Huge tax cuts and a borrowing surge: The Chancellor has opted to boost short term growth and interest rates while setting the public finances on an unsustainable path – here are five key takeaways from today’s #MiniBudget – THREAD🧵
1 - £45 billion of tax cuts were announced today – going far beyond election promises to cancel corporation tax increases and reverse this year’s National Insurance rise. These are the largest tax cuts to be announced in a single fiscal event since the 1970s. 

2 - A record increase in borrowing: The decision to combine the largely unavoidable higher deficit caused by rising energy prices/interest rates with permanent tax cuts will drive up borrowing by £411 billion in coming years. No Chancellor has increased borrowing by so much. 

3 – Future spending could be on the cards: The Chancellor has said that debt falling remains his key metric for fiscal sustainability – but achieving that during the middle of this decade could require spending cuts of £35 billion in 2026-27. 

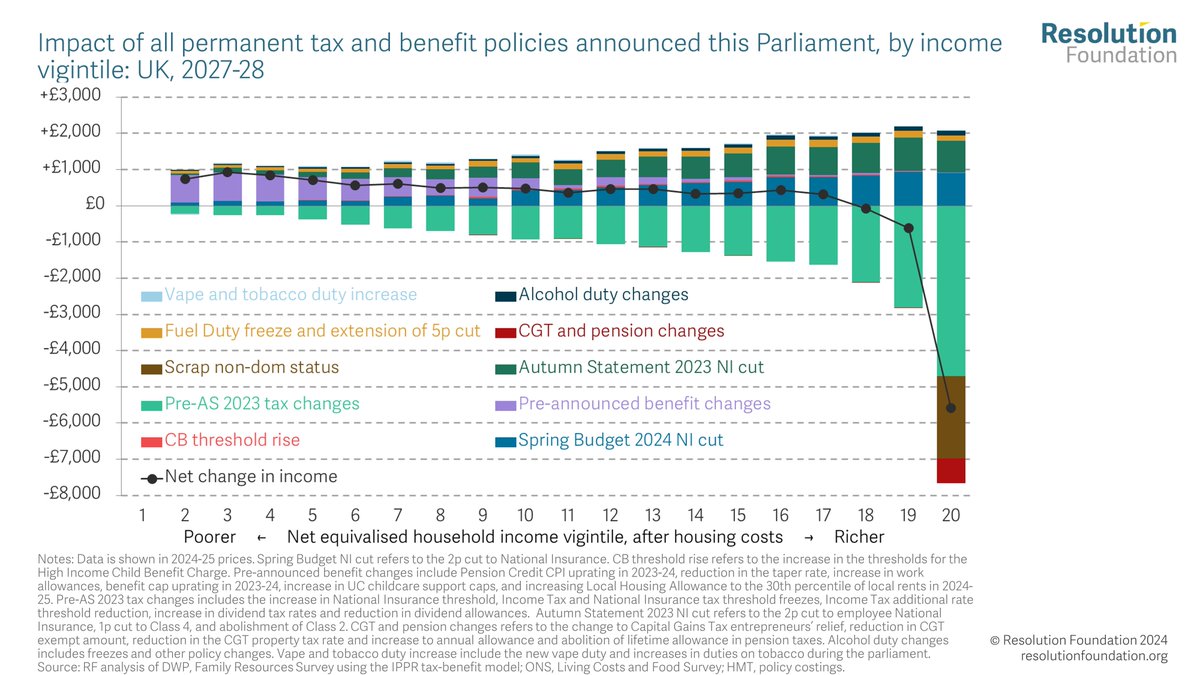
4 – Almost two-thirds (65%) of the gains from personal tax cuts announced will go to the richest fifth of households: Almost half (45%) will go to the richest 5% alone, while just 12% of the gains will go to the poorest half of households. 

5 – Caution needed on growth: While energy support will boost GDP this winter, the borrowing required will also mean higher interest rates. Growth in the years ahead is likely to be driven far more by the path of energy prices than the tax cuts announced today. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh