1/Need help reading spine imaging? I’ve got your back!
A #tweetorial about the ABCs of reading spine MRs & CTs.
#medtwitter #FOAMed #FOAMrad #medstudenttwitter #medstudent #neurorad #radres #neurosurgery #spine #orthopedics @medtweetorials @stefantigges
A #tweetorial about the ABCs of reading spine MRs & CTs.
#medtwitter #FOAMed #FOAMrad #medstudenttwitter #medstudent #neurorad #radres #neurosurgery #spine #orthopedics @medtweetorials @stefantigges

2/A is for alignment. Normal spinal alignment is perfectly in balance, resulting in the minimal energy needed for erect posture. Even subtle changes in alignment need compensatory changes to maintain posture, resulting in more work/energy expenditure & pain. 

3/The goals for alignment on imaging: (1) look for unstable injuries & (2) look for malalignment that causes early degenerative change. Abnormal motion causes spinal elements to abnormally move against each other, like grinding teeth wears down teeth—this wears down the spine 

4/B is for bones. On CT, the most important thing to look for w/bones is fractures. You may see focal bony lesions, but you may not. On MR, it is the opposite—you can see marrow lesions easily but you may or may not see edema associated w/fractures if the fracture is subtle. 

5/Assess the ligaments w/the bones. Unlike long bones, ligaments in the spine cover along the bones like saran wrap. Anterior longitudinal along the vertebral body front, posterior longitudinal along the vertebral body & posterior ligamentous complex along posterior elements 

6/On CT, you can infer ligamentous injury from the alignment—if the space is too wide, the ligament can’t be intact. On MR you can see edema in the ligament (suspect ligamentous injury) or focal disruption (see the ligamentous injury) 

7/C is for canal on CT & cord on MRI. On CT, look at canal contents for any large masses or collections that could compromise the canal. You won’t see it all, but you have to try. On MR, assessing the canal is easy. You can also see the cord itself to check for edema/injury 

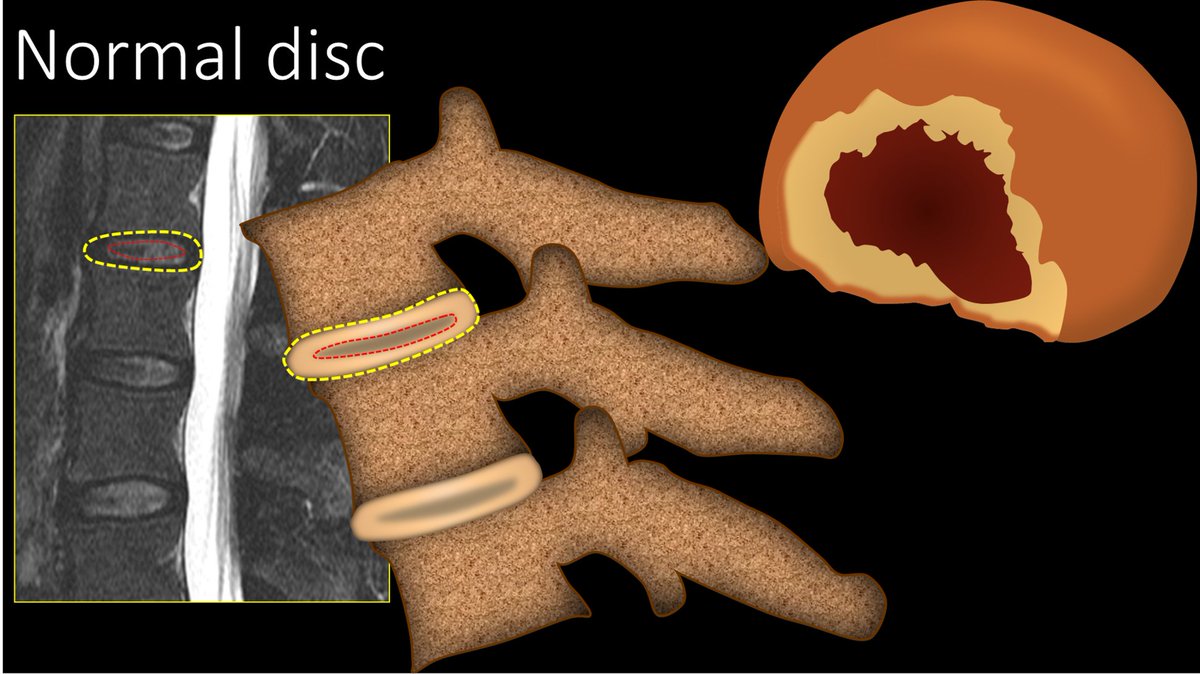
8/D is for discs or degenerative findings. Normal discs should look like a kidney on its side, with a little indentation in the middle just like the renal hilum. Any change to this reniform shape means that there is a disc bulge. 

9/Normal discs also have a very distinctive appearance on sagittal imaging. You should see a T2 bright disc with a dark nucleus pulposus center. It looks like the cross section of a jelly filled donut 
10/If you lose that jelly filled donut appearance, and the discs look flatter or darker without a definable center—more like flat pancakes than jelly donuts—then the disc is degenerated. 

11/Several things can happen to a degenerated disc. First, you can get a bulge. I think of a bulge like gaining weight—you slowly get fatter & loosen your belt. For a disc, the annulus degenerates, gets looser & the disc gets a pot belly—so you lose the renal hilum indentation. 

12/Next you can get a protrusion. If a bulge is loosening your belt (i.e., the annulus is more lax but still intact), a protrusion is like a hernia. The annulus suddenly tears and disc herniates out. This means it is more focal and can happen more acutely. 

13/Next is an extrusion. Extrusion is when herniated disc become like toothpaste. B/c it’s squishy like toothpaste, an extrusion can move up or down away from the parent disc. Extrusion base can be smaller than the rest of it bc it can squish through small holes like toothpaste 

14/Finally is a free fragment. This is when a piece of the extrusion breaks off from the rest of the disc—like when you break off some toothpaste onto your toothbrush. You can see this on imaging bc the fragment is usually a different signal than the parent disc—much T2 brighter 

15/Besides the disc, you should also look at the facet joints. A normal facet joint looks like a hamburger. When the facet starts to look more like a mushroom than a hamburger, with overhanging osteophytes, that’s when I call it degenerated 

16/In the c-spine, there are also uncovertebral joints. These are at the lateral vertebral body. Normally they should be smooth. On coronal images, they look like little devil horns. When they start to get osteophytes & look more like moose antlers, then they are degenerated. 

17/So every spine dictation becomes formulaic, like a mad libs fill in the blank. Go through your ABCs and look for abnormalities in each. When you get to the D, if the study was done for degenerative changes, you should evaluate each level individually. 

18/At each level, it is also a fill in the blank formulaic dictation. You should assess disc, facets, & possibly uncovertebral joints, looking for the signs we have talked about that show they are degenerated. Then you should say what they are doing to the canal & neural foramina 

19/So now you know how to approach spine imaging studies in a systematic way—so that your dictations will have all the necessary elements to strike that perfect balance between enough detail and enough brevity. I told you I had your back! 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















