In 2013, Dell Inc was a struggling PC and hardware firm. CEO Michael Dell took it private in a $25B buyout and turned it into an IT infrastructure + cloud giant (re-listing as Dell Technologies in 2018)
The $4B that Dell put up in the deal is now worth $40B.
Here's the story🧵
The $4B that Dell put up in the deal is now worth $40B.
Here's the story🧵

We start in 1984, when @MichaelDell was a freshman pre-med student at University of Texas.
He was not a typical student: The 19yo launched a company called PC's Limited with $1k, selling computers (assembled from stock parts) from his dorm room. It was soon making $80k a month.
He was not a typical student: The 19yo launched a company called PC's Limited with $1k, selling computers (assembled from stock parts) from his dorm room. It was soon making $80k a month.

Apple's Macintosh was released in 1984. While Steve Jobs offered a pricy integrated PC, Dell provided a lower-priced options by:
◻️Going direct-to-consumer (order over phone)
◻️Offering made-to-order options which kept inventories low
Dell would drop out of school after 1 year.
◻️Going direct-to-consumer (order over phone)
◻️Offering made-to-order options which kept inventories low
Dell would drop out of school after 1 year.

In 1988, the company re-branded as Dell Computers and IPO'd at a market cap of $85m (for reference, Microsoft went public in 1986 @ $780m).
Dell was 23.
Dell Computers joined the Fortune 500 in 1992 and Dell -- at age 26 -- was the youngest CEO on the list (net worth = $300m+).
Dell was 23.
Dell Computers joined the Fortune 500 in 1992 and Dell -- at age 26 -- was the youngest CEO on the list (net worth = $300m+).

Boosted by online sales (which began in 1996), Dell Computers overtook Compaq to become the world's top PC seller in 2001.
Dell retired in 2004 but returned in 2007. In the following years, a host of devices (smartphone, laptops, Chromebook, tablets) took share from PCs.
Dell retired in 2004 but returned in 2007. In the following years, a host of devices (smartphone, laptops, Chromebook, tablets) took share from PCs.

From 2007 to 2012, Dell Inc. spent $14B on acquisitions to jumpstart its business amidst a saturated PC market (PC sales peaked in 2011).
Nothing worked: Dell Inc. stock lagged the NASDAQ for years.
Change was needed. And a plan came out of Michael Dell's family office (MSD).
Nothing worked: Dell Inc. stock lagged the NASDAQ for years.
Change was needed. And a plan came out of Michael Dell's family office (MSD).

MSD Capital takes its name from Dell's initials. The family office was formed in 1998 and managed his multi-billion dollar fortune including investments with PE firm Silver Lake.
In 2012, Silver Lake's Egon Durban pitched the idea of taking Dell private (to pivot the business).
In 2012, Silver Lake's Egon Durban pitched the idea of taking Dell private (to pivot the business).
In February 2013, Dell tried taking the company private at $24.4B (a 40% premium).
Investor Carl Icahn felt the offer was too low (pre-offer, Dell shares were trading 1/3rd of 5-yr highs) and fought the deal.
Dell finally won out in October 2013 w/ a $25B deal (he put up $4B):
Investor Carl Icahn felt the offer was too low (pre-offer, Dell shares were trading 1/3rd of 5-yr highs) and fought the deal.
Dell finally won out in October 2013 w/ a $25B deal (he put up $4B):

Dell and Durban weren't done.
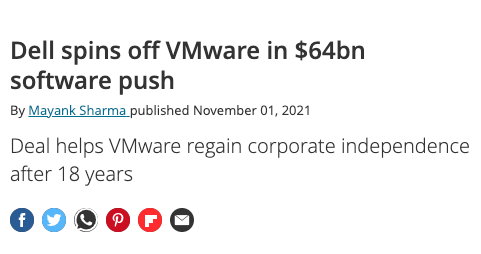
For years, Dell tried to acquire EMC, a giant data storage firm that owned an 81% stake in VMWare (a leader in cloud-computing and virtualization).
EMC was "in-play" for offers after Hewlett-Packard tried to acquire it. It was pricey, though: $65B.
For years, Dell tried to acquire EMC, a giant data storage firm that owned an 81% stake in VMWare (a leader in cloud-computing and virtualization).
EMC was "in-play" for offers after Hewlett-Packard tried to acquire it. It was pricey, though: $65B.
Already coming off a huge leveraged-buyout, Dell had to find a way to finance the acquisition.
The solution: a tracking stock, which is a type of equity that "tracks" a division of a larger company.
To close the deal for EMC, Dell issued a tracking stock worth 53% of VMWare.
The solution: a tracking stock, which is a type of equity that "tracks" a division of a larger company.
To close the deal for EMC, Dell issued a tracking stock worth 53% of VMWare.
In a complicated transaction, Dell bought EMC (and its juicy VMWare stake) for $67B, the largest tech acquisition ever at the time.
The VMWare tracking stock saved Dell a $12B cash outlay. And Dell raised $50B in debt w/ VMWare as collateral. The deal closed in September 2016.
The VMWare tracking stock saved Dell a $12B cash outlay. And Dell raised $50B in debt w/ VMWare as collateral. The deal closed in September 2016.

VMWare is a cash-printing machine. And after the deal, this was its ownership structure:
◻️53% in tracking stock (incl. Carl Icahn)
◻️28% for Dell/Silver Lake
◻️19% (stake not owned by EMC that was listed on NYSE)
In 2018, Dell made a move to buy out the VMWare tracking stock.
◻️53% in tracking stock (incl. Carl Icahn)
◻️28% for Dell/Silver Lake
◻️19% (stake not owned by EMC that was listed on NYSE)
In 2018, Dell made a move to buy out the VMWare tracking stock.
At first, Dell offered $9B from VMWare's balance sheet to buyout shareholders of the tracking stock at $0.60 on the dollar.
Icahn (again) fought back and the offer moved to $14B. To close the deal, Dell decided to bring the company public as Dell Technologies in December 2018.
Icahn (again) fought back and the offer moved to $14B. To close the deal, Dell decided to bring the company public as Dell Technologies in December 2018.
At first, the re-listed Dell sold off. With a $50B+ debt pile, the market valued Dell <$0 based on its VMWare stake.
Dell said it would spin off the entire 81% VMWare stake and the market cheered it on. The deal closed last Fall.
The private turnaround has made Dell a fortune.
Dell said it would spin off the entire 81% VMWare stake and the market cheered it on. The deal closed last Fall.
The private turnaround has made Dell a fortune.
Before going private in 2013, Dell owned 16% of a PC maker. Now he owns:
◻️52% of Dell Technologies (a $100B revenue IT infrastructure business); stake = $19B
◻️43% of VMWare (a $12B revenue cloud business); stake = $21B
In 9yrs, Dell's investment has grown from $4B to $40B.
◻️52% of Dell Technologies (a $100B revenue IT infrastructure business); stake = $19B
◻️43% of VMWare (a $12B revenue cloud business); stake = $21B
In 9yrs, Dell's investment has grown from $4B to $40B.
A key difference w/ Dell buying Dell Inc and Elon buying Twitter is debt: Dell Inc had the cash flow to support more of it.
Michael Dell personally put up 16% ($4B) of the $25B Dell deal. Elon may put up as much as 64% ($33.5B) of the $46.5B Twitter deal (huge skin in the game).
Michael Dell personally put up 16% ($4B) of the $25B Dell deal. Elon may put up as much as 64% ($33.5B) of the $46.5B Twitter deal (huge skin in the game).

If you enjoyed that, I write business threads 1-2x a week.
Def follow @TrungTPhan to catch them in your feed.
Here's one you might like:
Def follow @TrungTPhan to catch them in your feed.
Here's one you might like:
https://twitter.com/TrungTPhan/status/1450855104685375493
PS. Check out my Saturday newsletter too: trungtphan.com/subscribe/
(And here's a glorious Dell meme)
(And here's a glorious Dell meme)

Sources
Seeking Alpha: seekingalpha.com/article/396234…
CNBC:
FT: ft.com/content/73ab20…
Forbes: forbes.com/sites/antoineg…
Seeking Alpha: seekingalpha.com/article/396234…
CNBC:
FT: ft.com/content/73ab20…
Forbes: forbes.com/sites/antoineg…
Had to write this thread after Michael tweeted this lol
https://twitter.com/MichaelDell/status/1519743807566147585
Broadcom eyeing a $50B acquisition of VMWare, of which Michael Dell owns >40% … deal of the century only gets better 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh