang mainly around 176 B.C. The Han was one of the earliest peoples to settle in Xinjiang.↘️ 

In 101 B.C., the Han empire began to station garrison troops to open up wasteland for cultivation of farm crops in Luntai, Quli and some other places. Later, it sent troops to all other parts of #Xinjiang for the same purpose.↘️ 
All the garrison reclamation points became the early settlements of the Han people after they entered XJ.
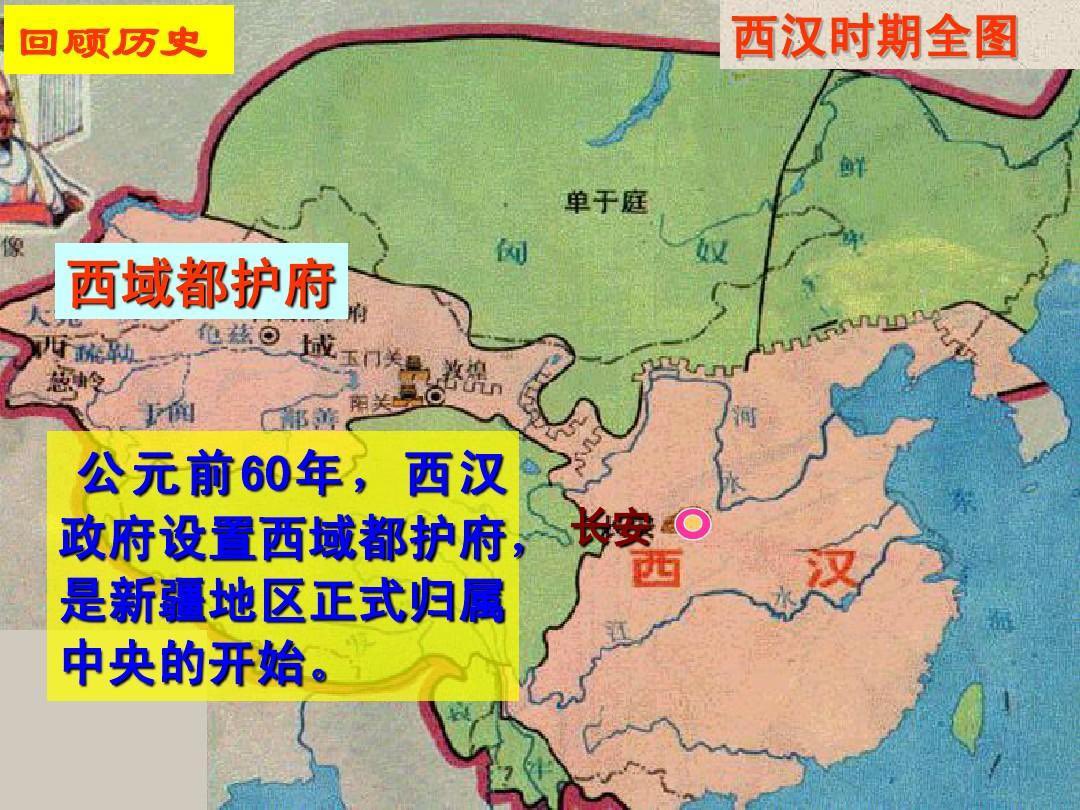
Since the Western Regions Frontier Command was established in 60 B.C., the inflow of the Han people to XJ, including officials, soldiers and merchants, had never stopped.↘️
Since the Western Regions Frontier Command was established in 60 B.C., the inflow of the Han people to XJ, including officials, soldiers and merchants, had never stopped.↘️
The period of the Wei, Jin and Southern and Northern Dynasties (魏晋南北朝 220 A.D.-589 A.D.) was a period of the large-scale merging of ethnic groups in China, witnessing frequent ethnic migration across the land of China, and↘️ 

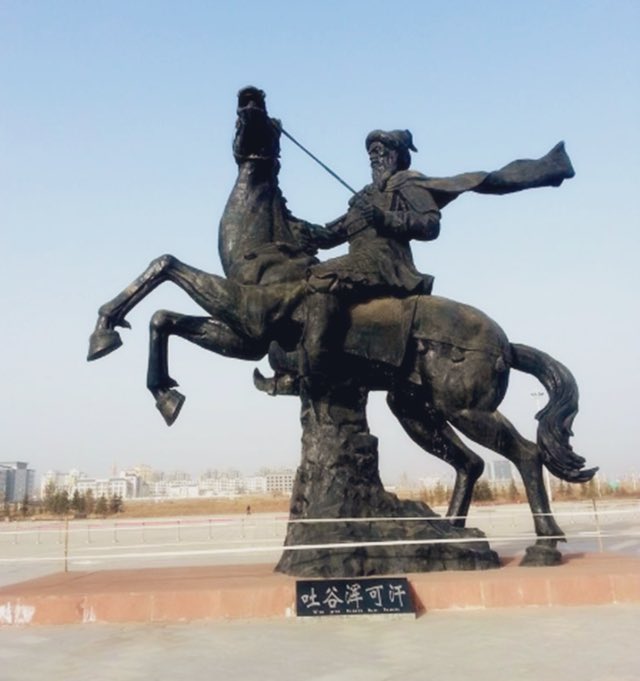
the entry into #Xinjiang by many ancient ethnic groups, such as the Rouran 柔然(Jorjan), Gaoche 高车, Yeda 哒 and Tuyuhun 吐谷浑. ↘️ 
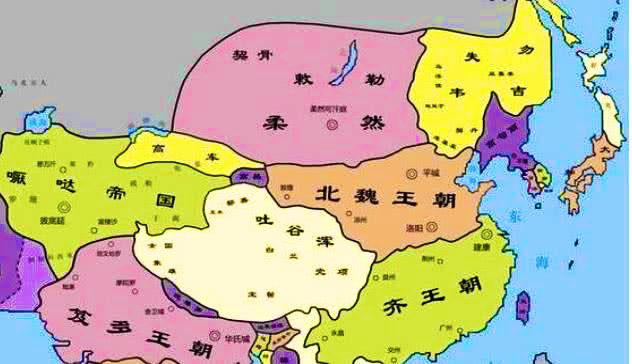
The Rouran(柔然)were descendants of the Donghu(东胡), an ancient people rising on the northern grasslands in the early fifth century. After establishing a powerful regime on the Mongolian grasslands in 402 A.D.,↘️ 

they struggled with the Northern Wei (北魏386-534) for domination of the Western Regions.
The nomadic Gaoche(高车), also called the Tolos(敕勒 )or Teli(铁勒), first appeared around Lake Baikal and the basins of the Orkhon and Tura rivers.↘️
The nomadic Gaoche(高车), also called the Tolos(敕勒 )or Teli(铁勒), first appeared around Lake Baikal and the basins of the Orkhon and Tura rivers.↘️

In 487, Avochilo, chief of the Puwurgur tribe of the Gaoche, and his brother Qunqi led more than 100,000 families to migrate westward, and founded the state of Gaoche to the northwest of Anterior Cheshi (the ancient city of Jiaohe near modern Turpan). ↘️ 

The Yeda(哒), rising in the region north of the Great Wall, moved eastward to the Tarim Basin, attacked the Rouzhi in the south and set up a state in the late fifth century. They crossed the Pamirs, and once controlled part of southern #Xinjiang .↘️ 

The Tuyuhun(吐谷浑), originating from the ancient Xianbei(鲜卑) people, moved westward from Liaodong (the region east of the Liaohe River in northeast China) in the early fourth century, and set up their own regime after conquering↘️ 

In the Sui (隋581-618) and Tang (唐618-907) dynasties, the ancient Turk(突厥)and Tubo(吐蕃) peoples exerted important influences on the course of #Xinjiang 's history.↘️ 
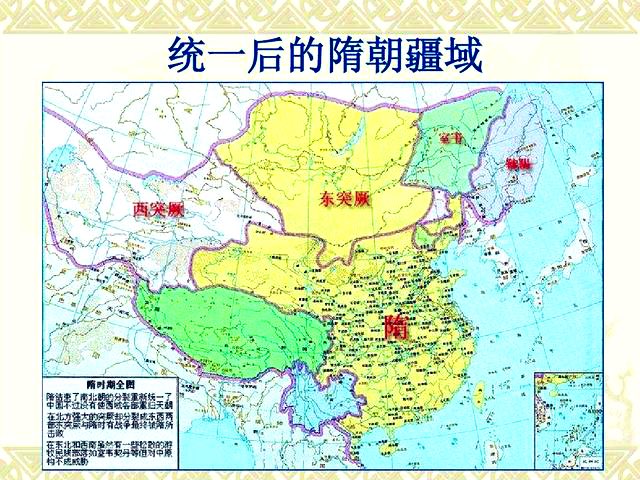
The Turks(突厥)were ancient nomads active on the northwestern and northern grasslands of China from sixth to eighth centuries. Tumen, a Turki leader, defeated the Rouran in 552, and set up a state centered in Mobei (the area north of the vast deserts on the Mongolian Plateau). ↘️ 

The Turki realm later split into the eastern and western sides which fought ceaselessly in their scramble for the khanate. In the middle of the eighth century, both the Eastern and Western Turki khanates disappeared, their descendants being assimilated by other ethnic groups.↘️ 
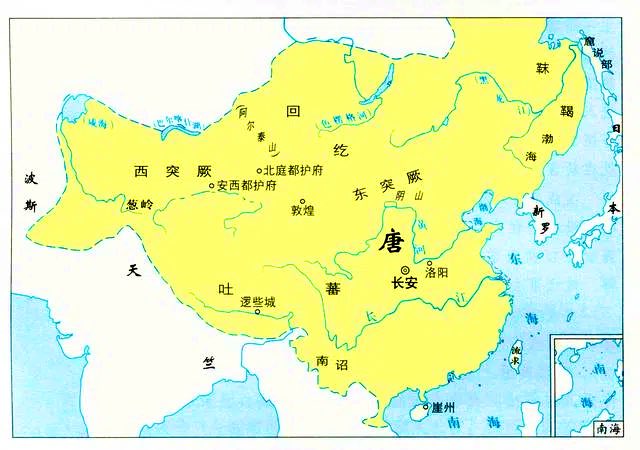
The Tubo were the ancestors of the Tibetans, rising to notice on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in the late sixth century. After occupying Qinghai, they began to vie with the Tang(唐) Dynasty for control of the Western Regions.↘️ 

In 755, An Lushan and Shi Siming (安史之乱)raised a rebellion in the Central Plains, and Tang(唐) troops stationed in the Western Regions were withdrawn to battle the rebels, whereupon the Tubo took the opportunity to occupy southern #Xinjiang and part of northern Xinjiang.↘️ 
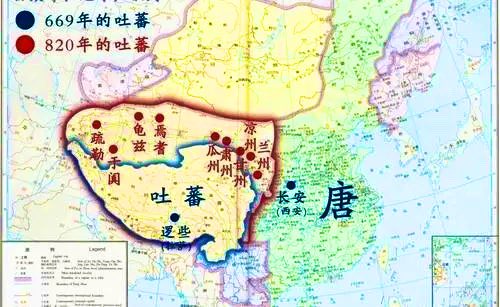
In 840, large numbers of Uighurs 回鹘 entered #Xinjiang . The Uighur, originally called Ouigour 回纥, sprang from the ancient tribe Teli 铁勒. They were first active in the Selenga and Orkhon river basins, and later moved to the north of the Tura River.↘️ 
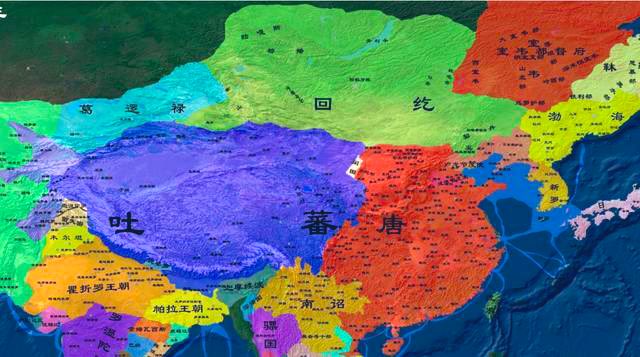
In 744, the Uighur founded a khanate in Mobei, and later dispatched troops twice to help the Tang central authorities to quell the An Lushan-Shi Siming Rebellion(安史之乱).↘️ 

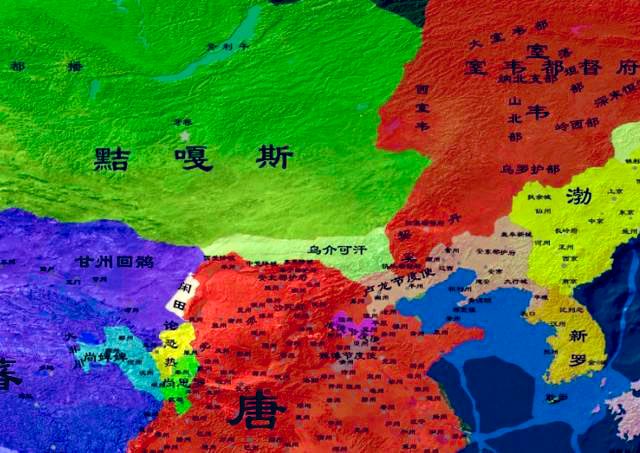
The Uighur Khanate collapsed in 840 because of natural disasters, internal strife and attacks by the ancient Jiegasi (黠戛斯) tribe. Consequently, most of the Uighur migrated westward.↘️ 
One of their sub-groups moved to the modern Jimsar and Turpan regions, where they founded the Gaochang Uighur Kingdom(高昌回鹘 ). Another sub-group moved to the Central Asian grasslands, scattered in areas from Central Asia to Kashi, and joined the Karluk and Yagma peoples in↘️ 
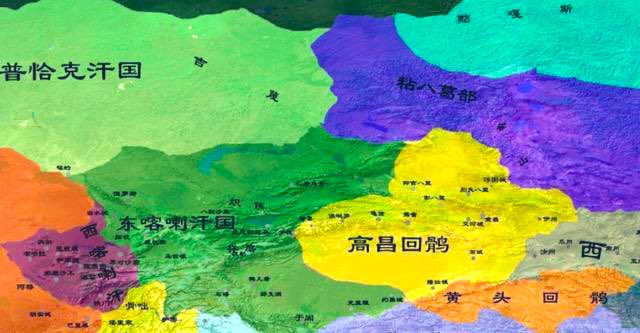
founding the Karahan Kingdom(喀喇汗王朝). After that, the Tarim Basin and its surrounding areas were under the rule of the Gaochang Uighur Kingdom and the Karahan Kingdom.↘️ 

The local residents were merged with the Uighurs that had moved west, thus laying the foundation for the subsequent formation of the Uygur ethnic group.↘️ 

In 1124, Yollig Taxin (耶律大石), a member of the ruling house of the Liao Dynasty (辽916-1125), led his people, the Khitan(契丹 )tribe, westward and conquered Xinjiang, where he established the kingdom of Western Liao.↘️ 
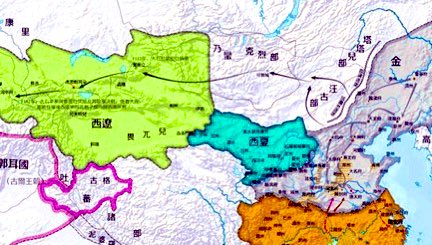
In the early 13th century, Genghis Khan (成吉思汗) led an expeditionary army to Xinjiang, where he granted the territories he had conquered to his children and grandchildren. The Uighurs further assimilated a portion of the Khitans and Mongolians.↘️ 

Oyrat(瓦剌) was the general name used for the Mongolians in Moxi (the area west of the vast deserts on the Mongolian Plateau) in the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644). The Oyrat first lived in scattered areas along the upper reaches of the Yenisaey River, ↘️ 
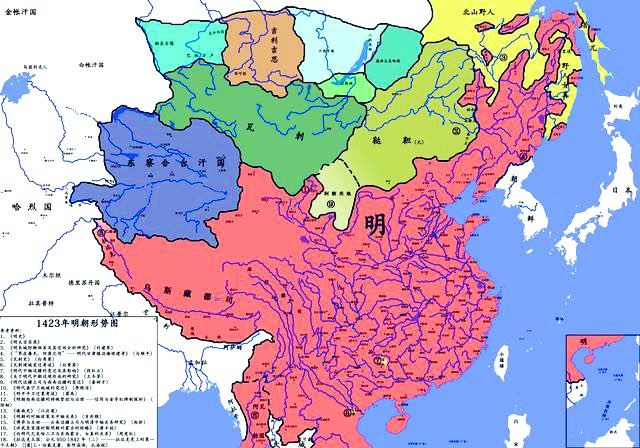
gradually spreading to the middle reaches of the Ertix and Ili river basins. The early 17th century saw the rise among them of the Junggar (准噶尔), Dorbot(杜尔伯特), Huxut (和硕特) and Turgut (土尔扈特) tribes.↘️ 

In the 1670s, the Junggar (准噶尔) occupied the Ili River basin, becoming leader of the four tribes, and put southern Xinjiang under their control.↘️ 

From the 1760s on, the government of the Qing Dynasty (清1644-1911) sent Manchu 满, Xibe 锡伯 and Suolun (Daur) 索伦(达斡尔) troops from northeast China to #Xinjiang in order to strengthen the frontier defense of the region, and they added to the ethnic mix in Xinjiang.↘️ 
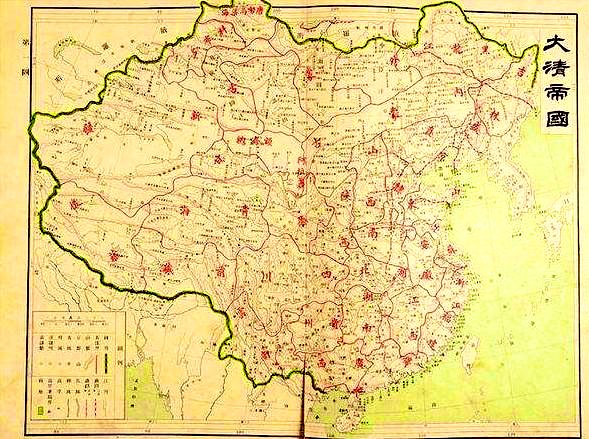
Afterwards, Russians and Tatars migrated into #Xinjiang . By the end of the 19th century, Xinjiang had 13 ethnic groups, namely, Uygur, Han, Kazak, Mongolian, Hui, Kirgiz, Manchu, Xibe, Tajik, Daur, Ozbek, Tatar and Russian. The Uygurs formed the majority, as they do today. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




