The most anticipated nephrology trial of the year has been published!
“Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease” #Kidneywk
@NEJM nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
“Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease” #Kidneywk
@NEJM nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
EMPA-KIDNEY trial is a randomized, parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial designed to assess the effect of empagliflozin on progression of kidney disease & CV disease, & to examine safety profile of the drug in a wide range of pts. w/ CKD
The trial included patients without diabetes, patients with an eGFR of less than 30 ml per minute per 1.73 m2, and patients with low levels of proteinuria
Eligible patients were with:
-eGFR of at least 20 but less than 45 ml/minute/1.73 m2, regardless of the level of albuminuria
OR
-eGFR of at least 45 but less than 90 ml/minute/1.73 m2 with UACR of at least 200 mg/g
-eGFR of at least 20 but less than 45 ml/minute/1.73 m2, regardless of the level of albuminuria
OR
-eGFR of at least 45 but less than 90 ml/minute/1.73 m2 with UACR of at least 200 mg/g
Pts. were required to be taking a clinically appropriate dose of a single-agent RAS inhibitor, but pts. could be included, as specified in the protocol, if an investigator judged that a RAS inhibitor was not indicated or would not be not tolerated
-Patients with or without diabetes were eligible
-Patients with polycystic kidney disease and those who had received a kidney transplant were excluded
-Patients were randomly assigned to receive empagliflozin (10 mg once daily) or matching placebo
-Patients with polycystic kidney disease and those who had received a kidney transplant were excluded
-Patients were randomly assigned to receive empagliflozin (10 mg once daily) or matching placebo
-6609 pts. randomized
-Baseline characteristics
📍Mean age 63.8 yr
📍33% were women
📍54% did NOT have diabetes
📍Mean eGFR was 37.3±14.5 ml/minute
📍34.5% of the patients had an eGFR < 30 ml/minute
📍Median UACR was 329 mg/g
📍48% had UACR of 300 or less
-Baseline characteristics
📍Mean age 63.8 yr
📍33% were women
📍54% did NOT have diabetes
📍Mean eGFR was 37.3±14.5 ml/minute
📍34.5% of the patients had an eGFR < 30 ml/minute
📍Median UACR was 329 mg/g
📍48% had UACR of 300 or less

📍Results
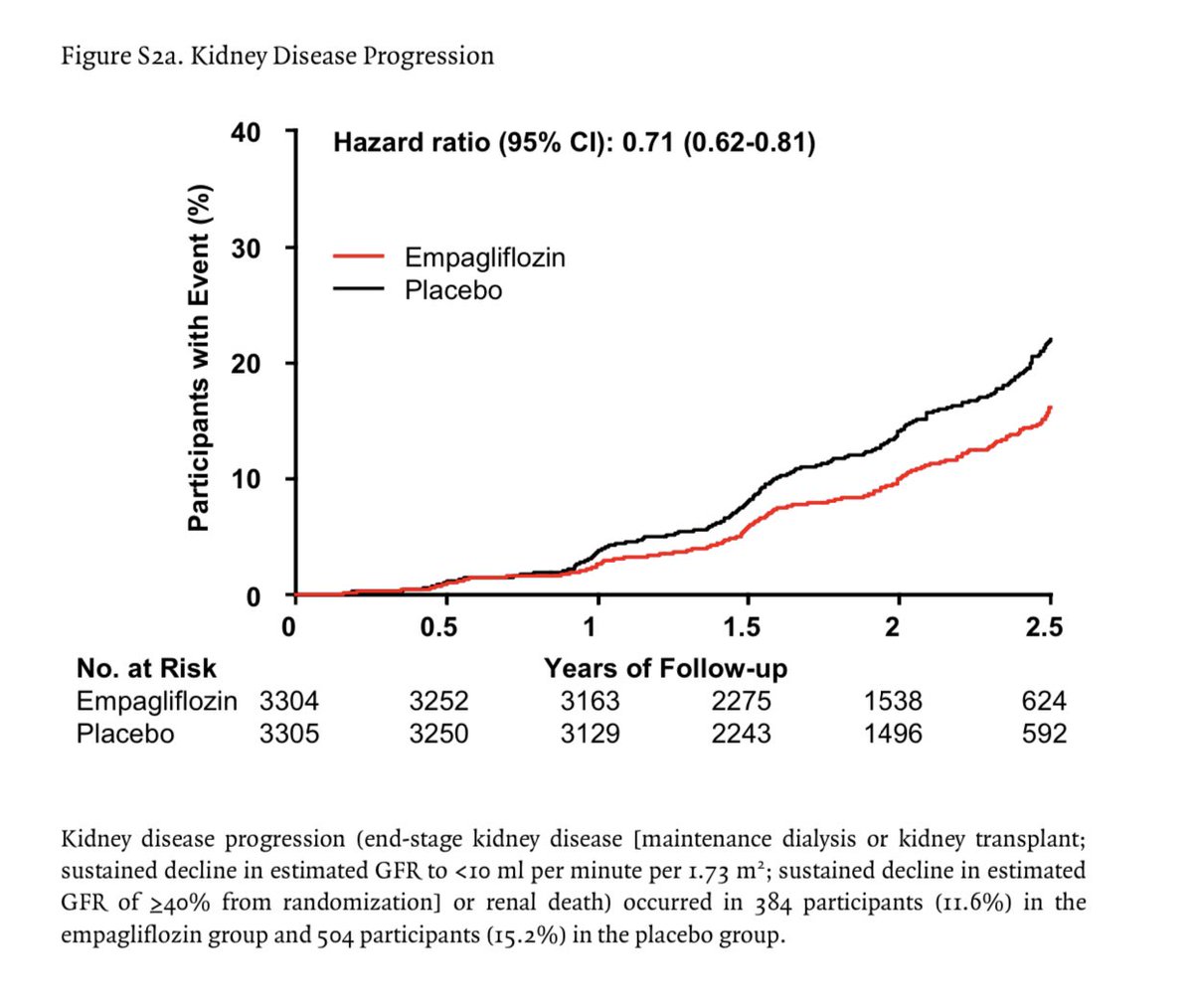
28% lower risk of progression of kidney disease or death from CV causes in Empagliflozin group vs placebo
Progression of kidney disease or death from CV causes occurred in 13.1% in the empa group and in 16.9% in the placebo group (P<0.001)👇🏽

28% lower risk of progression of kidney disease or death from CV causes in Empagliflozin group vs placebo
Progression of kidney disease or death from CV causes occurred in 13.1% in the empa group and in 16.9% in the placebo group (P<0.001)👇🏽


27% lower risk of composite outcome of ESKD or death from cardiovascular causes in the Empagliflozin group vs placebo 

📍Rate of decline in eGFR was slower in the Empa group vs placebo group
Overall, the between-group difference in the eGFR slope from randomization to the final follow-up visit was 0.75 ml/ minute/year, favoring empagliflozin👇🏽


Overall, the between-group difference in the eGFR slope from randomization to the final follow-up visit was 0.75 ml/ minute/year, favoring empagliflozin👇🏽



Rate of decline in eGFR was slower in the empagliflozin group than in the placebo group in all key subgroups, including in the subgroup of patients with a low UACR
Rate of eGFR decline were larger in the subgroups of patients with faster rates of annual decline (i.e., patients with a higher eGFR or a higher baseline urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio)👇🏽 

-Benefits of empagliflozin treatment were consistent among patients with or without diabetes and regardless of the eGFR at randomization
-The proportional risk reduction may have been larger among patients with higher UACR👇🏽

-The proportional risk reduction may have been larger among patients with higher UACR👇🏽


Treatment with empagliflozin was effective regardless of diabetes status and was effective in patients with a broad range of eGFRs, down to approximately 20 ml/minute/1.73 m2
Empagliflozin slowed the rate of long-term eGFR decline among patients with a UACR of less than 300 at baseline (including patients with a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio of <30)
EMPA-KIDNEY trial adds to the existing evidence by showing consistent benefits among 3569 patients (54.0%) without diabetes and, separately, among 2282 patients (34.5%) with an eGFR of less than 30 ml/min/1.73 m2
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh