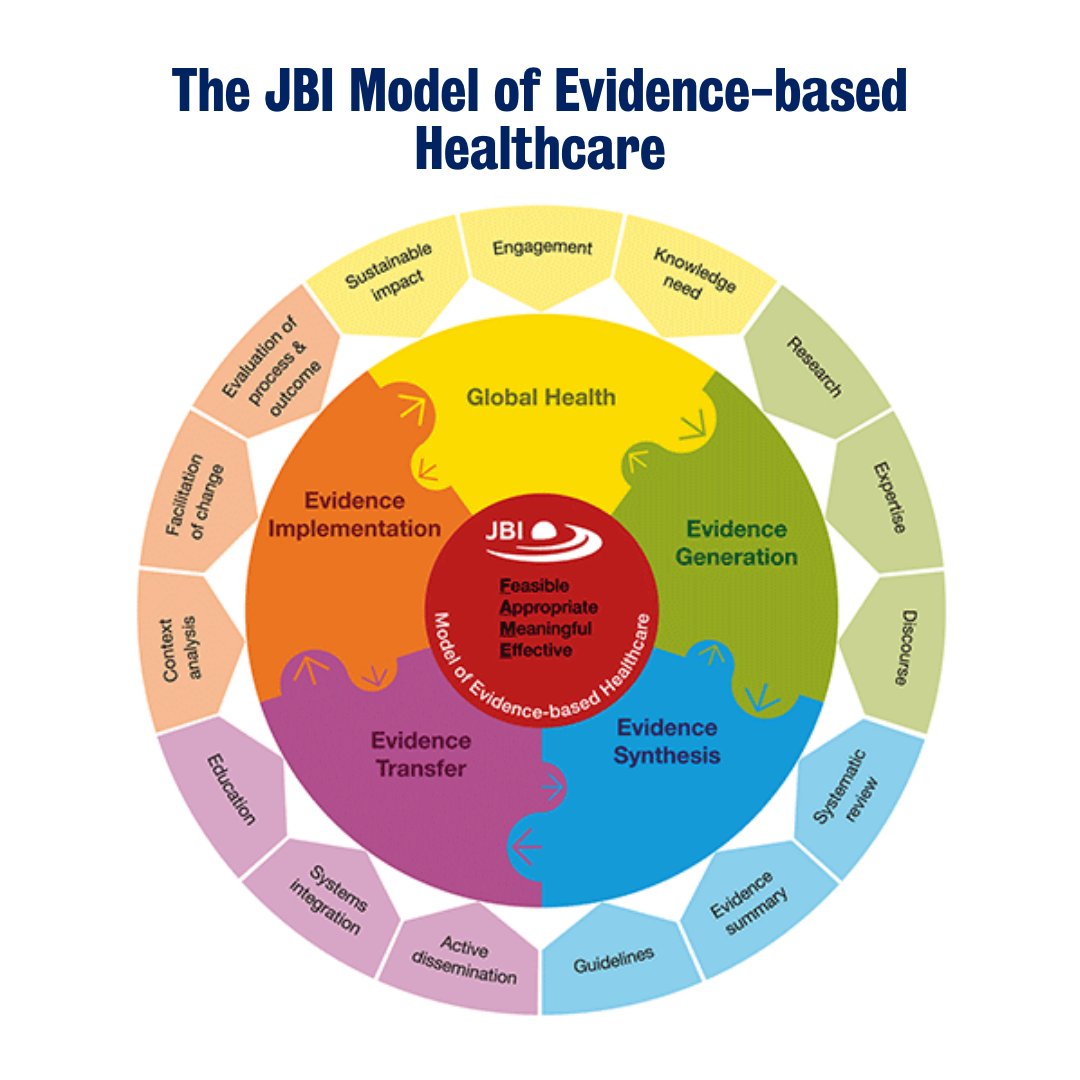
JBI’s approach to evidence-based healthcare is unique. JBI considers #EBHC as decision-making that considers the feasibility, appropriateness, meaningfulness and effectiveness (FAME) of healthcare practices. Read below to learn more about the JBI Model of EBHC. 

The inner circle represents the pebble of knowledge while the inner wedges provide JBI’s conceptualization of the steps involved in the process of achieving an evidence-based approach to clinical decision making. 

The outer wedges operationalize the component parts of the Model and articulate how they might be actioned in a pragmatic way. The arrows indicate that the flow can be bi-directional. 
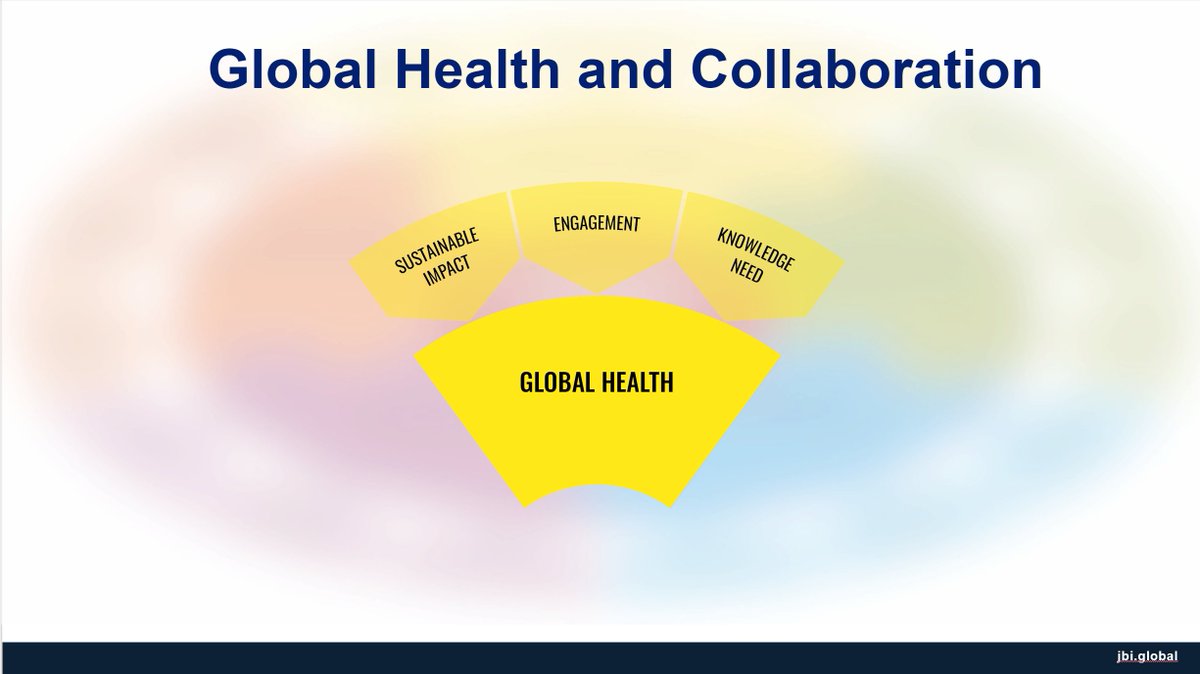
JBI believes that evidence-based healthcare should be driven by the needs of global health. The achievement of improved global health is seen as both the goal (or endpoint) & the ‘driving force’ of evidence-based healthcare. 
The evidence generation wedge of the Model identifies discourse (or narrative), experience and research as legitimate means of knowledge generation. 

Evidence synthesis is the evaluation or analysis and collation of research evidence and opinion on a specific topic to aid in decision making in healthcare. The three main components of this wedge are systematic reviews, evidence summaries and guidelines. 

Fundamental to the process of evidence-based decision making is the ability of those at the point of care to access synthesized research evidence. Evidence transfer is the coactive, participatory process to advance access to and uptake of evidence in local contexts. 

Evidence implementation is a purposeful and enabling set of activities designed to engage key stakeholders with research evidence to inform decision making and generate sustained improvement in the quality of healthcare delivery. 

To learn more about JBI’s FAME approach to #EBHC, go to jbi.global/jbi-model-of-E… #ThinkFAME #JBIEBHC
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh