The Sound of Footsteps!!!
“it's possible to learn more about neurologic status from watching a patient walk than from any other single procedure”
Russell Nelson DeJong (1907-1990)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia
1/
“it's possible to learn more about neurologic status from watching a patient walk than from any other single procedure”
Russell Nelson DeJong (1907-1990)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia
1/
Phases of gait
Critical incidents!
Stance (60%): (1) heel strike (2) foot flat (3) heel off
(4) toe-off
Swing (40%): (5) toe clearance (6) heel strike
via: Morgan E
2/
Critical incidents!
Stance (60%): (1) heel strike (2) foot flat (3) heel off
(4) toe-off
Swing (40%): (5) toe clearance (6) heel strike
via: Morgan E
2/
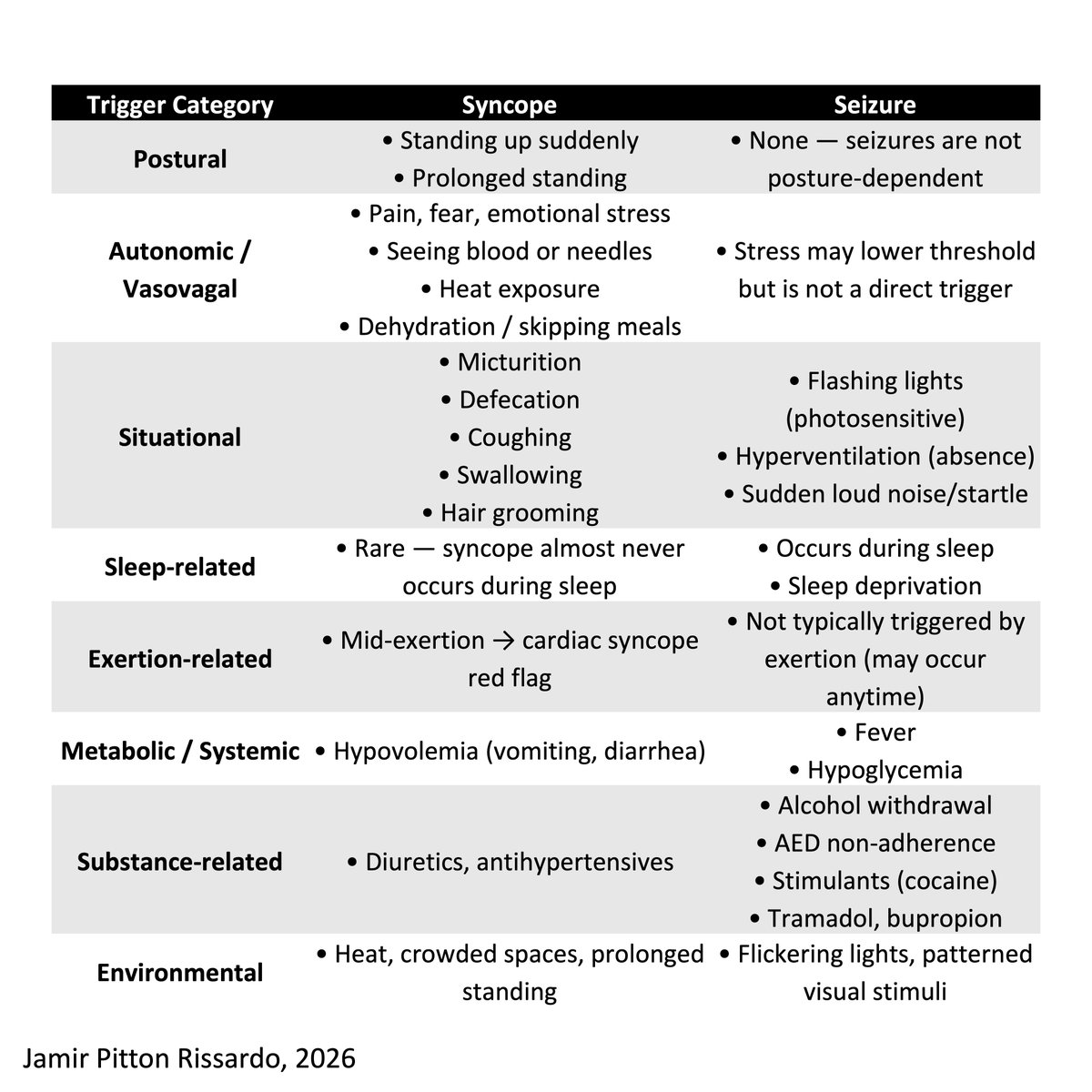
Cerebellar ataxic gait
“Wide based, reeling, careening (drunken sailor)”
- inability to walk tandem
- step length varies unpredictably
- turning may bring out a stagger
- acute alcohol intoxication
via: Matthewhr1
3/
“Wide based, reeling, careening (drunken sailor)”
- inability to walk tandem
- step length varies unpredictably
- turning may bring out a stagger
- acute alcohol intoxication
via: Matthewhr1
3/
Hemiparetic (spastic hemiparesis) gait
“Involved leg spastic, circumduction, often with foot drop”
- pyramidal lesion
- sound by toe scraping, & wear of shoe at toe
- freq: stroke; arm flex, adduct, intern rotated; leg extend
via: onlinemedicalvideo
4/
“Involved leg spastic, circumduction, often with foot drop”
- pyramidal lesion
- sound by toe scraping, & wear of shoe at toe
- freq: stroke; arm flex, adduct, intern rotated; leg extend
via: onlinemedicalvideo
4/
Hemiparetic (spastic hemiparesis) gait
“Involved leg spastic, circumduction, often with foot drop”
via: Dr. Rishikesh A. Bhakare
5/
“Involved leg spastic, circumduction, often with foot drop”
via: Dr. Rishikesh A. Bhakare
5/
Scissoring gait
“Stiff legged, scissoring (wooden soldier)”
- congenital spastic diplegia and myelopathies
- narrow base
- steps are short and slow, feet seem to stick to the floor
- swaying without true loss of coordination
via: Alhadapediatrics
6/
“Stiff legged, scissoring (wooden soldier)”
- congenital spastic diplegia and myelopathies
- narrow base
- steps are short and slow, feet seem to stick to the floor
- swaying without true loss of coordination
via: Alhadapediatrics
6/
Scissoring gait
“Stiff legged, scissoring (wooden soldier)”
youtube.com/shorts/d0LmaJn… via: Neurologia BP
7/
“Stiff legged, scissoring (wooden soldier)”
youtube.com/shorts/d0LmaJn… via: Neurologia BP
7/
Parkinsonian gait
“Small steps, flexed posture, shuffling, festination”
- upper extremities are flexed, except fingers extended
- decreased arm swing
- en-bloc turning
- start hesitation
via: Dr. Prodigious
8/
“Small steps, flexed posture, shuffling, festination”
- upper extremities are flexed, except fingers extended
- decreased arm swing
- en-bloc turning
- start hesitation
via: Dr. Prodigious
8/
Apraxic gait
“loss of the ability to use the legs properly in walking”
- frontal lobe disease
- disorganized walking skills
- shuffling small steps
- normal motor and sensory function on couch examination
via: Jenwit Thippawan
9/
“loss of the ability to use the legs properly in walking”
- frontal lobe disease
- disorganized walking skills
- shuffling small steps
- normal motor and sensory function on couch examination
via: Jenwit Thippawan
9/
Steppage (equine) gait
“high steppage pattern to clear the toes from the floor, double tap”
- foot drop and sensory ataxia
- double tap # sound: toe first (foot drop) heel first (sensory)
via: emrcpian
10/
“high steppage pattern to clear the toes from the floor, double tap”
- foot drop and sensory ataxia
- double tap # sound: toe first (foot drop) heel first (sensory)
via: emrcpian
10/
Steppage (equine) gait
“high steppage pattern to clear the toes from the floor, double tap”
via: Alain Wambe
11/
“high steppage pattern to clear the toes from the floor, double tap”
via: Alain Wambe
11/
Myopathic (waddling) gait
“Exaggerated ‘sexy’ hip motion, waddling, lumbar hyperlordosis”
- muscular dystrophy
- broad base
via: onlinemedicalvideo
12/
“Exaggerated ‘sexy’ hip motion, waddling, lumbar hyperlordosis”
- muscular dystrophy
- broad base
via: onlinemedicalvideo
12/
Myopathic (waddling) gait
“Exaggerated ‘sexy’ hip motion, waddling, lumbar hyperlordosis”
via: Dr. Yemin Ahmed
13/
“Exaggerated ‘sexy’ hip motion, waddling, lumbar hyperlordosis”
via: Dr. Yemin Ahmed
13/
Trendelenburg’s sign
“abnormal drop of the pelvis on the side of the swing leg due to hip abductor weakness”
“pelvic ptosis”
via: openmichigan
14/
“abnormal drop of the pelvis on the side of the swing leg due to hip abductor weakness”
“pelvic ptosis”
via: openmichigan
14/
Trendelenburg’s gait
“abnormal drop of the pelvis on the side of the swing leg due to hip abductor weakness”
youtube.com/shorts/ZUPQp5o… via: kenzothiazepine
15/
“abnormal drop of the pelvis on the side of the swing leg due to hip abductor weakness”
youtube.com/shorts/ZUPQp5o… via: kenzothiazepine
15/
Antalgic gait
“an abnormal pattern of walking secondary to pain that ultimately causes a limp, whereby the stance phase is shortened relative to the swing phase”
via: Dr. Prodigious
16/
“an abnormal pattern of walking secondary to pain that ultimately causes a limp, whereby the stance phase is shortened relative to the swing phase”
via: Dr. Prodigious
16/
Sensory ataxic gait
“Wide-based, steppage”
- post columns or peripheral nerves
- “spinal ataxia”
- pt is extremely dependent on visual input for coordination (# cerebellar ataxia)
- “steppage gait” heel first
- ‘Frankenstein’ gait
youtube.com/shorts/hq4buUL… via: Tony scaria
17/
“Wide-based, steppage”
- post columns or peripheral nerves
- “spinal ataxia”
- pt is extremely dependent on visual input for coordination (# cerebellar ataxia)
- “steppage gait” heel first
- ‘Frankenstein’ gait
youtube.com/shorts/hq4buUL… via: Tony scaria
17/
Spastic-ataxic gait
“proportion of each abnormality depends on the particulars of the case”
- Ataxic component: cerebellar or sensory
via: Dr. Sourya Acharya
18/
“proportion of each abnormality depends on the particulars of the case”
- Ataxic component: cerebellar or sensory
via: Dr. Sourya Acharya
18/
Marche à petits pas
“Small steps, slow shuffling”
- resembles parkinsonian, but lacks rigidity and bradykinesia
- length of steps less than foot’s length
- frontal lobes, NPH, multi-infarct dementia
via: Osama SM Amin
19/
“Small steps, slow shuffling”
- resembles parkinsonian, but lacks rigidity and bradykinesia
- length of steps less than foot’s length
- frontal lobes, NPH, multi-infarct dementia
via: Osama SM Amin
19/
Cautious (senile) gait
“velocity slows, steps shorten, and the base widens”
- 'healthy person walks on an icy surface'
- aging vestibular system, impaired proprioceptive by distal neuropathy in the elderly, and impaired vision
via: Global news
20/
“velocity slows, steps shorten, and the base widens”
- 'healthy person walks on an icy surface'
- aging vestibular system, impaired proprioceptive by distal neuropathy in the elderly, and impaired vision
via: Global news
20/
Magnetic gait
“inability to lift the feet off the floor”
- NPH
via: Hydrocephalus association
21/
“inability to lift the feet off the floor”
- NPH
via: Hydrocephalus association
21/
Magnetic gait
“inability to lift the feet off the floor”
youtube.com/shorts/Enp5map… via: Dr.Pawan Soni
23/
“inability to lift the feet off the floor”
youtube.com/shorts/Enp5map… via: Dr.Pawan Soni
23/
Functional gait
“recognizing positive clinical features of functional gait disorders”
- complex
- inconsistency
- incongruity
youtube.com/shorts/zJIZtob… via: Pogakula Udaykiran
24/
“recognizing positive clinical features of functional gait disorders”
- complex
- inconsistency
- incongruity
youtube.com/shorts/zJIZtob… via: Pogakula Udaykiran
24/
Astasia
“inability to stand”
- functional?
- everything normal, except for the inability to stand
- freq assoc to abasia
doi.org/10.1002%2Fmdc3… via: Mov Disord Clin Pract
25/
“inability to stand”
- functional?
- everything normal, except for the inability to stand
- freq assoc to abasia
doi.org/10.1002%2Fmdc3… via: Mov Disord Clin Pract
25/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh