1/ The palatial period of Minoan Crete is intertwined with the appearance and consolidation of Linear A', which during the Neopalatial Period was the main writing system. With the appearance of the first palaces, the Linear A must have already been in use. 

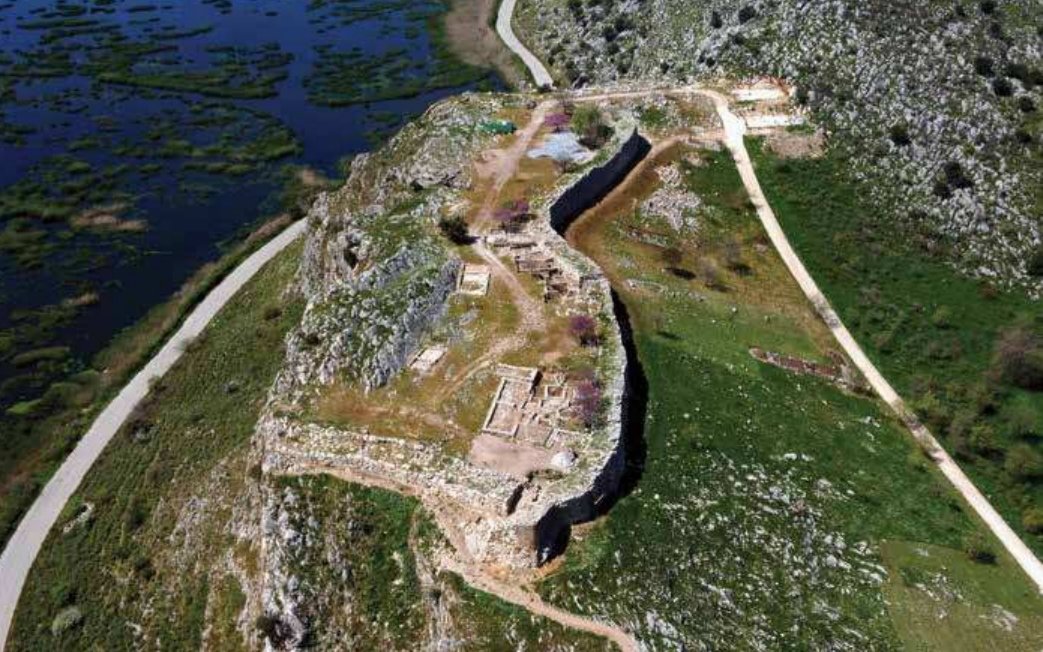
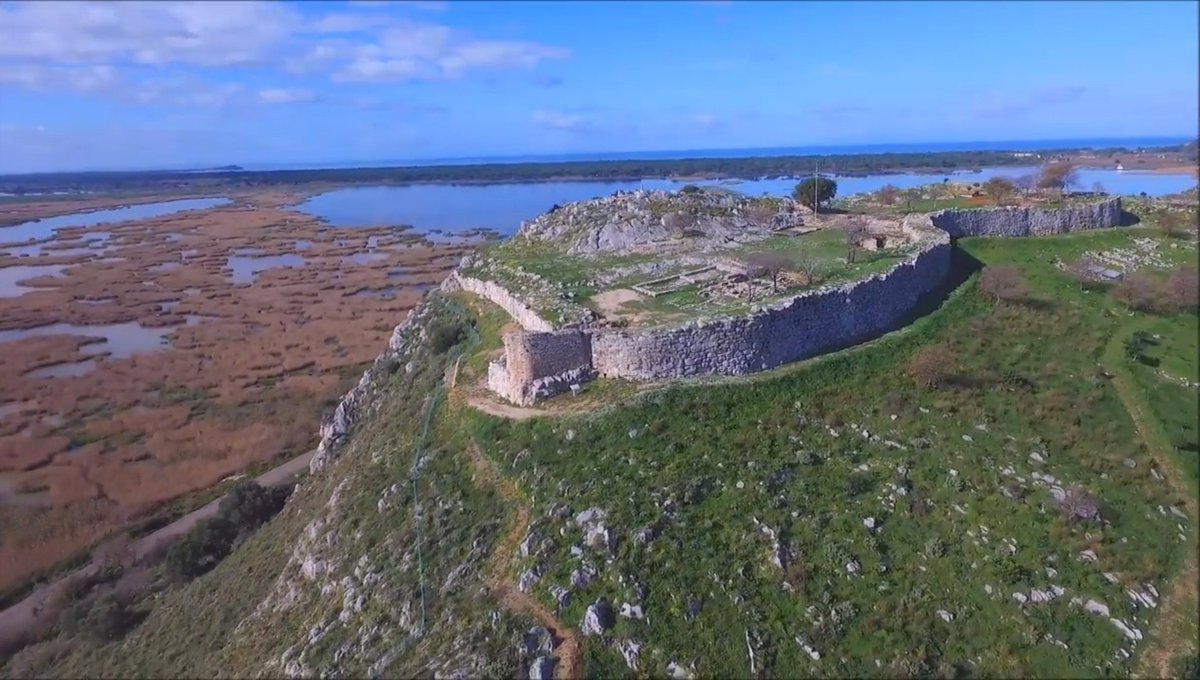
2/This fact is demonstrated by the existence of the considered oldest sample of Linear A', a part of a tablet from the Southwestern House in Knossos (KN 49), which dates to MM IIA (1800 BC). However, there is the opinion that the birthplace of Linear A was the palace of Phaistos. 

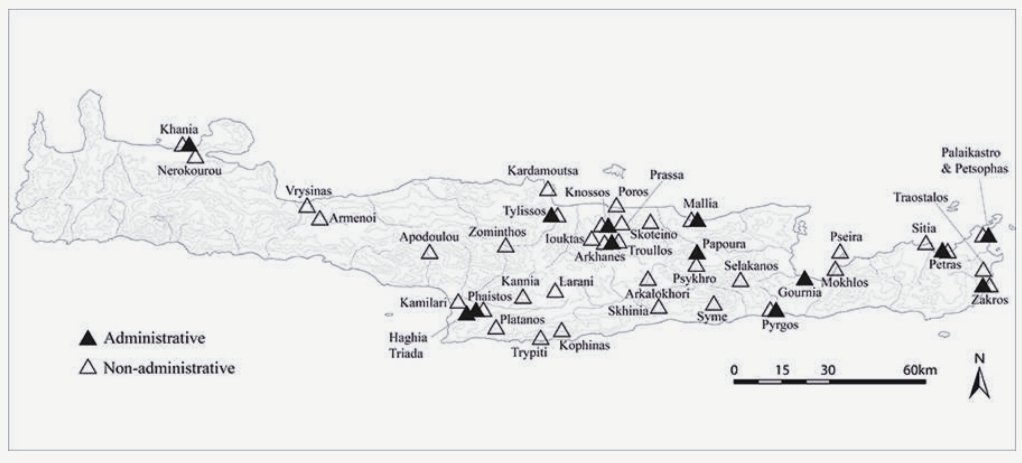
3/ Most likely the Linear A' came from the oldest Cretan Hieroglyphs, without this suggesting that they also rendered the same language. In Knossos, Phaistos, Malia and Petras the two scriptures coexisted for a long time. 

4/ In total, approximately 1500 Linear A' texts have been found, of which a part has been recovered outside Crete (Mainland Greece, Aegean islands, Ionia) and in some cases outside the Aegean area (Israel). ➡️ 
➡️ Of particular importance is the finding of administrative texts in Samothrace, Keos, Melos and Thera,a fact that conceals the existence of a strong Minoan presence in the Cyclades and the islands of the NE Aegean, within the context of the Minoan Thalassocracy. 

5/ The 90% of the texts come from clay documents of an administrative nature, i.e. tablets, roundels, seals and noduli. ➡️ 
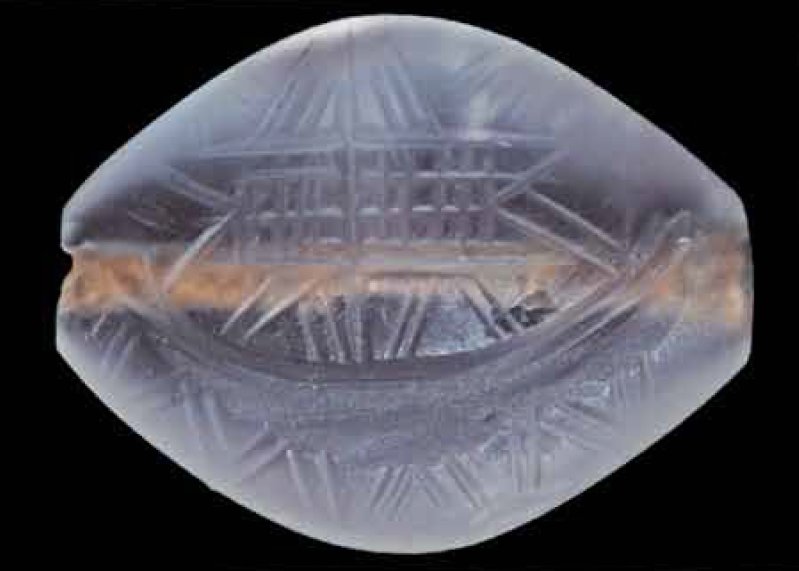







➡️ At the same time, Linear A' texts have also been found in non-administrative contexts, such as engraved and painted inscriptions on clay vessels, inscriptions on other vessels, architectural parts and metal objects. 
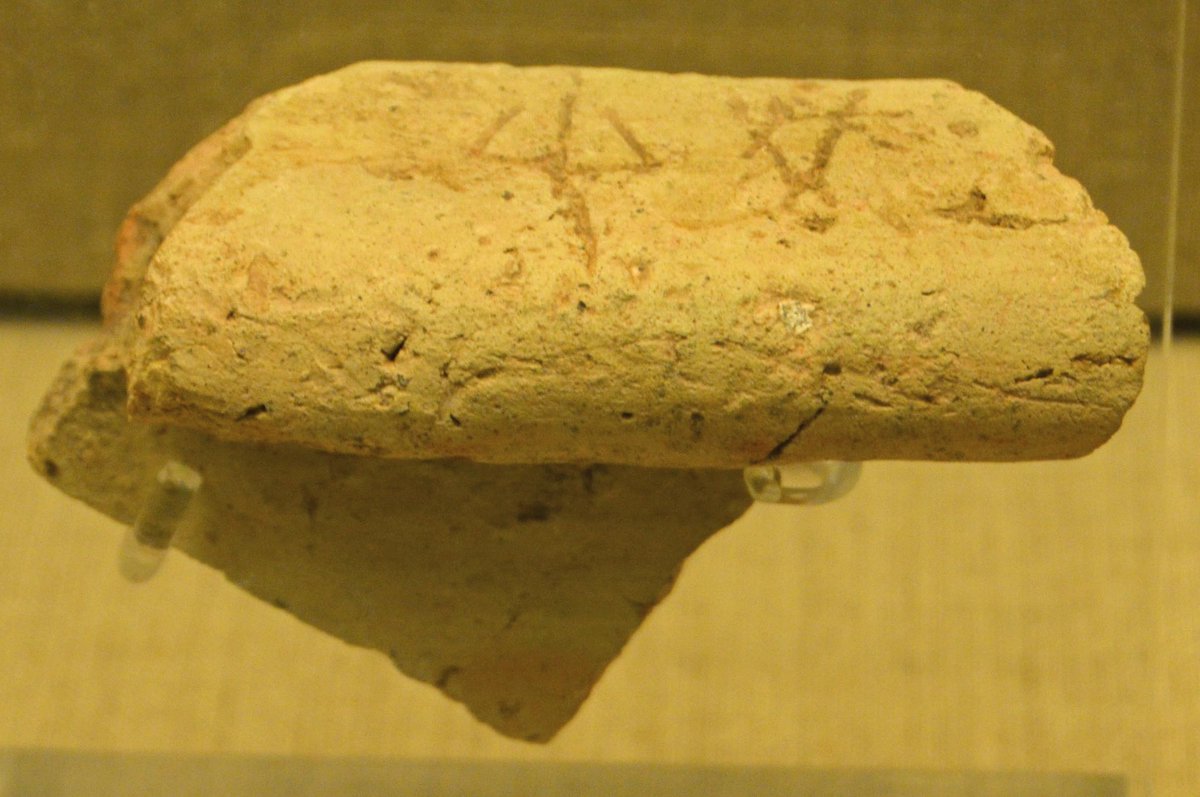





6/ Most of the documents, which are palimpsests (were written - erased - rewritten), come either from files that were incomplete when their conservation disaster occurred, or from files that were completed and stored, placed several times in wooden boxes. 

7/ The textual records show that the Linear A' is a logo-syllabic type of writing, meaning that it includes syllabograms (phonetic signs representing syllables) and logograms / ideograms (pictorial symbols that denote groups of people or goods). 

8/ The Linear A' uses 97 syllabograms, a number of logograms, metrograms and fractionograms. The syllabograms render syllables with one vowel, with consonant - vowel or consonant - semiconsonant - vowel (nwa). The Linear A' uses only three vowels: a, i, u. 



9/ Several syllabograms represent consonant clusters, while the standard word order appears to be verb-subject-object, attesting to a syntactic closeness to Egyptian hieroglyphics and contrasting with the majority of Indo-European languages (S-V-O). 

10/ In contrast to the Cretan Hieroglyphs, Linear A' texts are quite orderly and written in almost straight lines, while they are read from left to right and from top to bottom. Groups of signs are separated by either a dot or a stroke. 

11/ In Linear A' several parts of speech appear, such as nouns (mainly names and toponyms), verbs, aggressive determinations, prefixes (I/J - vowel and A-SA + word root) and suffixes (-TE/TI). ➡️ 

➡️ The presence of prefixes and affixes suggests that Linear A is an agglutinative rather than an vocative language. 



12/ Linear A' administrative texts present us a well-build palatial bureaucratic system, which records the stored products, livestock, raw materials and finished products that were associated with workshops, palatial tracts of land, as well as the staff employed by the palace. 

13/ At the same time, they record movements of goods and contributions to the palaces, while it is recorded the distribution of agricultural products and raw materials to the workshops ➡️ 

➡️ for the production of the final product, to export or even as payment for services rendered to the palace by individuals or communities. 

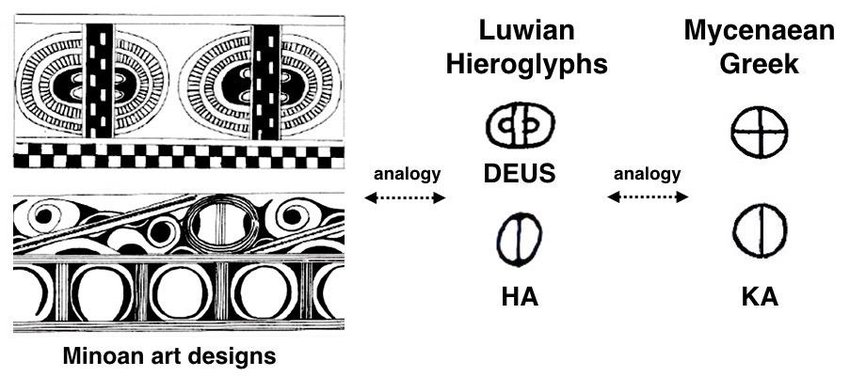
14/ According to the data so far, Linear A' is considered an isolated language, meaning a language that does not belong to any known lingual family. ➡️ 

➡️ Despite persistent efforts to decipher the Minoan language by identifying it with some known language (Semitic, Luwian, Hurrian), this has not been possible. 
15/The lack of sufficient surviving evidence, the short and standardized nature of most inscriptions, which do not contain complete syntactic structures, the lack of an indisputable cognate language, and the lack of any bilingual inscription have contributed to its undecipherment 

16/ Nevertheless, Linear A' is a given that it was used as a writing model for the development of Linear B', a language which reflected an Indo-European language, the Greek. ➡️ 

➡️ The two scripts show a similarity of about 70% in terms of syllabic points, but the complex/compound signs of Linear A' are not present in Linear B' and the logograms show substantial differences. 

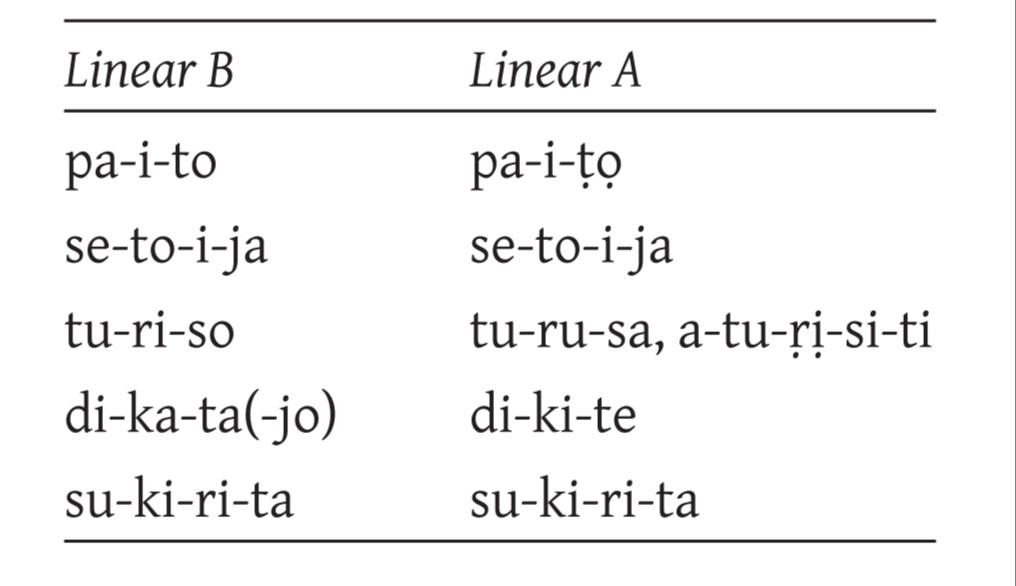
17/ Also, the similar administrative nature of the two scripts, the close relationship between them and the existence of common syllabic sequences (pa-i-to = Phaistos), probably indicate a similar phonetic interpretation of the similar signs between the two scripts. ➡️ 
18/ Linear A' was a script used primarily for administrative purposes, but several times it indicates a religious and private use, which lasted until the mid-14th century BC (after the Mycenaean conquest of Crete), ➡️ 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh