If there's one thing that's become a signature of the war in Ukraine, it's the flying tank turret - a problem for both sides, as their Soviet-era tanks have the same flawed designs. But has the wrong suspect been fingered as the murderer? A CSI: UA thread. / 1 

The physics of an exploding T-72 tank are straightforward. An impacting anti-tank missile such as a Javelin, NLAW or RPG-29 causes heat, blast and fragmentation inside the tank. This sets alight explosive material on board, as well as the tank's fuel. /2
The sudden massive increase in pressure causes the turret to blow off in a so-called "jack-in-the-box" effect, which can propel it tens of metres off its turret ring. Extreme explosions like the one at the top of this thread can demolish the entire tank. /3
Alternatively, if the hatches are open and only the propellant on board catches fire, a very rapid deflagration ("cooking off") can occur which leaves the tank mostly intact but completely burns it out. Neither event is usually survivable, obviously. /4
The T-72 has a design feature that has widely been blamed for this. Unlike Western tanks, Soviet-designed tanks carry ammunition in a carousel within the crew compartment. Western tanks carry it in a separate compartment designed to channel a blast away from the crew. /5 

As this picture of a dismantled T-72B carousel shows, the commander and gunner literally sit on seats on top of the ammunition carousel. It's extremely cramped when the hatches are closed - standing up is impossible. Having it explode under you is a Bad Thing. /6 

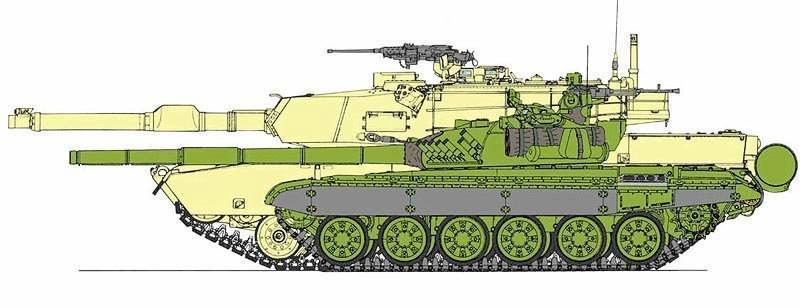
Designing the T-72 like this eliminated the need for a fourth crewman (the loader), enabled it to reload faster and made it smaller, lighter and cheaper than Western tanks, while still equipping it with a very powerful gun - as this T-72/M1A1 Abrams size comparison shows. /7 
The carousel has widely been blamed for the phenomenon of "turret tossing". But is the real culprit staring us - or rather Russian and Ukrainian tankers - in the face? /8
Let's first consider what a T-72 carries. This varies between models, as the T-72 has gone through many design changes over the years. The carousel holds 22 propellant charges in the top ring, 22 shells in the bottom ring. A standard load should weigh about 564 kg (see pic). /9 
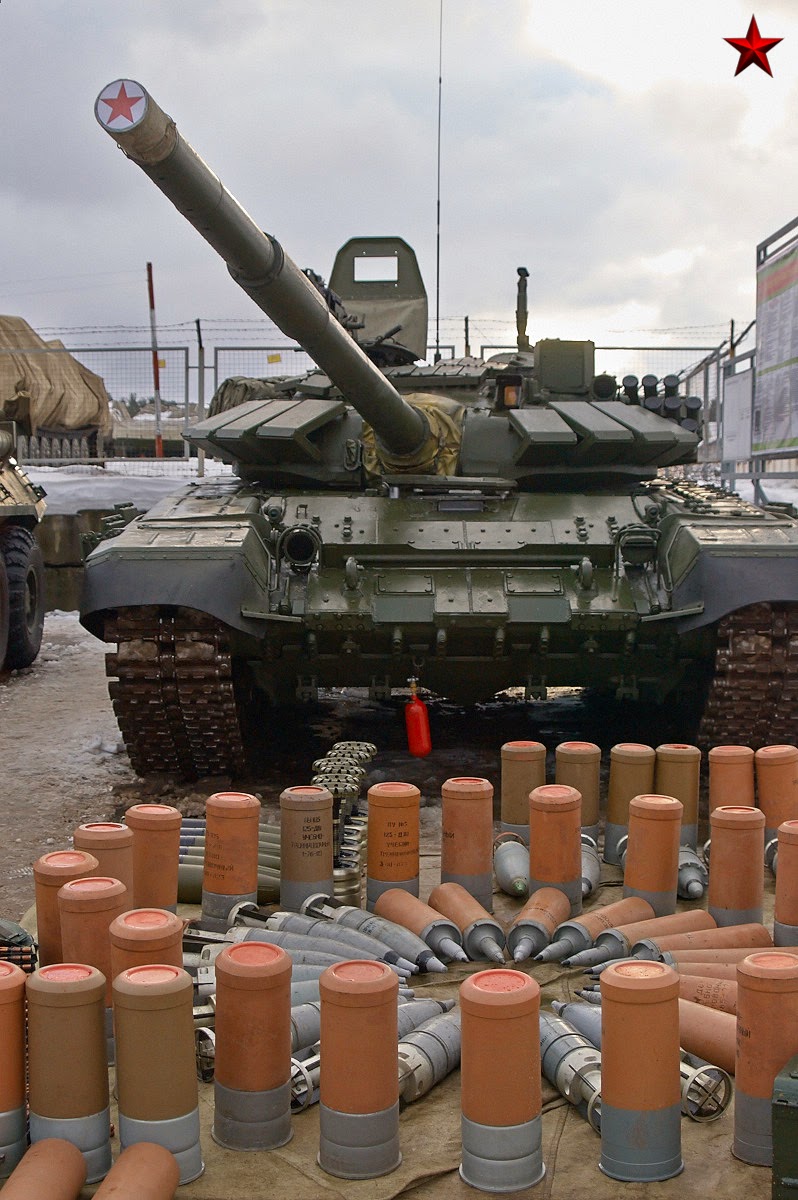

In addition, T-72s also carry ammunition and propellant stored outside the carousel. The amount varies between models; a T-72B can carry 45 rounds total, with the rounds not held in the carousel being stored in nooks and crannies around the tank's interior. /10 

Here's what it looks like inside - a view of the engine compartment bulkhead and the side hull wall of the T-72B, with the ammunition clipped to the exposed wall. Note that it's completely unprotected. Extra propellant is stored next to the fuel tanks. /11 

What kind of ammunition and propellant do Soviet-era tanks use? The Soviets standardised on 125 mm smoothbore guns, which can fire a variety of ammunition. They use four main kinds of anti-tank and high explosive ammunition. The exact loadout would depend on the mission. /12 

A 1979 T-72 operating manual advises that the carousel should be loaded with 11 rounds of HE-Frag ammunition (for infantry support) and 11 of APFSDS and HEAT ammunition (to use against armoured vehicles). Each HE-Frag and HEAT shell contains between 1.6-3kg of high explosive. /13
The propellant comprises 4Zh40 (Zh40) charges, each weighing 5.66 kg. It's effectively a modern equivalent of gunpowder - it deflagrates (burns rapidly) rather than exploding, generating hot gas that pushes the projectile out of the gun. /14 

The autoloader enables the gunner to select the ammunition and load it automatically, along with the propellant. An ingenious mechanical computer enables the autoloader to identify the ammunition types in the carousel and load the selected one. /15
So is the carousel the cause of those spectacular explosions? There's reason to think it might not be the direct culprit. /16
First, the carousel is actually quite well protected. It's recessed deep within the hull, as this image shows. When in use, its top is covered by a heavy steel plate, which should protect against fragments entering via the turret. /17 

It's also well protected within the body of the tank. As this image shows, to hit the carousel from the side, a projectile would have to penetrate the wheels *and* the side armour before it could reach the carousel. A hit on the turret wouldn't necessarily compromise it. /18 

A 1991 Soviet study of Iraqi tanks following the Gulf War showed that the vast majority of hits were on the turret, not the lower half of the hull where the carousel is located. /19 

The most likely conclusion from this is that the spectacular explosions we've seen are not initiated by the carousel, but by the ammunition and propellant stored in recesses in the turret and crew compartment. When they go up, they likely cause the carousel to explode too. /20
The Russians and Ukrainians could in theory mitigate this risk by removing the explosive material in the turret. However, they would likely be reluctant to do so, as it would remove a large portion of the tank's ammo and propellant charges, reducing its effectiveness. /21
So for the foreseeable future, expect to see many more turrets flying off tanks on the battlefields of Ukraine. /end 

(Many thanks to the excellent Tankograd blog for most of the images (link below) and Sgt Iryna Rybakova of the Ukrainian 93rd Mechanized Brigade for the final photo.) thesovietarmourblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/t-72-s…
@Nrg8000 @UAWeapons @RALee85 @Yarotrof @TrentTelenko @WarintheFuture @KofmanMichael @IAPonomarenko @JoshManning23 @McFaul @DomNicholls @michaeldweiss
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh