
Do Bone Marrow Haematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells (#stemcells) influence #fattyliver, Core Liver Networks, and liver cancer?
Very happy to share our findings in this (5 min read) Tweetorial🧵
More details on bioRxiv:
#livertwitter
Very happy to share our findings in this (5 min read) Tweetorial🧵
More details on bioRxiv:
https://twitter.com/biorxiv_sysbio/status/1515390223940784131
#livertwitter

2. In our previous publication in @CellSystemsCP, we used network analysis (#WGCNA) to identify the preserved liver networks (Core-Modules) between species and screened for their genetic regulators (module-eQTLs).
Infographic by Misaki Ouchida:
misakiouchida.com
Infographic by Misaki Ouchida:
misakiouchida.com
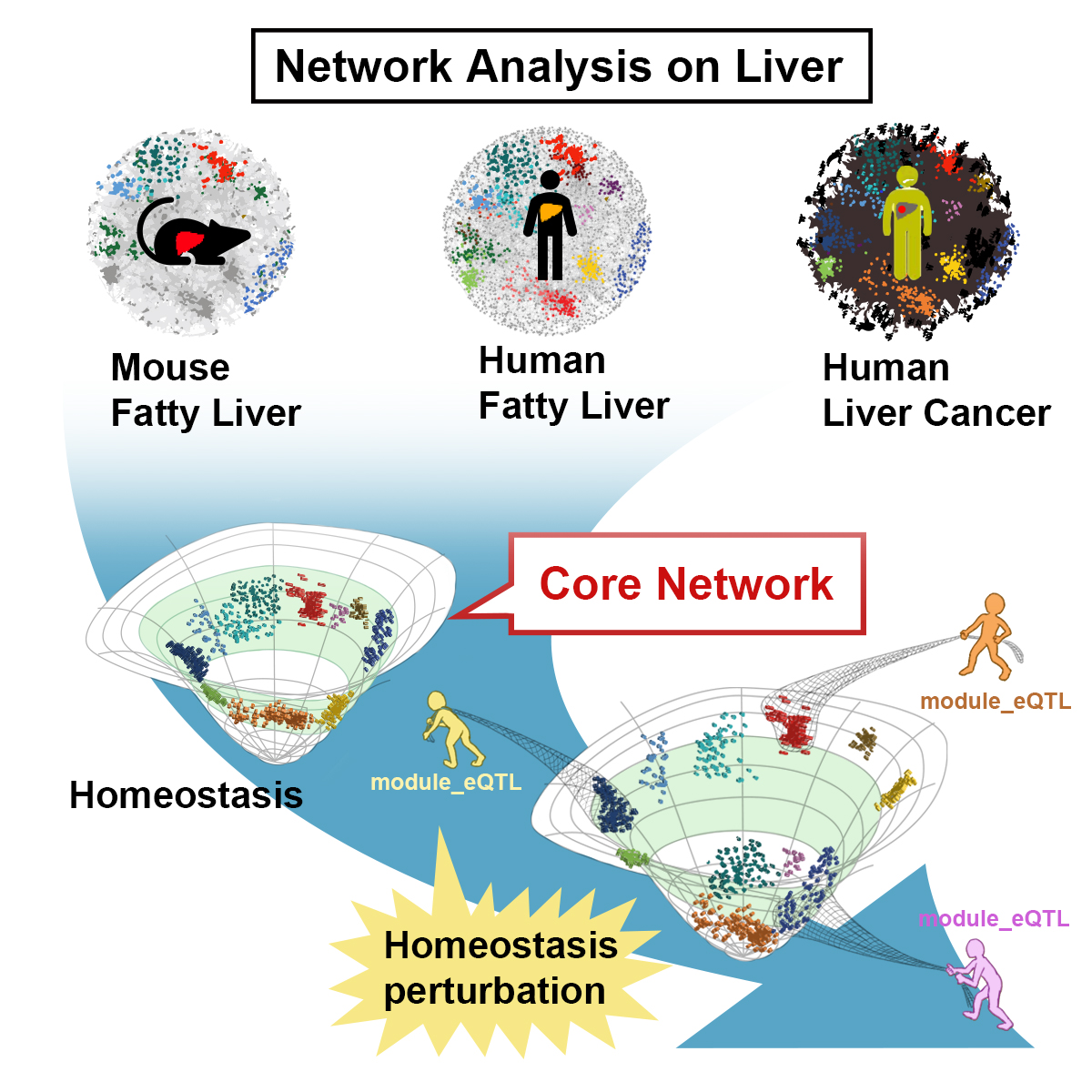
3. Here you can find a concise review/commentary on our previous paper on core liver networks in @CellRepMed
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
4. Here, you can see directionally different behaviour of immune networks between mouse fatty liver models and human fatty liver. Diet 5 (ChR) shows the highest immune response in mice, while immune network is down-regulation in human. 
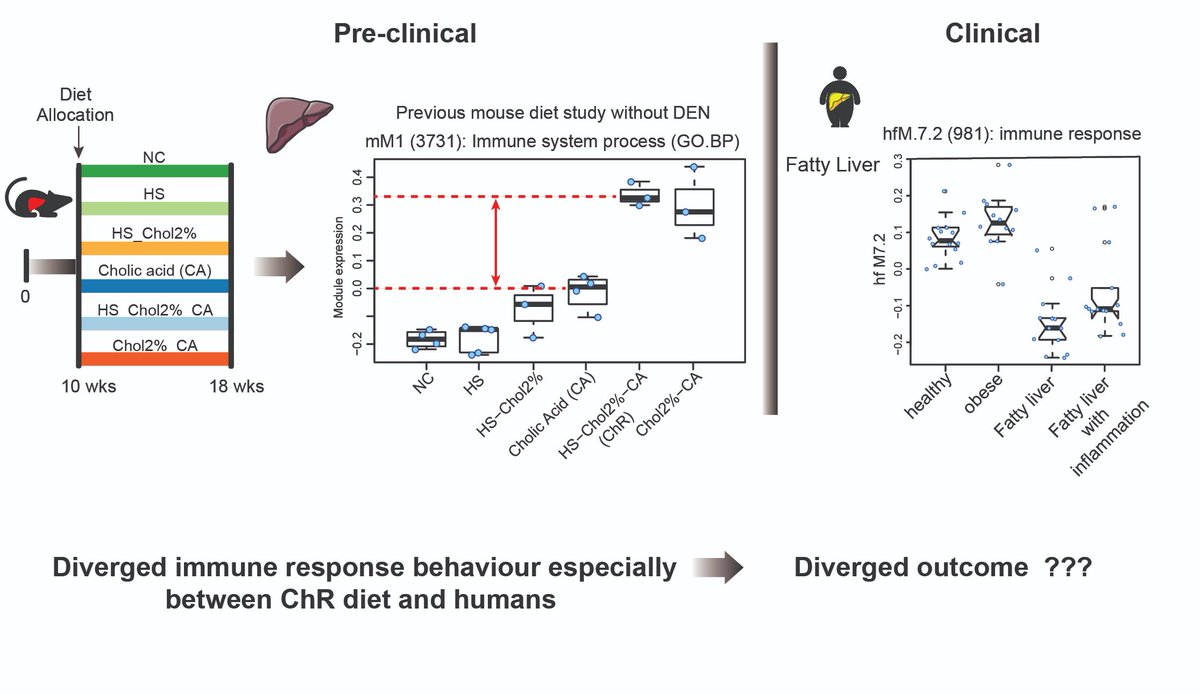
5. Then, we detected a divergence in behaviour of immune (& metabolic) modules between mice and humans. Human fatty liver increases the risk of liver cancer, then the directionally opposite behaviour of mice networks in Diet 5 (ChR) should delay tumour growth in this group. 

6. As expected, despite presence of inflammation, liver injury, and exposure to sugar, ChR diet delayed tumour growth. Thus, the diverged networks in mice can lead to a diverged outcome from humans. 

7. Then, working on pre-clinical models, we should consider the behaviour of their networks. A directionally different network behaviour makes it hard to directly transfer the gained knowledge from mice to humans. This can contribute to failures in clinical trials.
8. However, the preserved networks could have common regulatory mechanisms. It is important to find their regulators in pre-clinical models and to then study their presence and dynamics in humans.
9. Interestingly, immunometabolic modules showed temporal behaviours and a chronic exposure to ChR diet reduced the intensity of immune response. This indicates some liver intrinsic factors could have switched on to regulate the degree of response to this diet. 

10. Over-stimulation of a system can lead to modulation of its response over time. Probably, the initial high level immune response by ChR diet has delayed tumour development. Then understanding the temporal behaviour (not just final) is important.
11. Both liver intrinsic and extrinsic factors could affect the degree of immune response. Our focus was on extrinsic factors. But the temporal immune response in our model could be related to liver counter-inflammatory mechanisms👇
science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
12. We noted the liver immune module was enriched for genes related to haematopoietic differentiation. We asked whether there is a link between haematopoietic stem cells (HSPCs) and fatty liver. Flow cytometry showed that liver networks mirrored BM HSPCs response.
#livertwitter
#livertwitter

13. Despite liver immune response, HSPCs response didn't reduce by long exposure to diet. Hence, liver intrinsic factors could be in play here. Possibly if HSPCs fitness decline and fail to maintain immune response (longer exposure/ageing), the risk of tumour formation increases
14. High Sugar (HS) & Cholic Acid (CA) diet groups showed a mild increase in liver immune & BM HSPCs response, but had higher tumour burden. Probably immune response didn’t reach to a protective level within liver. This protective threshold is known as ‘cancer-immune set point’.
15. Conceptually, ChR diet induced and maintained an above cancer-immune set point level initially, and hence delayed tumour development.
More on cancer-immune set point here:
nature.com/articles/natur…
More on cancer-immune set point here:
nature.com/articles/natur…
16a) Now, how we can translate these findings to human fatty liver?
We discovered a link between BM HSPCs and fatty liver in pre-clinical models. We believe such a cross-talk exists in human fatty liver, with slightly different dynamics.
We discovered a link between BM HSPCs and fatty liver in pre-clinical models. We believe such a cross-talk exists in human fatty liver, with slightly different dynamics.
16b) The state of BM HSPCs fitness should be important in fatty liver disease progression and response to therapies, including #immunotherapy (IO).
16c. A strategy to induce an above cancer-immune set point response in fatty liver with HCC:
Implementing combinatorial therapies to target liver intrinsic mechanisms (local effect) in coordination with therapies to induce a systemic (i.e., BM HSPCs) immune response.
Implementing combinatorial therapies to target liver intrinsic mechanisms (local effect) in coordination with therapies to induce a systemic (i.e., BM HSPCs) immune response.
17. Here you can read about the issues with immunotherapy (IO) in fatty liver disease with liver cancer (Hepatocellular carcinoma [HCC])
nature.com/articles/s4158…
nature.com/articles/s4158…
18. This would not be possible without the hard work of many at @Sydney_Uni, @WestmeadInst @sahmriAU @BioinfoCRO . A big thanks to everyone: Ghazal, Peter Langfelder, Daniel, @TGrantBelgard ... & funding bodies: 🙏Sydney Medical School Foundation, @SWTCRC @CCNewSouthWales @nhmrc
@d2unroll please unroll
Here is the link to our previous paper:
doi.org/10.1016/j.cels…
doi.org/10.1016/j.cels…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh



