1/ There is the opinion that the Minoan Cretans were a peaceful people, who dominated through trade and their cultural superiority in the Aegean Basin during the first half of the 2nd millennium BC. But maybe was the reality different?
#Minoans #warfare #Crete #Aegean
#Minoans #warfare #Crete #Aegean

2/ It is clear that the economic prosperity through the involvement in the international trade of the time, as well as the particular Cretan religious worldview contributed decisively to the formation of the identity of both the Minoan elite and the rest of social groups. 



3/ At the same time, however, and according to a more penetrating interpretation of the archaeological data, it appears that war was in fact a defining feature of Minoan society and that the model of the warrior-hunter-athlete was one of the dominant expressions of male identity. 

4/ During the Pre-palatial Period, appropriate political, religious and economic practices were formed by specific emerging social groups which they initially imposed on their local societies and then on the entire island through a centralized - theocratic palatial system. 

5/ It goes without saying that this process took place through intense competition and conflicts between groups fighting for primacy, a fact which presupposes the existence of some war practices, ➡️ 

➡️ which seem to be documented mainly through the presence of the Aegean-type dagger in burial assemblages and on sealstones. 
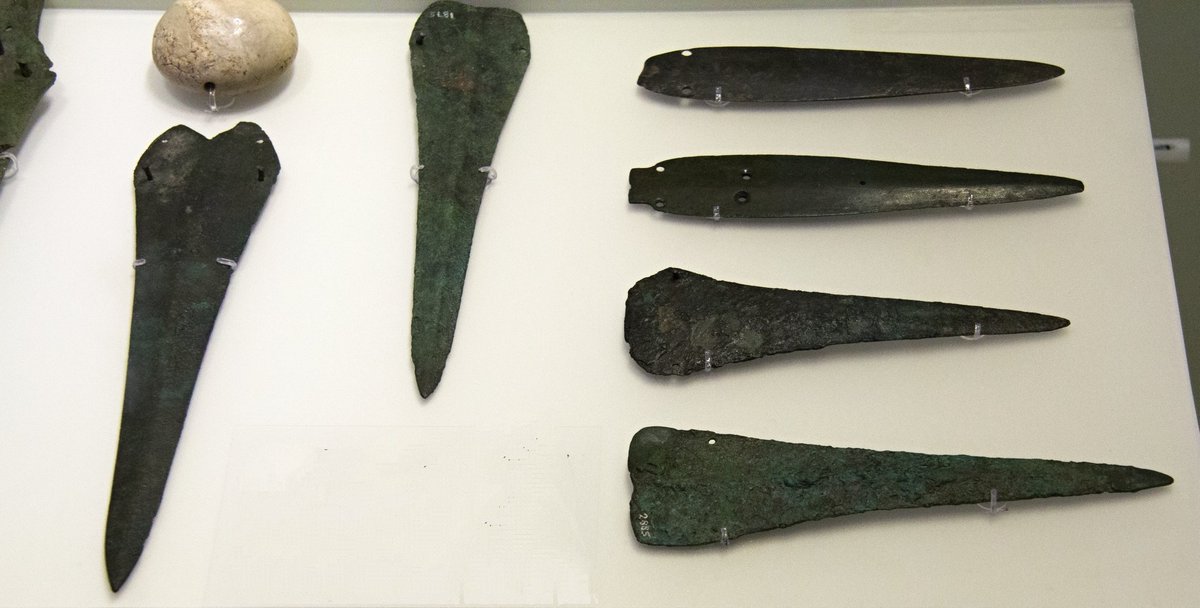

6/ During the Final Neolithic - Early Bronze Age in the Aegean, the dagger played a significant role in highlighting the identity of the warrior-hunter, being an object of prestige, everyday use and a weapon. ➡️ 

A rare depiction of daggers combat on a seal stone of the EM III/MM I period demonstrates that the close contact battle was the primary type of combat engagement in this period. 

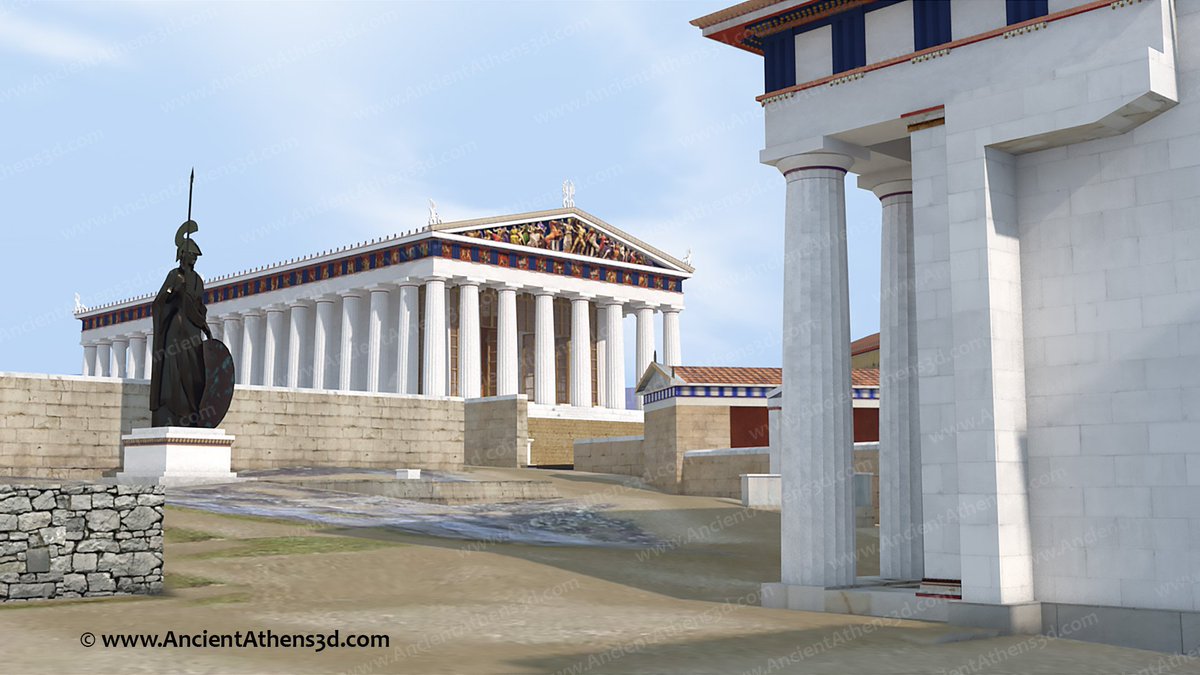
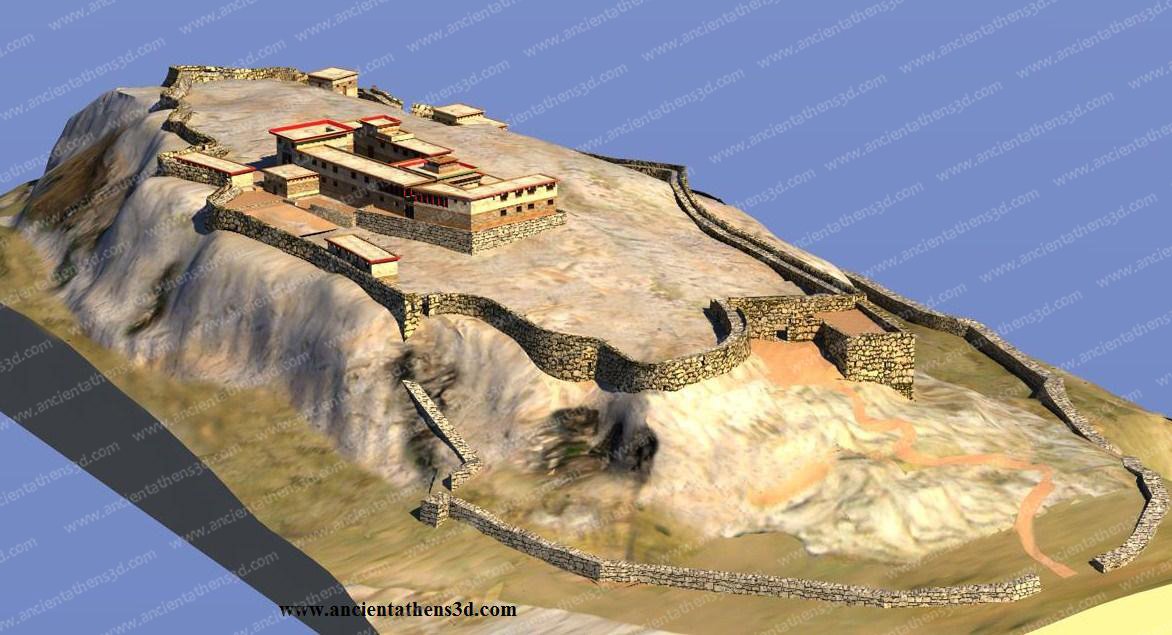
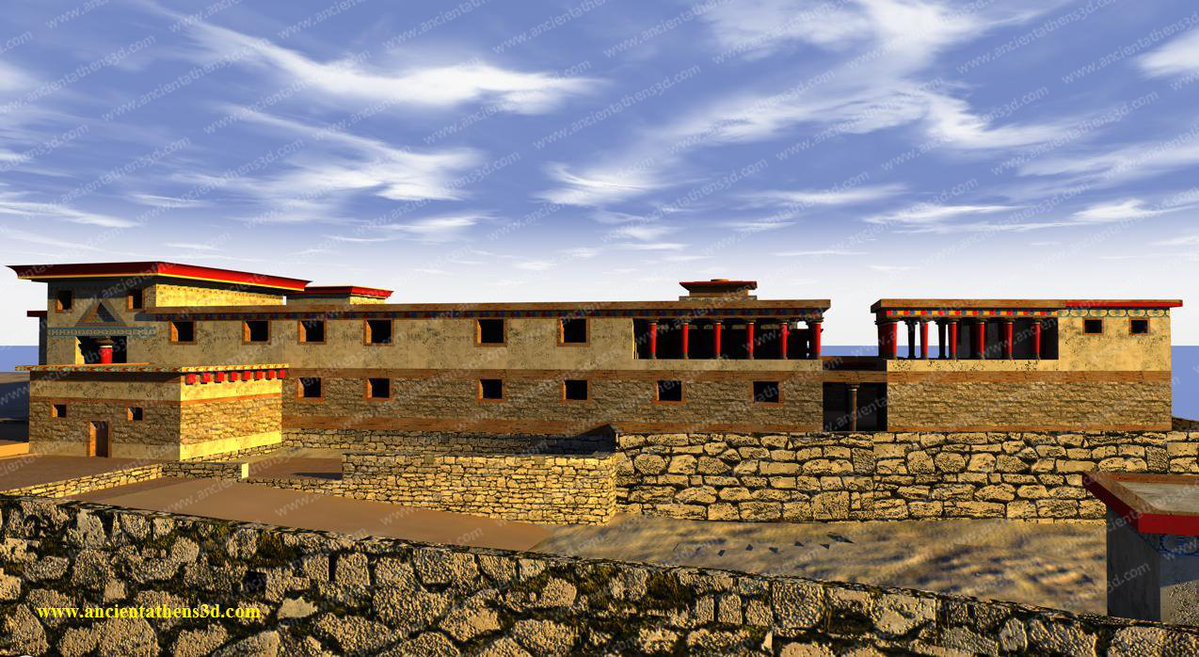
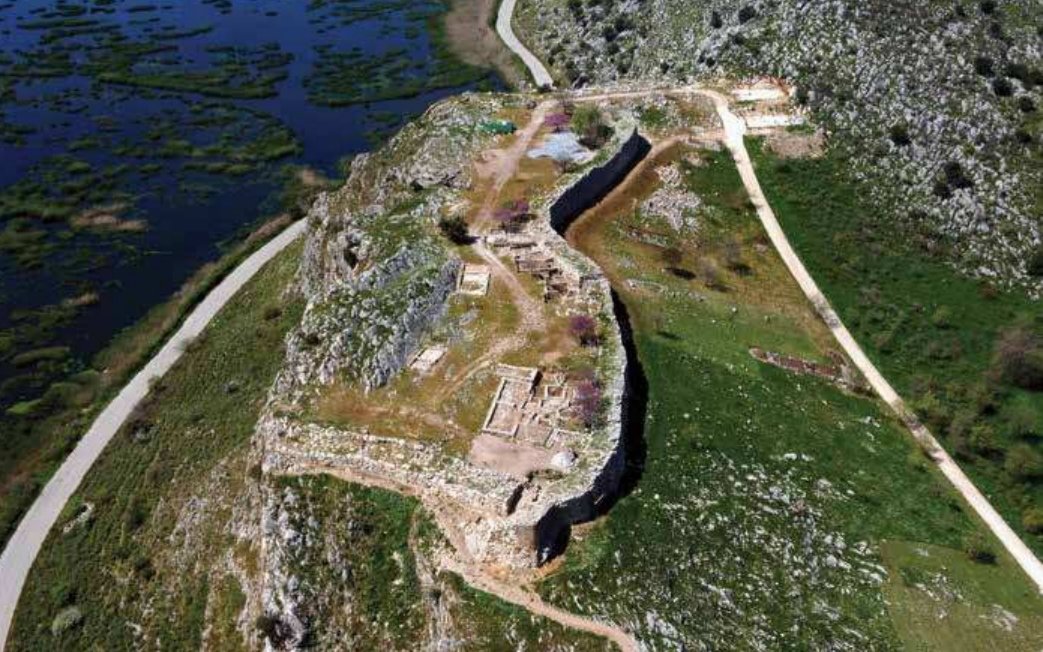
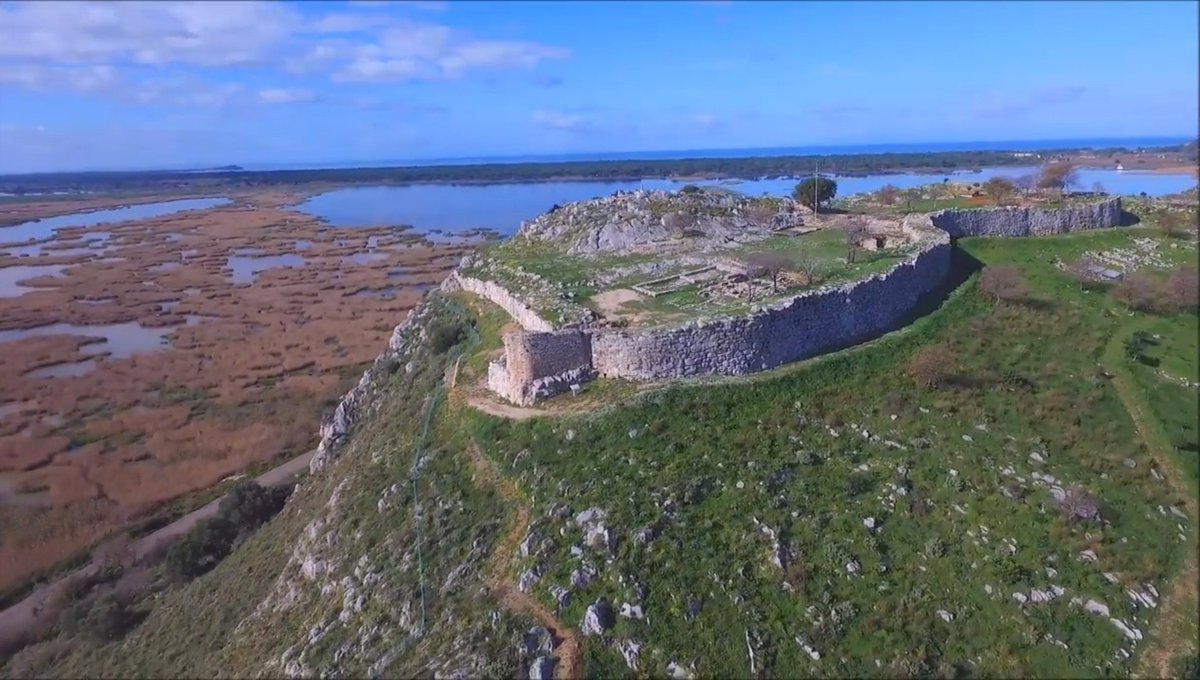
7/ On the other hand, the EM III fortifications in Aghia Fotia and the nearby fortified proto-palace in Petra, suggest to us that the course to the establishment of the early palaces (1900 BC) was bloody in the midst of social unrests and upheavals, ➡️ 

➡️ the extent of which is indeterminate and ended either with the predominance of the stronger elites in each region, or there was a final compromise between a few rulers who took control of the early palaces. 

8/ It is very possible that these fortifications were subject to the yeasty framework of this turbulent period, ➡️ 
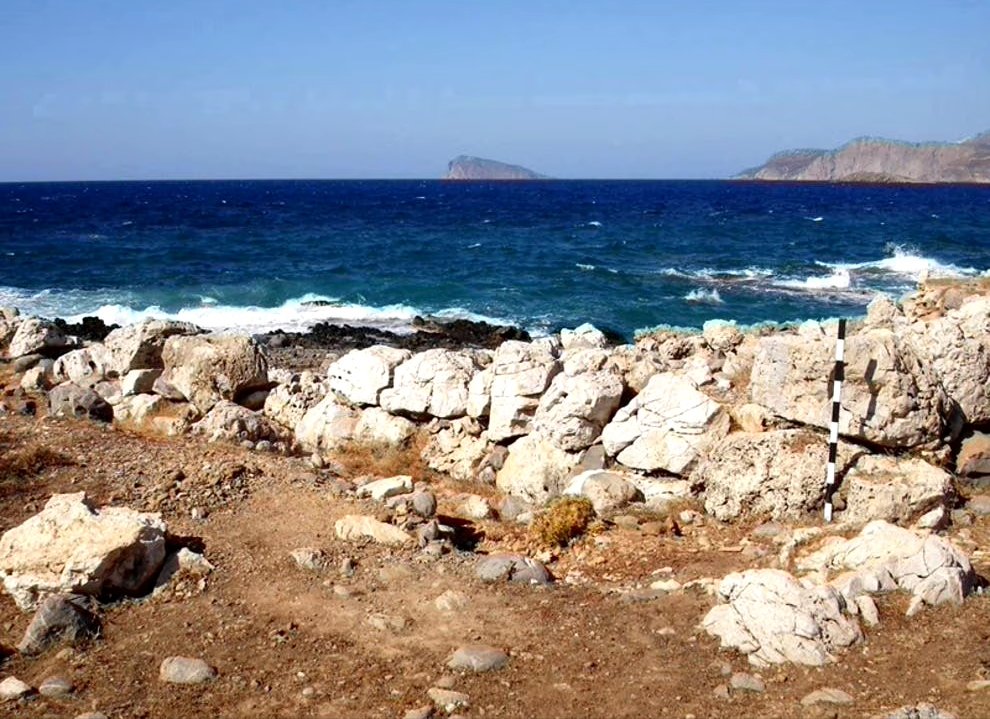

➡️ however the fortification of the palace in Petras in combination with the fortifications in Malia and Zakros may also have a symbolic deterrent character for anyone who wanted to usurp the authority of the local ruling elite. 

9/ With the establishment of the palatial system and the subsequent primacy of Knossos, the competitive - conflict climate does not seem to have ceased to exist, ➡️ 

➡️ but on the contrary took a new form through the questioning of the primacy of the ruling elites both internally by selfish interests among the members them, as well as at the regional level by local factions eyeing for autonomy. 

10/ An element that confirms the above claim is the presence of small-scale checkpoints and observatories in various parts of the Cretan territory, especially after the MM II period, ➡️ 

➡️ while at the same time there are indications of violent destruction of sites by the human factor, such as the looting and abandonment of the YM I villa in Mochlos. 

11/ However, the top manifestation of the military background of the Minoans is the Minoan Thalassocracy during the Neopalatial Period, ➡️ 

➡️ when the Minoans dominated the Aegean, establishing trading posts on various Aegean islands, while at the same time their trading ships traveled to the countries of the East. 



12/ In my opinion, the Minoan control in the Aegean was carried out both with the creation of a powerful fleet and with the existence of a trusted military order, ➡️ 

➡️ which imposed the Minoan presence on the islands of the Archipelago with firm hand and at the same time contributed to the suppression of all pirate or other activity against Minoan commercial interests. 

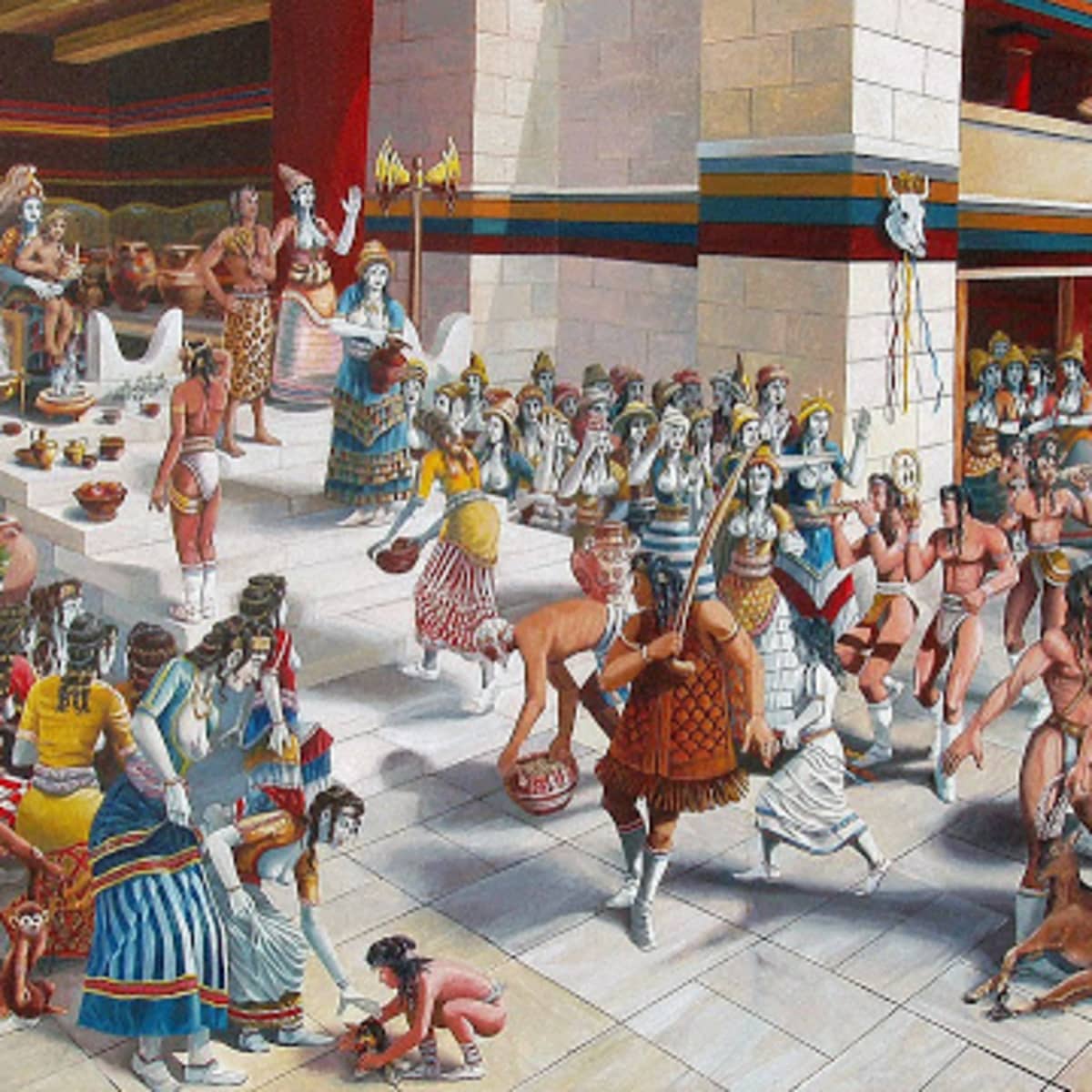
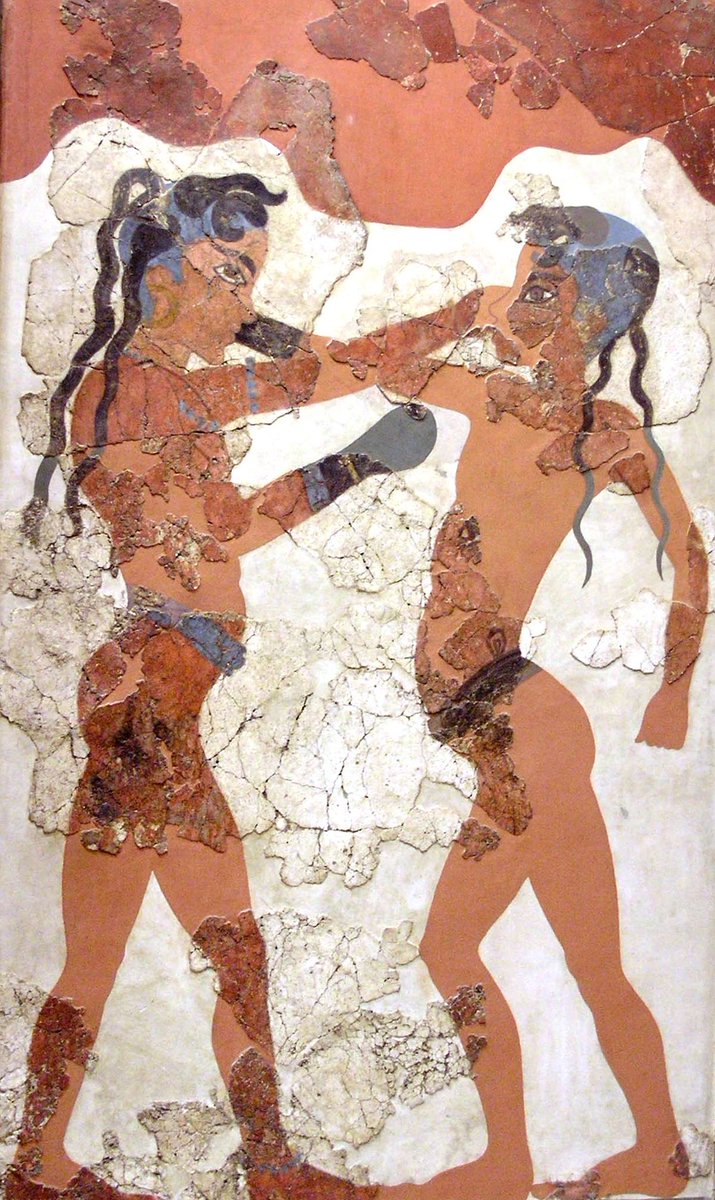
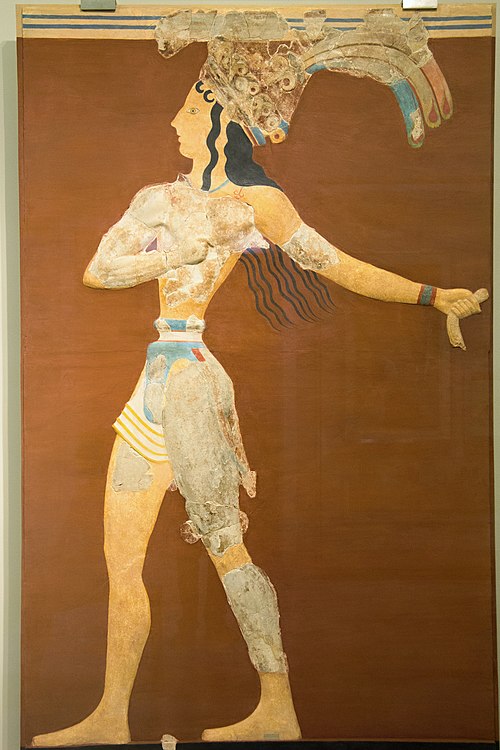
13/ The Minoan figural art presents us with many examples of the occupations of the ruling elite men, such as the involvement with the hunting, sports, bull-leaping, battle. ➡️ 

➡️ They are often depicted with brawny physique and distinctive headdress, wearing helmets and holding shields, sometimes in battle scenes and sometimes in hunting scenes. 

14/ During the palatial period, it is common to see scenes of hand-to-hand combat, where warriors wear helmets, hold shields and spears or swords, and rarely use bows. ➡️ 

➡️ Although these scenes often quote the exploits of heroes or deities, they are a reflection of the Minoan warrior-hunter prototype. 



15/Of particular importance is the presence of bronze and coroplast figurines that show warriors girded with daggers,presenting an early symbolic importance of armor as an object of prestige and religiosity,while in other cases they show athletes with their hands raised in fists. 

16/ During the Neopalatial Period, the appearance of new dynamic elites within the ruling class is observed, which attempt to highlight their martial virtues by glorifying their individual superiority, but at the same time, Minoan Crete as a great regional power. 
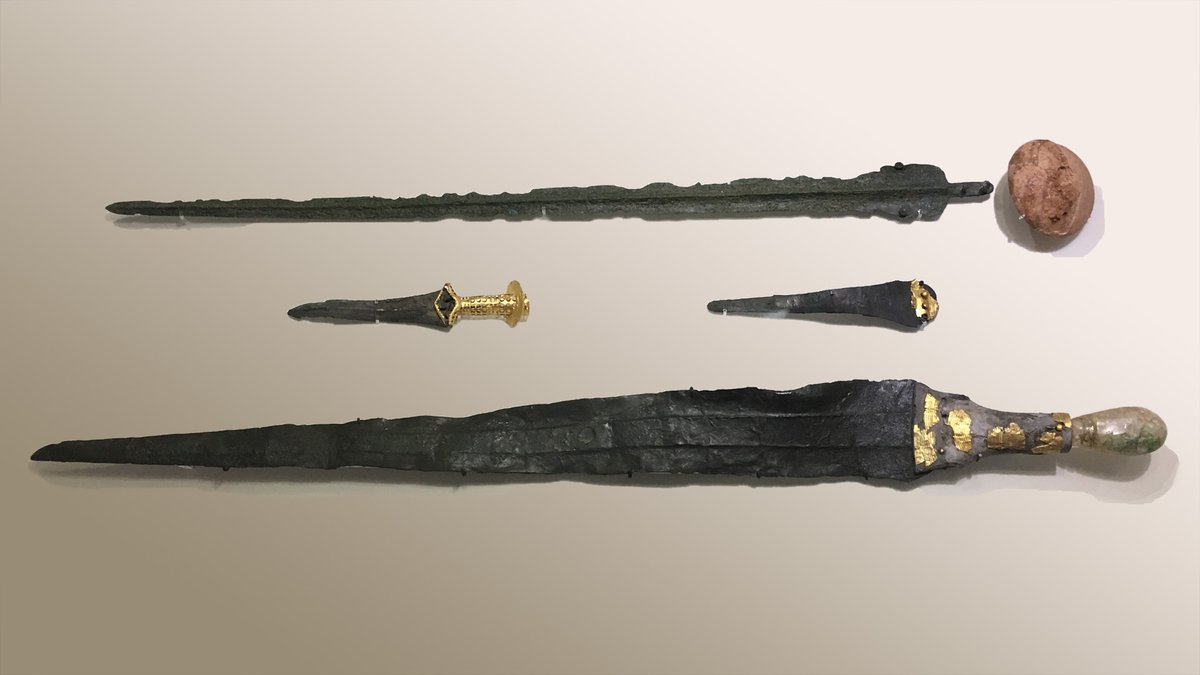



17/It's important to list here a series of Minoan weapons technologically transferred to the Mycenaeans, which evolved: light body armor,various types of bronze or ivory helmets,octagonal and turret-shaped shield, type A/B sword and dagger, long and short spear, bronze battle-axe 
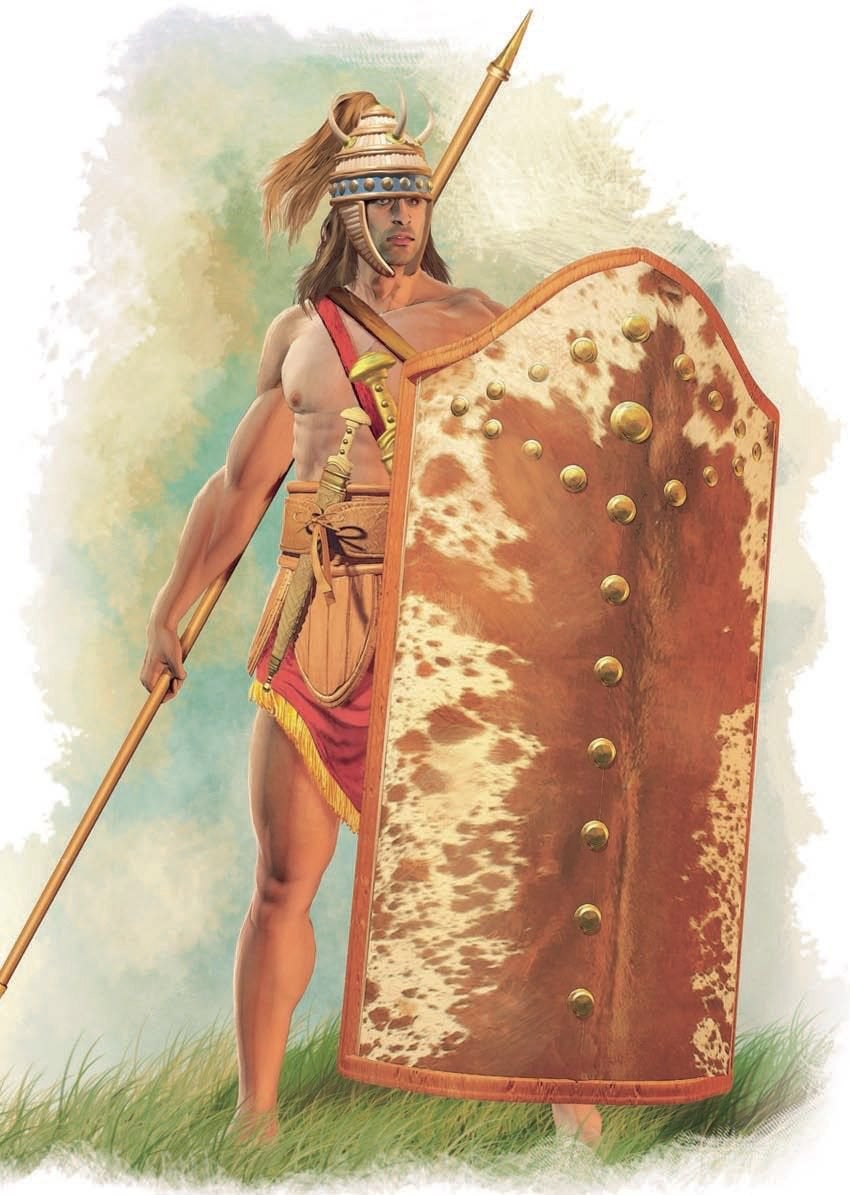

18/ To summarize, we would say that the Minoan Cretans had a long tradition related to war and individual armament, with the palatial system based on the triptych:➡️ 
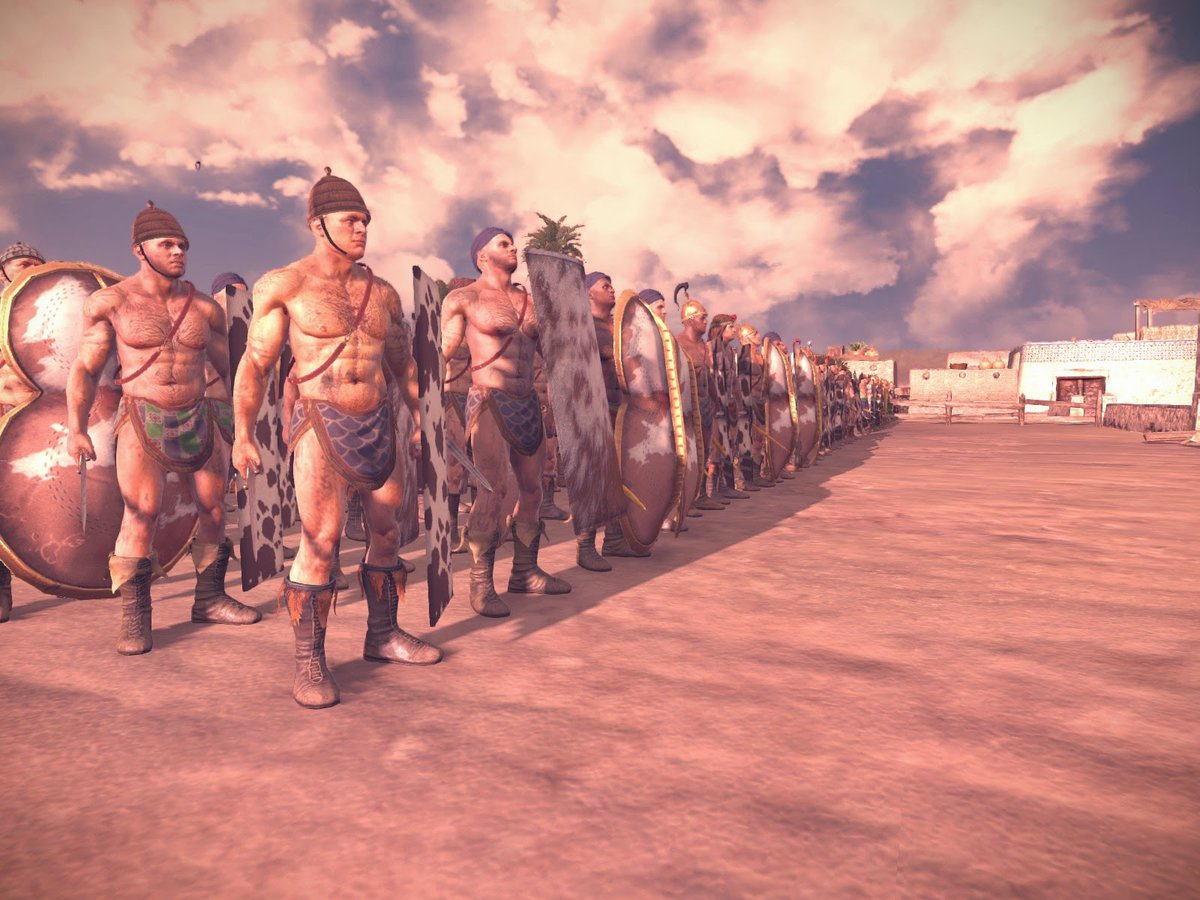

➡️ economy (trade - bureaucracy), religion (priesthood) and army, which was a means of control, pressure, deterrence and glorification. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh