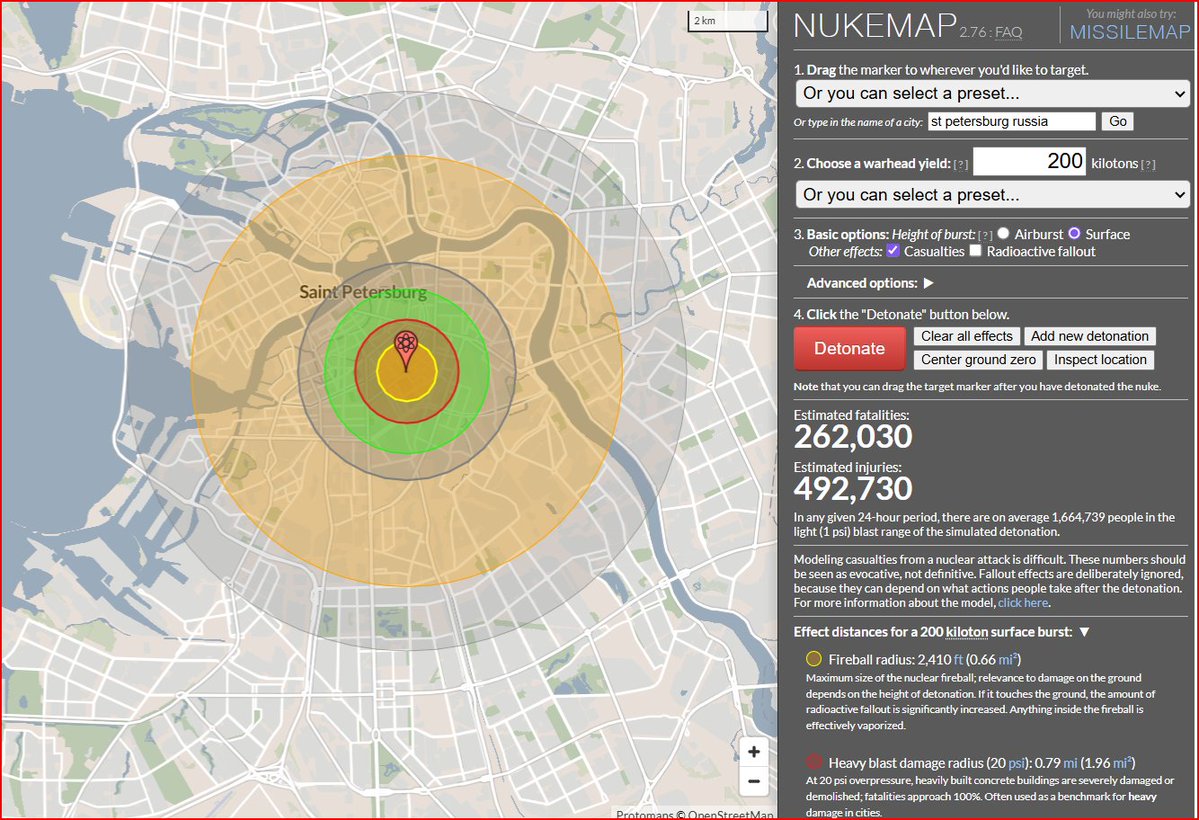
SMERCH MLRS system & some US vs Russian Army social history🧵
People have pointed to the cranes for reloading the BM-27 (220mm) & BM-30 (300mm) Smerch as evidence of mechanized logistics in the Russian Army.
It takes more than a crane to have a mechanized logistics system.
1/
People have pointed to the cranes for reloading the BM-27 (220mm) & BM-30 (300mm) Smerch as evidence of mechanized logistics in the Russian Army.
It takes more than a crane to have a mechanized logistics system.
1/
https://twitter.com/OSINT88/status/1517249371510910976
When you look at a US Army MLRS or HIMARS launcher.
You see containerized pod six-packs with cranes built into the launcher and in the trucks that pick up & deliver them.
You see a persistent use of capital to replace labor for increased productivity per unit time.
2/



You see containerized pod six-packs with cranes built into the launcher and in the trucks that pick up & deliver them.
You see a persistent use of capital to replace labor for increased productivity per unit time.
2/




And please carefully note, this emphasis in the US Army predates Frederick Taylor's four principles of Scientific Management.
The M1819 Hall rifle & carbines built with interchangeable, mass produced, parts vastly reduced the number of trained artisans needed to build &
3/


The M1819 Hall rifle & carbines built with interchangeable, mass produced, parts vastly reduced the number of trained artisans needed to build &
3/



...maintain its firearms.
The reason for the crane on the Uragan BM-27 & Smerch BM-30 reload trucks is their rockets were individually too darned big for a group of minimally trained & hungover conscripts move without damaging both the rocket & themselves.
4/



The reason for the crane on the Uragan BM-27 & Smerch BM-30 reload trucks is their rockets were individually too darned big for a group of minimally trained & hungover conscripts move without damaging both the rocket & themselves.
4/




An apples to apples comparison of the US MLRS or HIMARS to the Smerch shows advantages for the US launchers.
1. Less manpower per launcher w/o a specialized reload vehicle
2. Faster reload time per launcher
3. More rockets can be fired per US Army MLRS or HIMARS per day.
5/


1. Less manpower per launcher w/o a specialized reload vehicle
2. Faster reload time per launcher
3. More rockets can be fired per US Army MLRS or HIMARS per day.
5/



4. And all these labor saving devices built into MLRS & HIMARS launchers are easily trained at low risk.
The Twelve 300mm Smerch rockets need to be individually fused & armed. As does the 40 rockets of a 122mm rocket launcher.
6/
The Twelve 300mm Smerch rockets need to be individually fused & armed. As does the 40 rockets of a 122mm rocket launcher.
6/

The US MLRS/HIMARS pod is factory loaded & sealed with all the fusing & arming being automated & remotely set via cab fire control computer.
Any US Army truck with a crane can lay out the pods for launchers to reload. No special rocket reload trucks are required.
7/

Any US Army truck with a crane can lay out the pods for launchers to reload. No special rocket reload trucks are required.
7/


The US Army has always been short of people. The American Frontier & Congressional dislike of standing a standing army saw to that from the Revolution to WW2.
8/



8/




WW2 conscription wasn't the answer to US Army manpower dreams. The USAAF & US Navy grabbed many of the best men and the needs of world wide logistics meant the US Army hit the wall of expansion in late 1942.
Mechanized logistics was the only way to move the mountains of
9/


Mechanized logistics was the only way to move the mountains of
9/



supplies needed world wide.
And not just for itself, but for all the United Nations including Russia.
10/

And not just for itself, but for all the United Nations including Russia.
10/


In contrast, the Russian Army in all its incarnations until the late 1990's always acted as if "There's more conscripts where that came from, comrade."
While the nostalgia for the Red Army the Putin Regime had blinded it to the demographic realities
11/



While the nostalgia for the Red Army the Putin Regime had blinded it to the demographic realities
11/




...that the 21st Century Russian Army lacked the White Russian & Ukrainian manpower to replicate the Red Army.
The mechanized logistics pioneered in the West was simply applied to logistical issues beyond the capabilities of a mass of ill-trained conscripts.
12/

The mechanized logistics pioneered in the West was simply applied to logistical issues beyond the capabilities of a mass of ill-trained conscripts.
12/


The fact that it took the Ukraine War for this gap in Russian logistical capability to be really NOTICED, let alone analyzed.
There has never been a real attempt at a comparative social history between the Russian and other Armies logistics.
13/
There has never been a real attempt at a comparative social history between the Russian and other Armies logistics.
https://twitter.com/Osinttechnical/status/1508973215321841664
13/
If "Armatures Study Tactics & Professionals Study Logistics," where does that leave Western professional military education?
14/
14/
https://twitter.com/UkrWarReport/status/1513121638841208835
I mean, Ralph Peters noticed all the non-mechanized manual labor in the Red Army going back for centuries & wrote it in his book Red Army in 1989.
Yet, in 2022 senior DoD intelligence models projected Russia could overrun Ukraine in 96 hours?
15/End
Yet, in 2022 senior DoD intelligence models projected Russia could overrun Ukraine in 96 hours?
15/End
https://twitter.com/Harlentropolis/status/1513193984230842374
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh