1/You don't need fancy programs to make great #Illustrations!
#Powerpoint is actually an extremely powerful illustrating tool--if you know the secret #hacks!
Here is a 🧵of videos explaining my best tips & tricks so you can make your own great figures, all just w/powerpoint!
#Powerpoint is actually an extremely powerful illustrating tool--if you know the secret #hacks!
Here is a 🧵of videos explaining my best tips & tricks so you can make your own great figures, all just w/powerpoint!

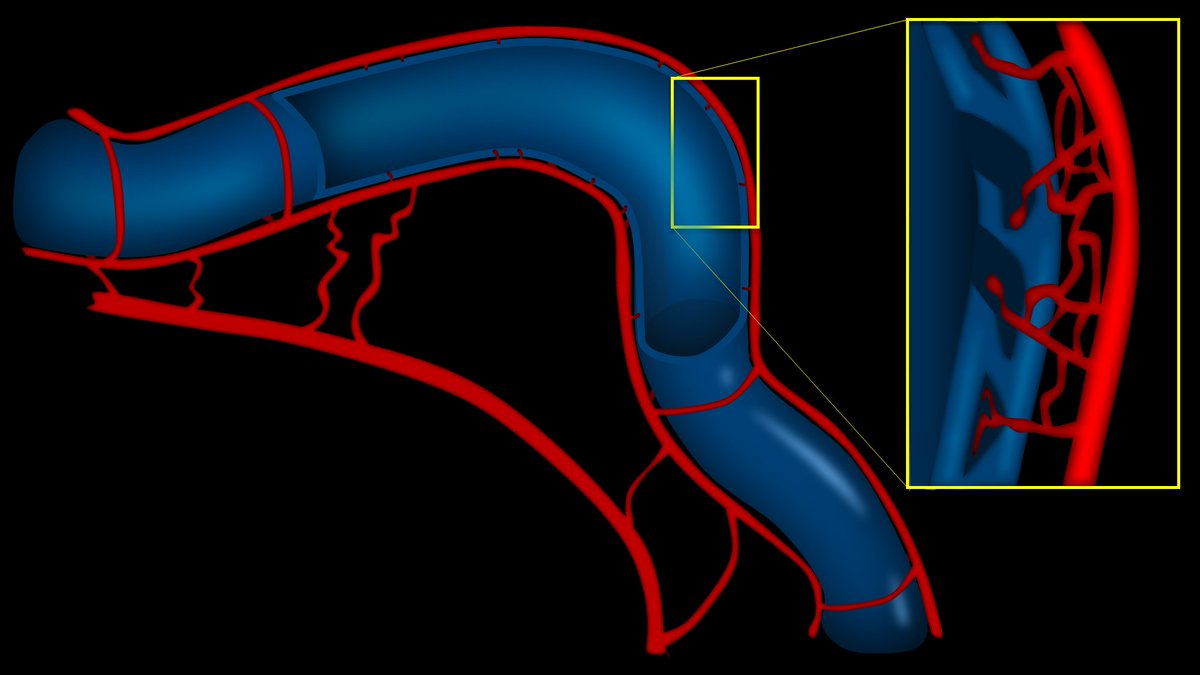
2/First, how to make a great 3D vessel in just 3 steps!
The video below shows you that all you need is a gradient, an edge shadow, and an inner glow to make an amorphous curve into a great figure of a vessel:

The video below shows you that all you need is a gradient, an edge shadow, and an inner glow to make an amorphous curve into a great figure of a vessel:
3/Next, how to get a metallic sheen.
To make metal look real & 3D, you need that bright line of metallic reflection.
The video below shows you how to make a bland colored object reflect light like it's pure gold, just using simple gradients:

To make metal look real & 3D, you need that bright line of metallic reflection.
The video below shows you how to make a bland colored object reflect light like it's pure gold, just using simple gradients:

4/And of course, one of PPT's most powerful drawing functions isn't even known by most people--the inner shadow function!
It makes figures of humans/bodies look more 3D.
The video below shows how to add 3D shadows right where you need it automatically

It makes figures of humans/bodies look more 3D.
The video below shows how to add 3D shadows right where you need it automatically

5/I am working on making more videos on my powerpoint drawing tips, tricks, & hacks. So keep following for more!
Remember, you don't need expensive programs to make amazing figures for your presentation. You just need powerpoint, some quick tricks, and your own imagination!
Remember, you don't need expensive programs to make amazing figures for your presentation. You just need powerpoint, some quick tricks, and your own imagination!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















