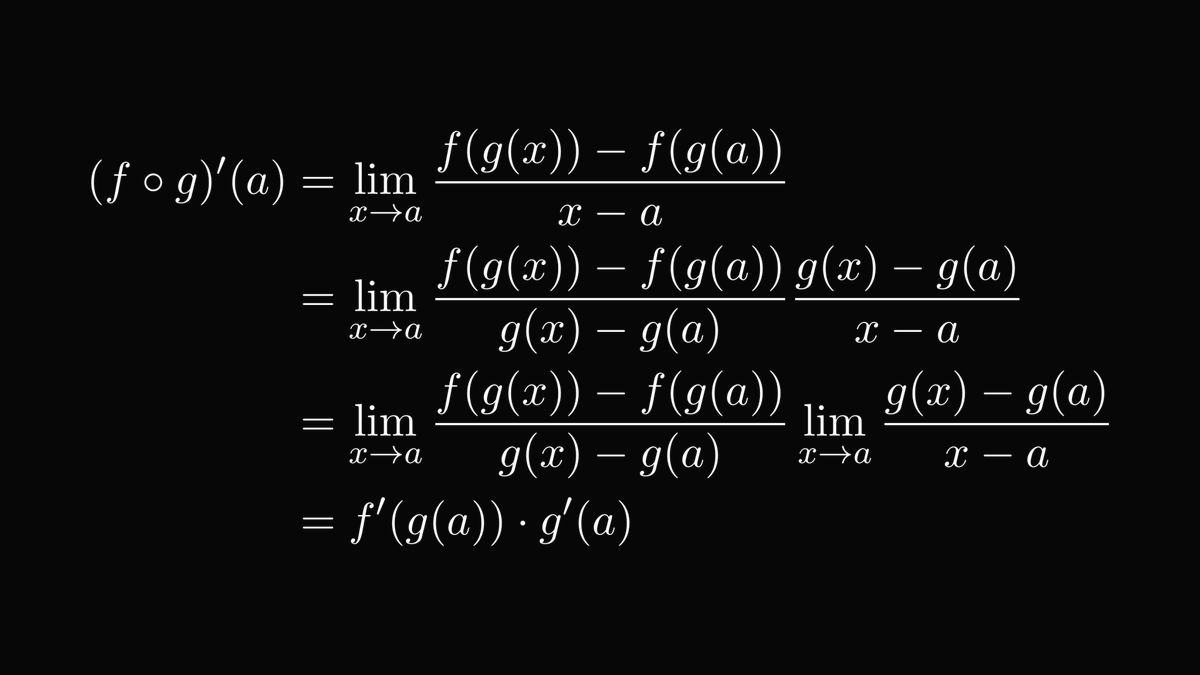Behold one of the mightiest tools in mathematics: the camel principle.
I am dead serious. Deep down, this tiny rule is the cog in many methods. Ones that you use every day.
Here is what it is, how it works, and why it is essential.
I am dead serious. Deep down, this tiny rule is the cog in many methods. Ones that you use every day.
Here is what it is, how it works, and why it is essential.

First, the story.
The old Arab passes away, leaving half of his fortune to his eldest son, third to his middle son, and ninth to his smallest.
Upon opening the stable, they realize that the old man had 17 camels.
The old Arab passes away, leaving half of his fortune to his eldest son, third to his middle son, and ninth to his smallest.
Upon opening the stable, they realize that the old man had 17 camels.

This is a problem, as they cannot split 17 camels into 1/2, 1/3, and 1/9 without cutting some in half.
So, they turn to the wise neighbor for advice.
So, they turn to the wise neighbor for advice.

The wise man says "hold my camel", and solves the problem by lending one to the boys.
Now the stable has 18. The eldest son takes 9 home, while the middle and smallest son leaves with 6 and 2, as their father wished.
The wise man takes his camel back, and everybody is happy.
Now the stable has 18. The eldest son takes 9 home, while the middle and smallest son leaves with 6 and 2, as their father wished.
The wise man takes his camel back, and everybody is happy.

Thus, the camel principle is born: adding and subtracting the same quantity doesn't change the equality, but can help in the computation.
In mathematics, you cannot live without this principle.
I'll show you two examples.
In mathematics, you cannot live without this principle.
I'll show you two examples.

The first one is the quadratic equation.
Its solution formula is one of the few things that everybody remembers from high school. Even if they are woken up in the middle of the night.
This formula is derived from the camel principle. Let me show you how!
Its solution formula is one of the few things that everybody remembers from high school. Even if they are woken up in the middle of the night.
This formula is derived from the camel principle. Let me show you how!
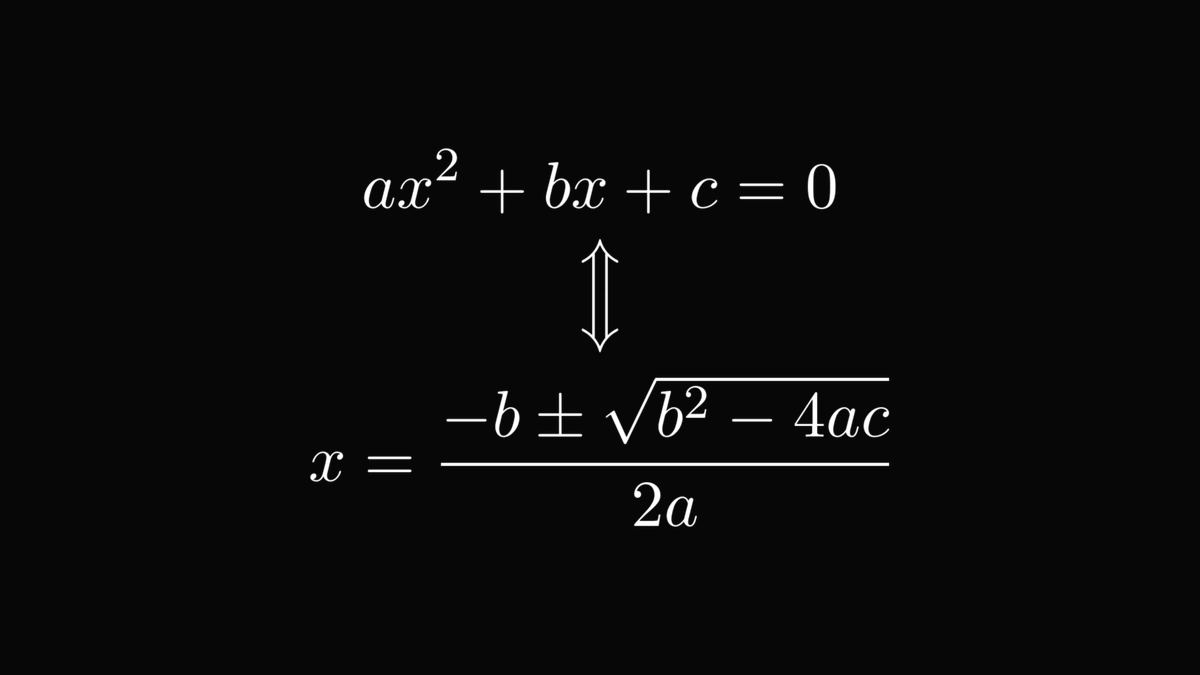
After factoring out 𝑎 from the equation, we notice that the famous identity
(α + β)² = α² + 2αβ + β²
might help to factor the quadratic equation into a product.
To achieve that, we apply the camel principle!
(α + β)² = α² + 2αβ + β²
might help to factor the quadratic equation into a product.
To achieve that, we apply the camel principle!

There is an alternative version of the camel principle, performing a similar feat: multiplying and dividing with the same quantity.
This doesn't change the equality either.
This doesn't change the equality either.

To illustrate, let's look at derivatives, the main engine behind mathematics, physics, and optimization.
(And tons of other fields that allowed technology to get where it is now.)
(And tons of other fields that allowed technology to get where it is now.)

How would you calculate the derivative of a composite function?
This is a quintessential question. Without this, you don't have backpropagation, gradient descent, and thus neural networks.
(At least until someone invents a clever alternative. But that'll take a while.)
This is a quintessential question. Without this, you don't have backpropagation, gradient descent, and thus neural networks.
(At least until someone invents a clever alternative. But that'll take a while.)

You guessed right: the camel principle!
(At least, the second version, where you multiply and divide with the same quantity.)
(At least, the second version, where you multiply and divide with the same quantity.)

(For those with the eagle's eyes: yes, the denominator can be zero. You can epsilon-delta your way out of that, but I won't do it here.)
And thus, we have the chain rule, one massive pillar of science and technology.
This is what we use to perform backpropagation, enabling us to train our neural networks in a reasonable time.
This is what we use to perform backpropagation, enabling us to train our neural networks in a reasonable time.

The lesson here: tiny mathematical curios such as the camel principle are often dismissed as "lacking any applications".
However, such short-sightedness frequently leads astray.
By understanding atoms, you are able to build skyscrapers.
However, such short-sightedness frequently leads astray.
By understanding atoms, you are able to build skyscrapers.
If you have enjoyed this explanation, share it with your friends and give me a follow! I regularly post deep-dive explainers such as this.
Understanding mathematics will make you a better engineer, and I want to help you with that.
Understanding mathematics will make you a better engineer, and I want to help you with that.
https://twitter.com/TivadarDanka/status/1588131890040434688
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh