1/ Old rations, faulty vehicles, missing radios, under-strength units: corruption has been blamed for hollowing out Russia's military and undermining its war in Ukraine. It's worth examining this problem and seeing how it's affected the Russian armed forces. 1st 🧵 in a series. 

2/ Russia is one of the world's most corrupt countries - Transparency International (TI) rates it 136th of 180 countries. State corruption is endemic. TI found that between 2008 and 2020, current and former Russian officials owned 28,000 properties in 85 countries. 

3/ It's not just the top brass who cash in. Even if you're only a middle-ranking official in Russia, your life goals are likely to be to set up your family in comfort in western Europe and send your children to a posh British school. Corruption is how you'll achieve that. 

4/ Scams and cheating are ubiquitous. If you ever wondered why Russian dashcam videos are all over YouTube, it's because drivers use dashcams as protection against scams such as pedestrians throwing themselves onto cars to claim insurance payouts.
Corruption is the thread which holds Putin's regime together, and money (in dollars or Euros, naturally, not low-value rubles) is its lifeblood. And nobody has more of it than Putin himself - at least an estimated $200 billion, salted away in secret funds worldwide.
6/ Like every other state institution in Russia, the armed forces are riddled with corruption at every level. This is nothing new: in his 1854 Sevastopol Sketches, Tolstoy wrote of Russian officers: "While they are in the service their main aim is the acquisition of money." 

7/ In 1998, Russia's Prosecutor General called the Russian Armed Forces "the most corrupt government structure in Russia". If anything, it's got worse since then. How does corruption in the Russian military operate, from the bottom to the top?
8/ Corruption starts even before someone joins the military. As @kamilkazani has noted, only the poor or the stupid allow themselves to be conscripted. The rest get out of it by bribing a doctor or recruiting officer. The 'fee' was reportedly between $5,000-$10,000 in 2007. 

9/ Up to 70% of those summoned for conscription buy their way out of it, leaving the armed forces with the poorest and least healthy. This leaves the Russian military with chronic problems of fitness and efficiency.
10/ Col Gen Vladimir Mikhailov stated in 2007 that more than 30 percent of the 11,000 men conscripted annually into the Russian Air Force were "mentally unstable," 10 percent suffered from alcohol and drug abuse, and 15 percent were ill or malnourished. 

11/ If you get conscripted, you'll be treated as the lowest of the low and exploited ruthlessly by older soldiers, known as 'dyedi' ('uncles'). This could include being forced into prostitution, doing unpaid labour, or even selling your own blood to earn a few rubles.
12/ In 2007, conscripts in St Petersburg told Russian media how older soldiers forced them to perform sexual services for influential middle-aged clients or face torture. Young soldiers were reportedly forced to go with clients in their cars. The dyedi kept a list of 'providers'. 
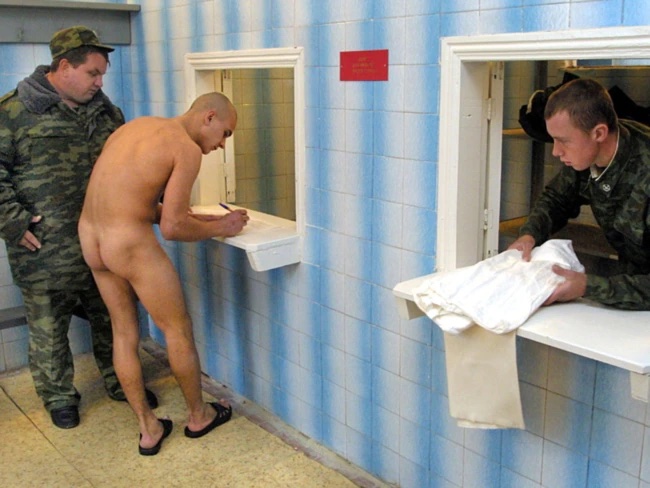

13/ Other soldiers spoke of being "sent out to the park to earn money". It was reportedly possible to pick up a soldier in the centre of Moscow or visit a nearby military base where clients could choose one for $100-500 - money that would go to the dyedi, not the conscript.
14/ If you're a contract soldier - a military professional - you're a step up but are still exploited. Salaries are low ($240 monthly before the Ukraine war). You may well need to buy your own uniforms, boots and fuel.
15/ Newer uniforms and boots of the right size are often unavailable because they've been stolen and sold off, so you'll need to purchase them online. Ironically, ex-NATO surplus boots are reportedly favourites for their comfort and durability. 

16/ You may also need to pay for your own accommodation. Although you will get a bed in a barracks for free, you may find that it's unheated because the money for electricity has been stolen or otherwise gone unpaid. Not much fun in Russia's cold climate. 

17/ There are, however, compensations to being a low-ranking soldier or junior officer - you may be posted to a military depot. These offer endless opportunities for theft. Avito, Russia's equivalent of eBay, is full of adverts for likely stolen items of military equipment. 


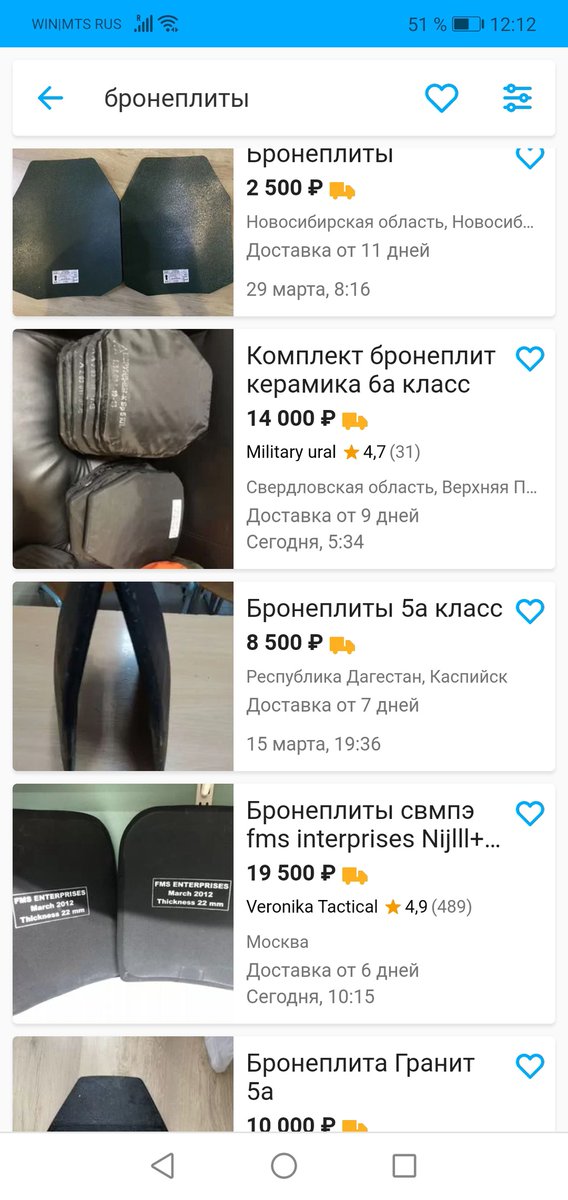
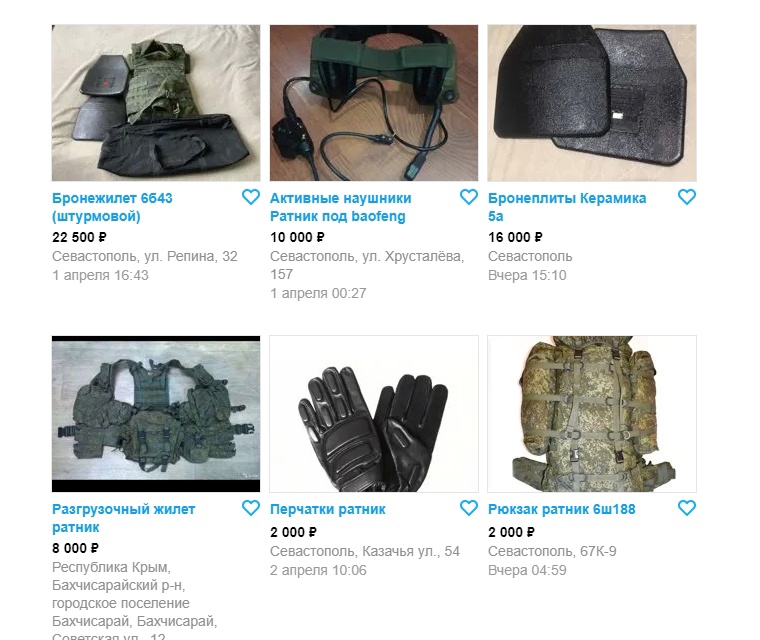
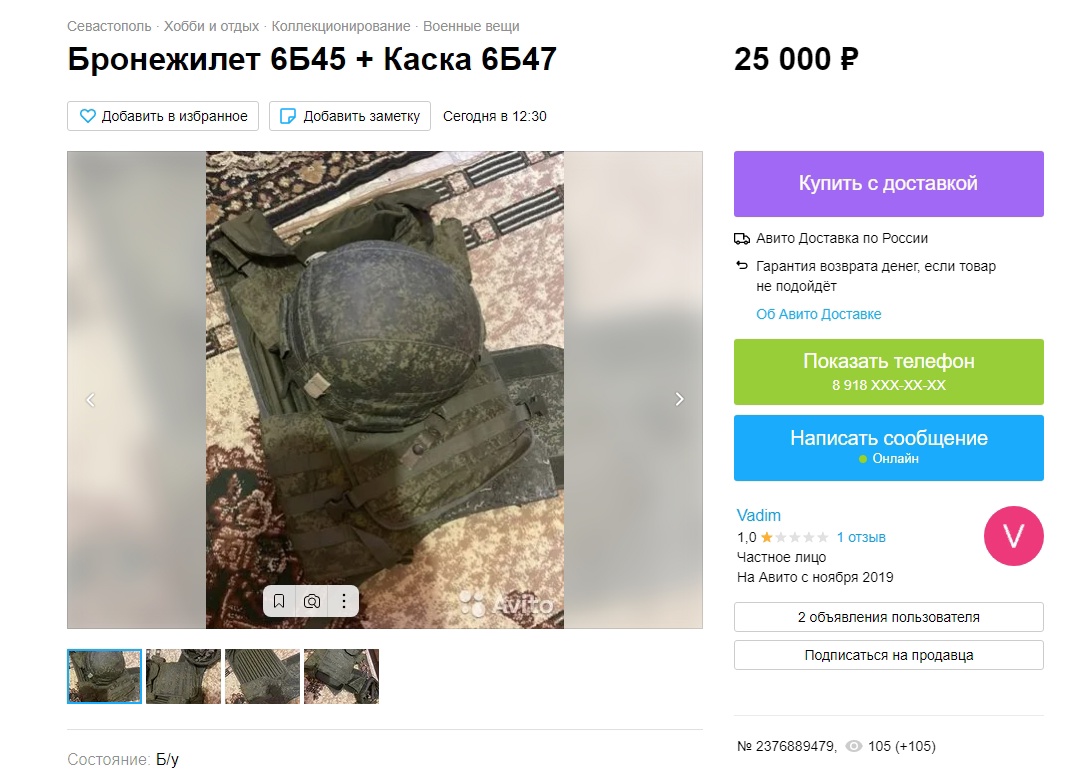
18/ Russian bloggers are currently crowdsourcing money to buy equipment for the frontline troops in Ukraine. Ironically, many of the items they're buying were likely stolen from Russian military depots in the first place. These are very good times for corrupt quartermasters.
19/ Even tanks aren't immune to the plague of looting. When reserve T-72s were shipped from storage depots to go to Ukraine in March 2022, they reportedly arrived without electronics, optics or even engines - all looted or stripped out. Only 1 in 10 was reportedly usable.
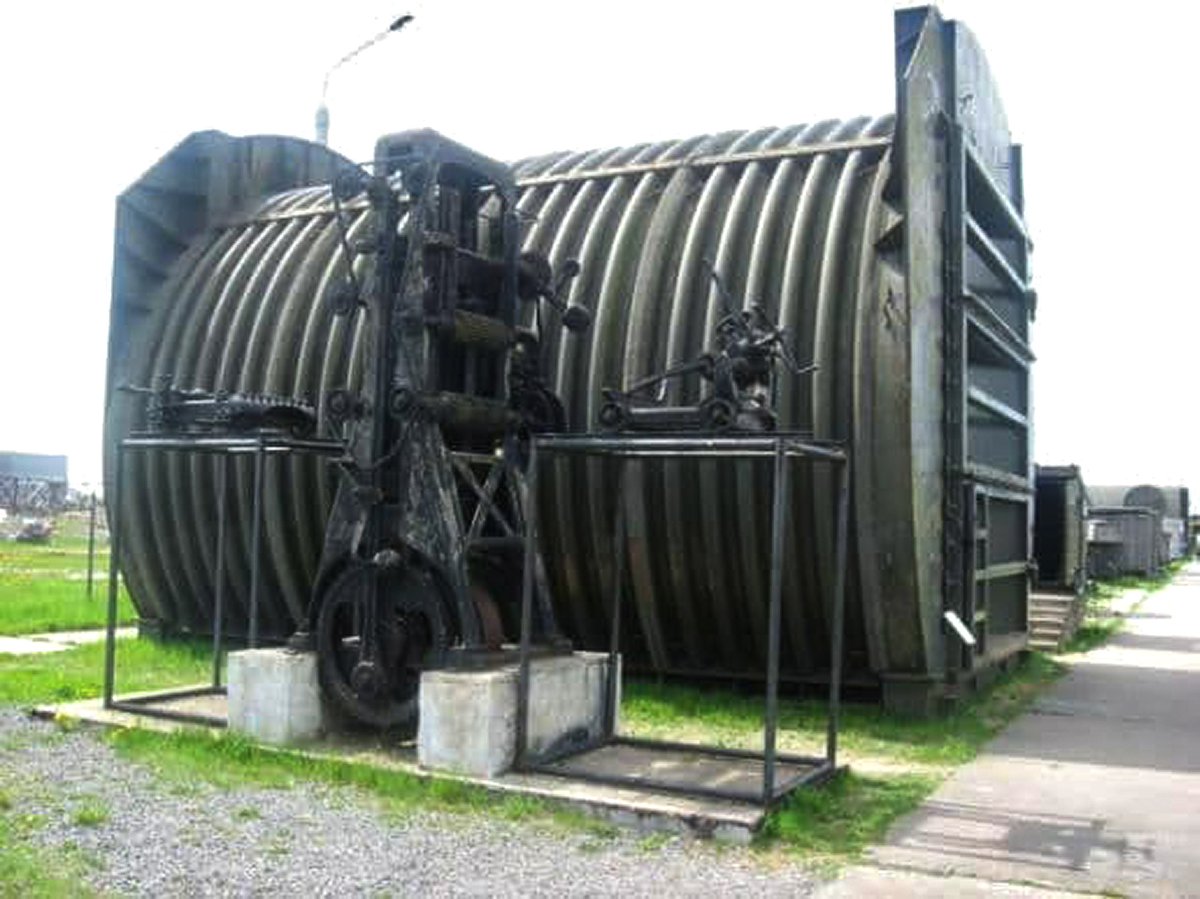
20/ In one remarkable instance, a 72-ton prefabricated Pantsir-2PU command bunker was stolen from a military base at Myaglovo, Leningrad Oblast in early 2020. Investigators were unable to discover what had happened to it, but it was most likely taken for the metal's scrap value. 

21/ In a similar incident, a submariner in the Northern Fleet stole parts of devices for controlling a nuclear submarine's reactor. He stole and sold rheostats made of a very expensive palladium-vanadium alloy, but disabled the reactor in the process. Not a good idea!
22/ Let's move up to the mid-ranking officers. Life is a lot cushier at this level as you can sign contracts, command troops and oversee bases. There are a lot more opportunities for corruption at ranks from major through colonel. 

23/ Your perks may include using conscripts to build your dacha, or hiring them out to others to work in building sites, fields or factories. Naturally, the conscripts get no compensation for this work. Even Russia's elite missile forces have not escaped this kind of abuse.
24/ You also have the possibility of stealing your men's wages, as they are paid in cash. Or manipulating budget allocations to claim money for non-existent extra personnel and pocket the difference. Non-existent troops are known as 'dead souls', after a classic Gogol poem. 

25/ 'Dead souls' are nothing new. In 1854, the Economist newspaper noted how much the Russian forces in the Crimean War were under strength. "The Russian armies are often armies on paper only. ... 
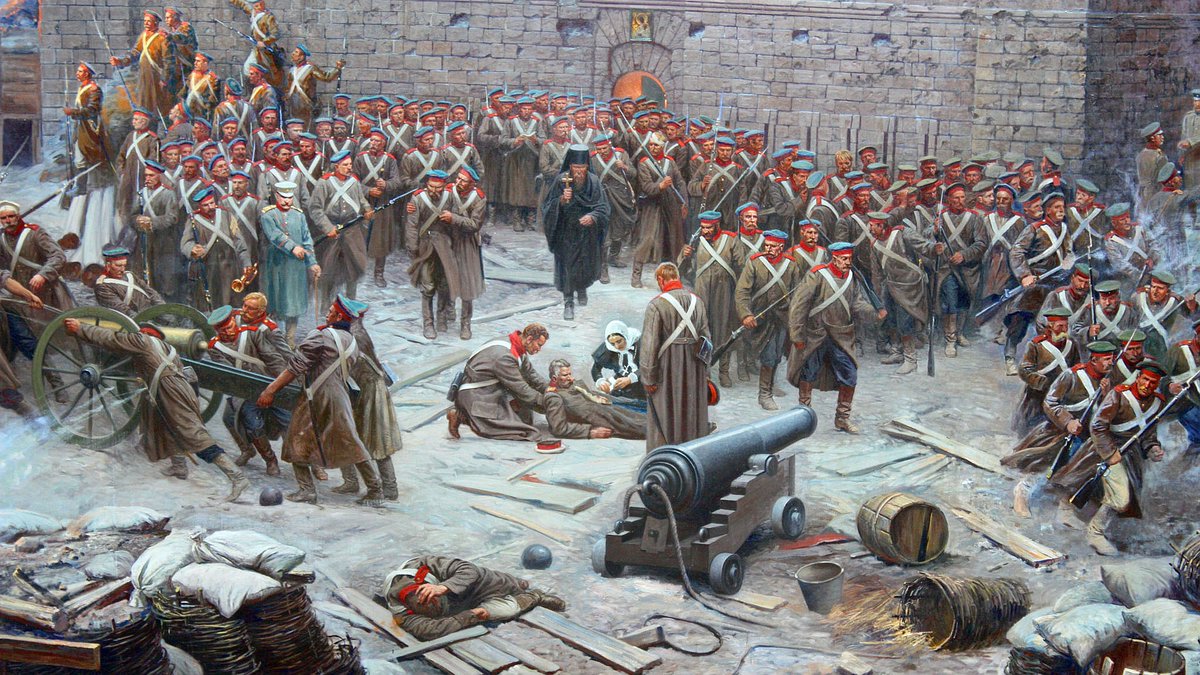

26/ "The colonels ... and officers ... have a direct interest in having as large a number on the books and as small a number on the field as possible - inasmuch as they pocket the pay and rations of the difference between these figures." Plus ça change.
27/ Remarkably, the Russian Army doesn't know how many soldiers it has. In 2001, Gen Nikolai Kormiltsev stated that the army had accounted for only 82% of its authorised personnel - something that was regarded as a major achievement. Things are unlikely to have improved since.
28/ Figures leaked to Novye Izvestia newspaper in 2003 indicated that there were at least 30,000 "dead souls" in the armed forces. The 2012 case of Col Sergey Ustinov and Maj Hovik Babayan, two Eastern Military District officers, illustrates how this scam works.
29/ Babayan was responsible for providing food services to troops under Ustinov's command. He forged documents, signed by Ustinov, showing 29,000 more soldiers were being fed than actually existed. The pair pocketed 6 million rubles for feeding the surplus 'dead souls'. 

30/ Researchers estimate that as many as one in ten Russian officers are corrupt. Military procurement is particularly rife with corruption. Let's first consider the case of Colonel Sergei Serkin, formerly the chief provisions officer for the North Caucasus Military District.
31/ In only two years in his position, Col Serkin acquired several apartments, a house and an Audi car with a total value of about $200,000. One of his schemes was accepting bribes to purchase 3,500 tons of low-quality codfish, normally used as cattle food, for army rations.
32/ Another officer, Col Evgeny Pustovoy, served as head of procurement for armoured vehicles. He was convicted in January 2022 for stealing more than $13 million by faking contracts for batteries between 2018 and 2020.
Storage bases are also ripe for corruption.
Storage bases are also ripe for corruption.
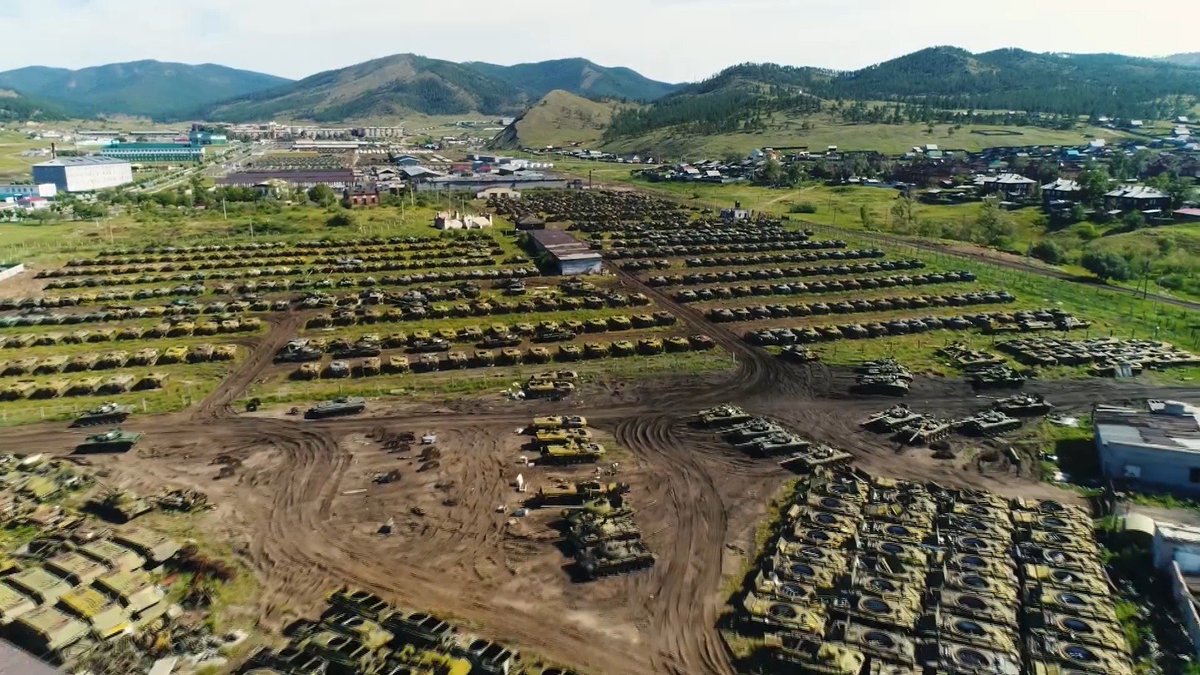

33/ Two Air Force officers, Lt Col Vladimir Storozhuk and Senior Warrant Officer Ivan Tolkachev, maintained a lucrative racket in Kubinka selling spare parts for planes and ammunition. They were caught after trying to sell top-secret Su-27 components for $250,000.
34/ A bigger 'officer gang' operated out of Malino military airfield about 88 km south-east of Moscow. They widely traded aircraft engines, equipment and air-to-air missiles, earning millions of dollars a year before being arrested.
35/ In the Far Eastern Military District, Col Alexander Berezhnoy served as the Russian Ministry of Defence's food department before being arrested on bribery charges in 2017. He earned 368 million rubles from awarding lucrative contracts to local entrepreneurs who'd bribed him.
36/ Another scam is the Orwellian "voluntary-compulsory requisition". Because of bureaucracy and corruption, requisitions for equipment and supplies are often slow to arrive. So to make up the difference, officers are compelled to pay for their own equipment and official travel.
37/ In one prosecuted instance, a commander and guard captain extorted over 137,000 rubles from their subordinates "for the needs of the division", threatening otherwise to "write a report on the improper performance of their official duties." They likely pocketed the money.
38/ It should be noted that the cases above, which were reported in Russia's heavily censored media, are just the tip of the iceberg. Many more cases are never detected, or if detected, never prosecuted, or simply covered up.
39/ In the next part of this thread (coming soon!) I'll tackle high-level military corruption. If you like really big corruption scandals, Russia's generals and admirals have just the thing for you. /end 

@OSINTEng @Militarylandnet @RALee85 @War_Mapper @Blue_Sauron @Osinttechnical @oryxspioenkop @TrentTelenko @MarkHertling @DomNicholls @Nrg8000 @UAWeapons @TrueFactsStated @WarintheFuture @KofmanMichael @michaeldweiss @aravosis @JoshManning23 @general_ben @tomiahonen
Part 2 here:
https://twitter.com/ChrisO_wiki/status/1536422857777025024?t=iLVptVIfVrOrL1Mn4mD0ag&s=19
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh










