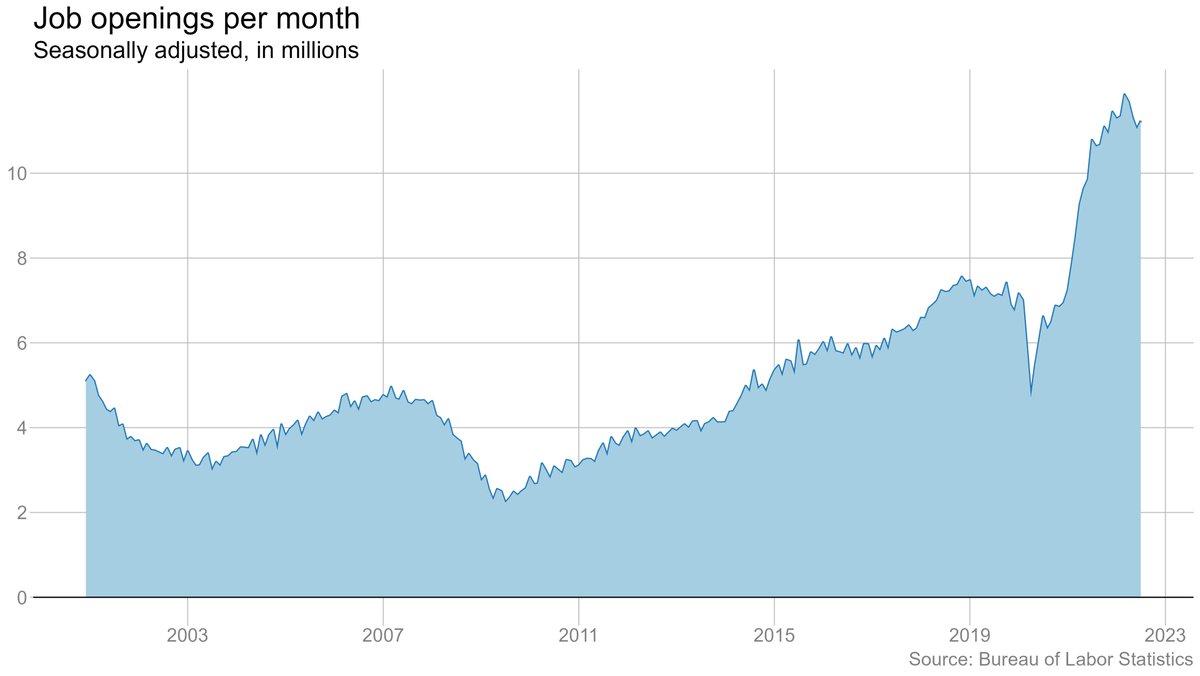
There were 11.2 million job openings at the end of July, UP slightly from June (though down from the spring). Quits down a hair. Layoffs basically flat (at a very low level).
#JOLTS
bls.gov/news.release/j…
#JOLTS
bls.gov/news.release/j…
Job openings are down from their peak, but they are still extraordinarily high by historical standards. The Fed is hoping it can cool the job market by bringing down openings without leading to more layoffs. Not a lot of evidence of that happening so far. 
There were a hair under two job openings for every unemployed worker in July. That ratio had dipped ever so slightly in May and June, but it's back to close to a record high. (Granted, records only go back 20 years or so.) 

The "Great Resignation" may not be over, but it is ebbing. 4.2 million people voluntarily quit their jobs in July, down from a peak of 4.5m+ last year.
Reminder that most of these people are leaving for *other jobs,* not stopping work entirely.
Reminder that most of these people are leaving for *other jobs,* not stopping work entirely.

Openings rates are still elevated across the board relative to before the pandemic. But they've come down significantly over the past year in some key industries, notably leisure and hospitality. 

I've talked to a lot of businesses lately that say it's become a bit easier to hire in recent months. Not a lot of evidence of that in the data yet, though. The number of hires for every posted job opening has stopped falling, but it hasn't really risen either. 

Most industries are generating fewer hires per posted opening than they were a year ago -- let alone than they were before the pandemic. 

Note: Many people have raised questions about whether a "job opening" means something different today than it used to. Maybe companies are posting jobs but not trying hard to fill them, or leaving openings up in the hope that the perfect person will come along, etc.
These are good questions! I don't have great answers. It seems plausible that the job openings figures overstate the amount of active recruitment going on, and perhaps by more than in the past. But it's also very clear that there are lots of openings right now.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh










