Throughout history, the magnificent elephant is much loved & an integral part of cultures around the world.
To mark #WorldElephantDay here are wonderful depictions of elephants in Islamic art & culture, starting with Al-Jazari's ingenious elephant clock invention
A thread...
To mark #WorldElephantDay here are wonderful depictions of elephants in Islamic art & culture, starting with Al-Jazari's ingenious elephant clock invention
A thread...

1/ Twelfth century engineer Al-Jazari was fascinated by every kind of mechanism & designed machines of all kinds, shapes & sizes.
His Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices (1206 AD) described 50 mechanical devices, including water clocks #WorldElephantDay
His Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices (1206 AD) described 50 mechanical devices, including water clocks #WorldElephantDay

2/ One of the engineering marvels of the medieval Islamic world is AI-Jazari's 800 year old automatic Elephant clock
A reproduction in Kasımiye Medrese , Mardin, Turkey
#WorldElephantDay
A reproduction in Kasımiye Medrese , Mardin, Turkey
#WorldElephantDay
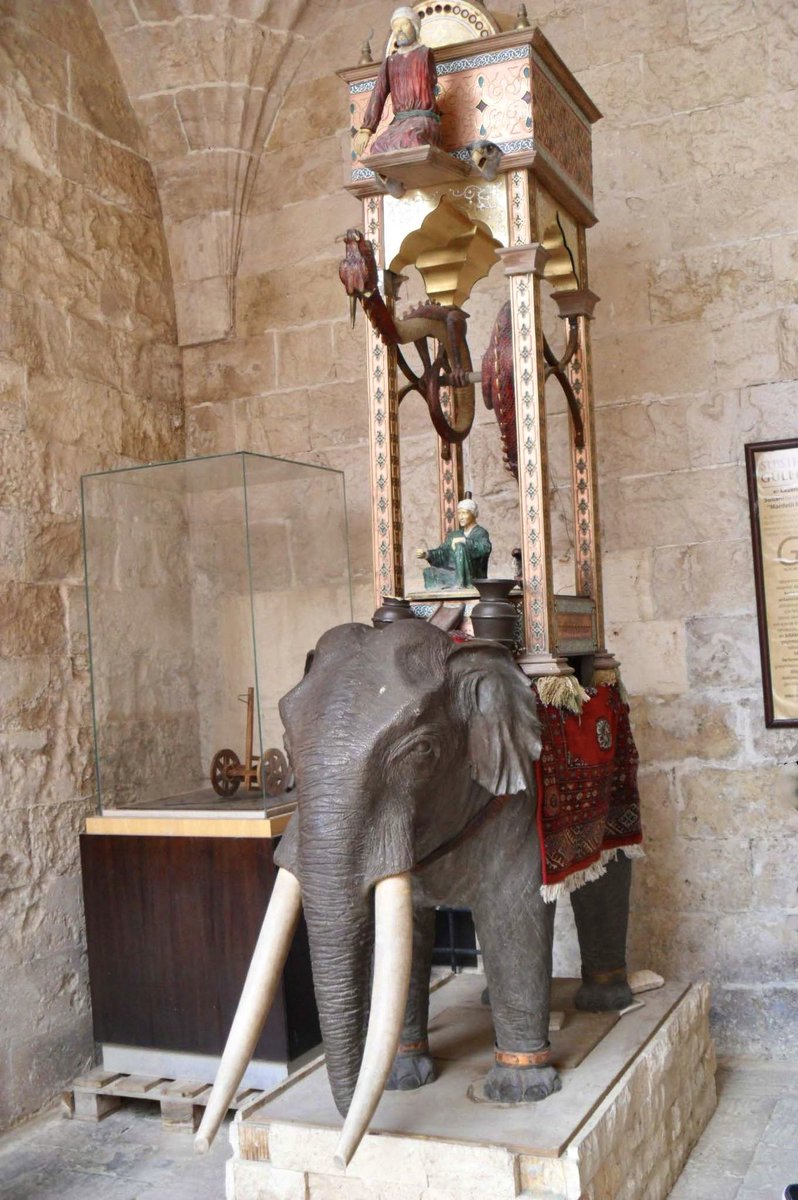

3/ Its moving parts were automated using a water-powered timer inspired by an Indian mechanism known as ghatika – the clock’s timer was a bowl that would slowly sink into a hidden water tank #WorldElephantDay
Find out how the mechanism worked here:
Find out how the mechanism worked here:
4/ Al-Jazari wrote: "The elephant represents the Indian & African cultures, the 2 dragons represent Chinese culture, the phoenix represents Persian culture, the water work represents Greek culture & the turban represents Islamic culture.’ #WorldElephantDay 

5/ The elephant clock gives physical form to the concept of multiculturalism, reflecting influences from across Muslim civilisation, including Indian, Egyptian, Greek, Chinese & Arab #WorldElephantDay
Ben Kingsley describes the Al-Jazari's Elephant Clock
Ben Kingsley describes the Al-Jazari's Elephant Clock
6/ The clock incorporated a figure of a scribe and his pen that move to indicate the number of minutes past the hour.
As well as telling the time, this grand beautiful water-powered Elephant clock was a symbol of status, grandeur, and wealth #WorldElephantDay
As well as telling the time, this grand beautiful water-powered Elephant clock was a symbol of status, grandeur, and wealth #WorldElephantDay

7/ Al-Jazari's elephant clock continues to delight today. Reproductions can be found across the world including in the Ibn Battuta Mall in Dubai, the Musée d'Horlogerie du Locle in Switzerland, & the Museum of Science & Technology in Islam in Saudi Arabia #WorldElephantDay 

8/ Elephants are featured widely in Islamic art. There are many depictions of elephants in Islamic manuscripts and miniature paintings from across South Asia & Central Asia
Portrait of the Elephant 'Alam Guman
ca. 1640, Mughal India
@metmuseum #WorldElephantDay
Portrait of the Elephant 'Alam Guman
ca. 1640, Mughal India
@metmuseum #WorldElephantDay

9/ This Mughal drawing of an elephant from 1630 is identified by a Persian inscription written by emperor Shah Jahan. It records that the animal's name is Mahabir Deb, it had been presented to the emperor by 'Adil Khan, & was worth 300,000 rupees
@V_and_A #WorldElephantDay
@V_and_A #WorldElephantDay

10/ The 2 affectionate elephants shown here are an illustration in the manuscript Manāfi˓-i ḥayavān (The Benefits of Animals). They are royal elephants, as seen from their caps and the bells on their feet
Persia, Maragha
Between 1297 & 1300
@MorganLibrary #WorldElephantDay
Persia, Maragha
Between 1297 & 1300
@MorganLibrary #WorldElephantDay

11/ One of the outstanding paintings of Muhammad Adil Shah’s reign. Wearing a gold robe, the Sultan directs the elephant while his African minister Ikhlas Khan rides behind waving a cloth.
1645, Mughal, India
@AshmoleanMuseum #WorldElephantDay
1645, Mughal, India
@AshmoleanMuseum #WorldElephantDay

12/ Nawab of Bahawalpur, Sadiq Muhammad Khan IV riding a Calligraphic Elephant
Persian inscription on top mentions all the titles of the Nawab
He was the 10th Nawab of Bahawalpur who ruled the State from 1879 to 1899
India Late 19th century, Salar jung Museum #WorldElephantDay
Persian inscription on top mentions all the titles of the Nawab
He was the 10th Nawab of Bahawalpur who ruled the State from 1879 to 1899
India Late 19th century, Salar jung Museum #WorldElephantDay

13/ A detailed colourful Mughal miniature painting of Prince Aurangzeb, son of Shah Jahan, on the elephant Sardar Gaj #WorldElephantDay 

14/ The royal elephant Madhukar, by Hashim, Mughal, Agra, c 1630- 40
The 17th c. saw Mughal art & culture spread across the world. So impressive was the dynasty for Europeans, that John Milton refers to its wonders in Paradise Lost
@FitzMuseum_UK #WorldElephantDay
The 17th c. saw Mughal art & culture spread across the world. So impressive was the dynasty for Europeans, that John Milton refers to its wonders in Paradise Lost
@FitzMuseum_UK #WorldElephantDay

15/ Here are some magnificent Mughal elephants at the wedding of Prince Dara-Shukoh, son of the Mughal Emperor Shah-Jahan. They are illustrated in the Padshahnamah, a history of Shah-Jahan's reign made in 1640-50
@RCT #WorldElephantDay
@RCT #WorldElephantDay

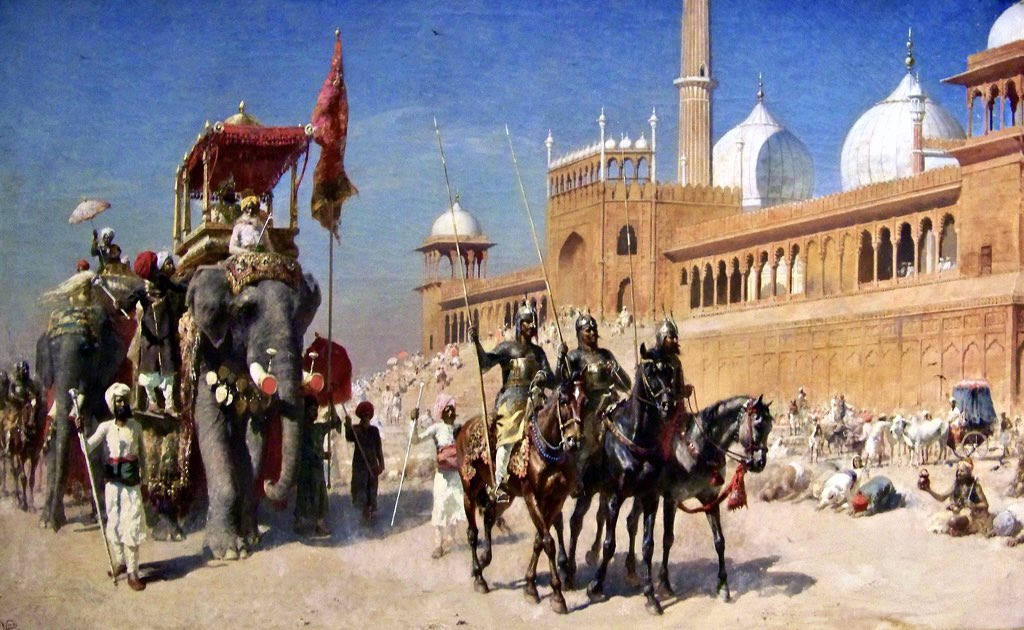
16/ Great Mogul And His Court Returning From The Great Mosque At Delhi India - Oil Painting by American Artist Edwin Lord Weeks Portland Museum of Art, Maine, 1918.1.
#WorldElephantDay
#WorldElephantDay

17/ This majestic elephant is made of moulded stonepaste, covered with a slightly opacified white glaze, with turquoise and cobalt-blue in-glaze staining (laqabi ware)
Syria, 12th or early 13th century AD
@KhaliliOnline #WorldElephantDay
Syria, 12th or early 13th century AD
@KhaliliOnline #WorldElephantDay

18/ Throughout history, the magnificent elephant is much loved and an integral part of cultures around the world.
Let's conserve and protect elephants from the numerous threats they face.
#WorldElephantDay2022
Let's conserve and protect elephants from the numerous threats they face.
#WorldElephantDay2022

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh