The dysfunctional little brain!!!
Part II
“regulates ‘rate, range, and force’ of movement”
Dutch anatomist Lodewijk 'Louis' Bolk (1866–1930)
resource.nlm.nih.gov/101434862
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/
Part II
“regulates ‘rate, range, and force’ of movement”
Dutch anatomist Lodewijk 'Louis' Bolk (1866–1930)
resource.nlm.nih.gov/101434862
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/

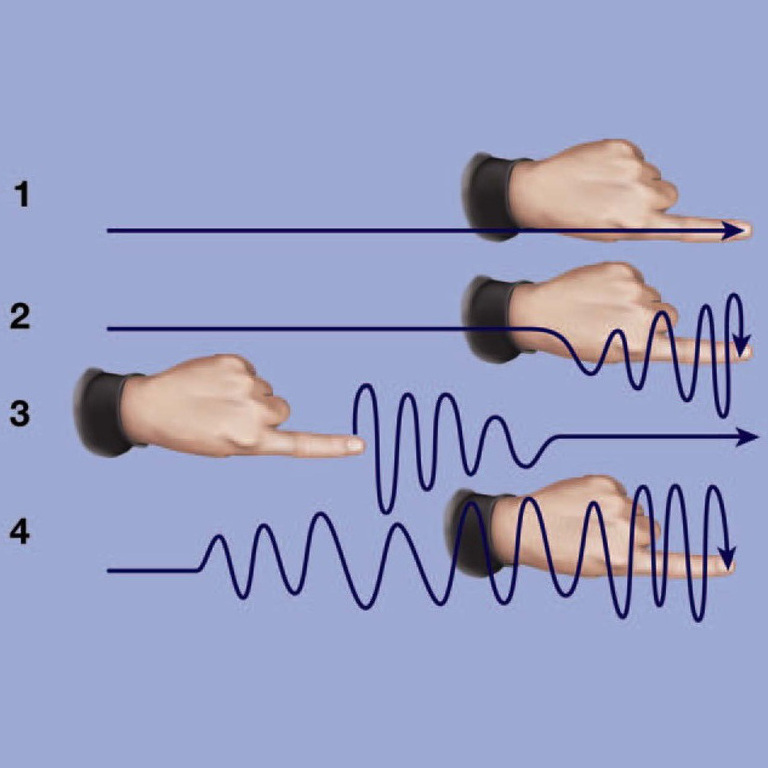
Cerebellar tremor
- intention (active, kinetic, or terminal) tremor
- increase in amplitude approaching to target
normal (1) cerebellar (2) PD (3) ET (4)
doi.org/10.1097/017206… via: JAAPA
2/
- intention (active, kinetic, or terminal) tremor
- increase in amplitude approaching to target
normal (1) cerebellar (2) PD (3) ET (4)
doi.org/10.1097/017206… via: JAAPA
2/
Cerebellar tremor
- intention (active, kinetic, or terminal) tremor
- increase in amplitude approaching to target
- 1st proximal muscles
via: Dr. Prodigious
3/
- intention (active, kinetic, or terminal) tremor
- increase in amplitude approaching to target
- 1st proximal muscles
via: Dr. Prodigious
3/
Cerebellar tremor
- intention (active, kinetic, or terminal) tremor
- increase in amplitude approaching to target
- 1st proximal muscles
via: Dr. Ataullah’s Tutorial
4/
- intention (active, kinetic, or terminal) tremor
- increase in amplitude approaching to target
- 1st proximal muscles
via: Dr. Ataullah’s Tutorial
4/
Cerebellar outflow pathway tremors
- postural tremor of the outstretched limbs, may also occur
- 1st proximal muscles
- when severe, can have myoclonic features
- rubral tremor (cerebellar outflow tremor)
5/
- postural tremor of the outstretched limbs, may also occur
- 1st proximal muscles
- when severe, can have myoclonic features
- rubral tremor (cerebellar outflow tremor)
5/
Cerebellar postural tremor
- postural tremor of the outstretched limbs, may also occur
- 1st proximal muscles
10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.11.016 via: Parkinsonism Relat Disord
6/
- postural tremor of the outstretched limbs, may also occur
- 1st proximal muscles
10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.11.016 via: Parkinsonism Relat Disord
6/
Cerebellar postural tremor
- postural tremor of the outstretched limbs, may also occur
- 1st proximal muscles
10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.04.013 via: Parkinsonism Relat Disord
7/
- postural tremor of the outstretched limbs, may also occur
- 1st proximal muscles
10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.04.013 via: Parkinsonism Relat Disord
7/
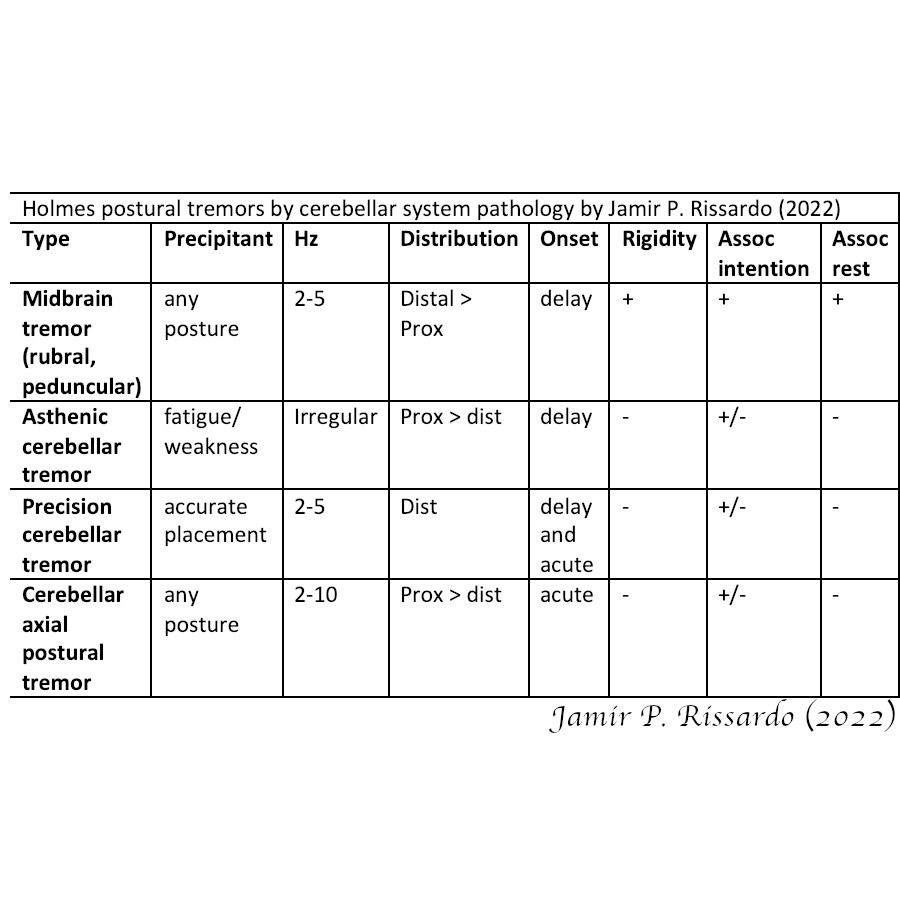
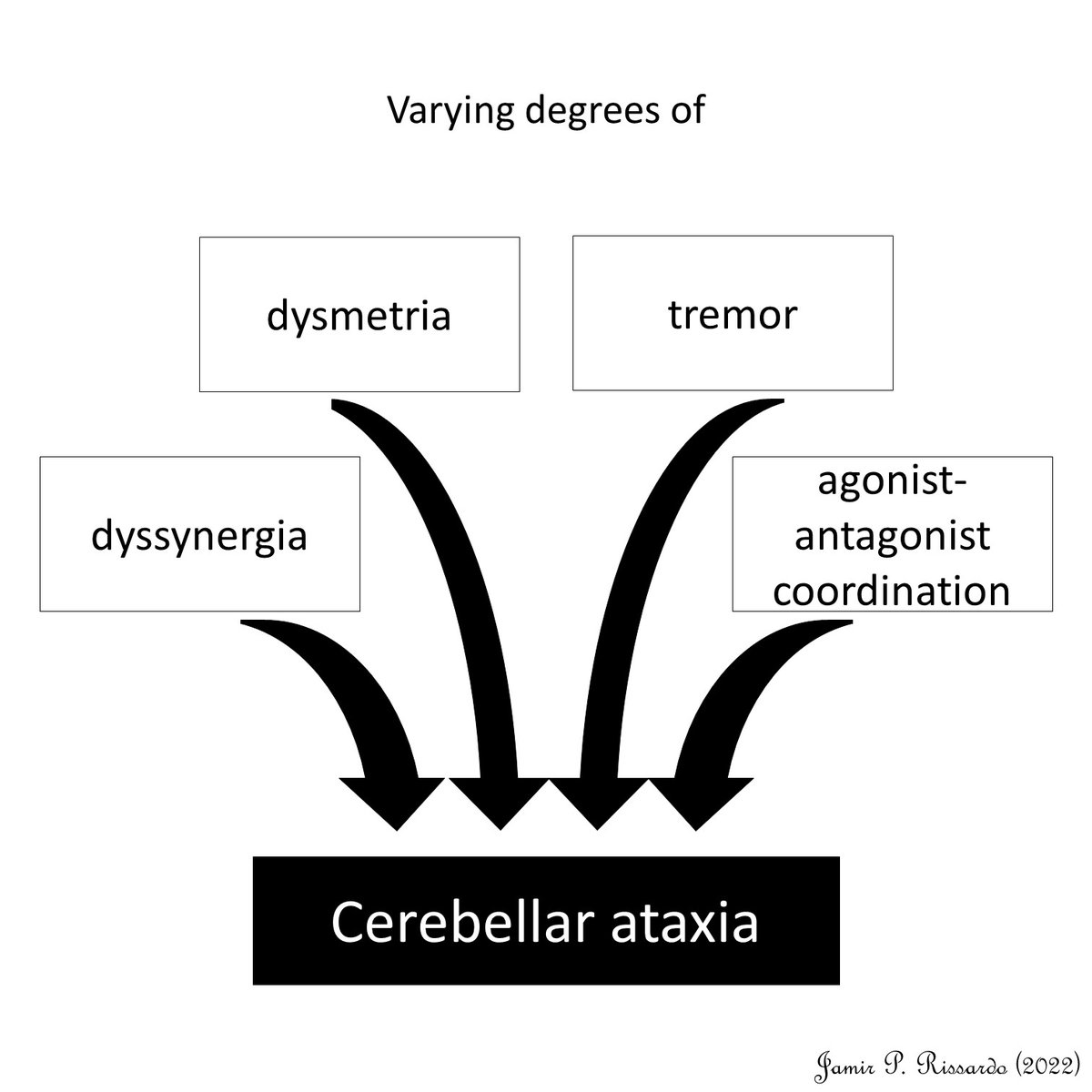
Finally, ataxia
What is cerebellar ataxia?
“varying degrees of dyssynergia, dysmetria, lack of agonist-antagonist coordination, and tremor”
- unspecific
- sensory ataxia ➡️ worse w/ eyes closed
8/
What is cerebellar ataxia?
“varying degrees of dyssynergia, dysmetria, lack of agonist-antagonist coordination, and tremor”
- unspecific
- sensory ataxia ➡️ worse w/ eyes closed
8/
Head titubation
- axial hypotonia
- slow-frequency cerebellar outflow tremor
via: Extensive Medicine
9/
- axial hypotonia
- slow-frequency cerebellar outflow tremor
via: Extensive Medicine
9/
Head titubation
- axial hypotonia
- slow-frequency cerebellar outflow tremor
doi.org/10.1212/WNL.00… via: Neurology
@AlbertoEspay
10/
- axial hypotonia
- slow-frequency cerebellar outflow tremor
doi.org/10.1212/WNL.00… via: Neurology
@AlbertoEspay
10/
Cerebellar ataxic gait
“Wide based, reeling, careening (drunken sailor)”
- inability to walk tandem
- step length varies unpredictably
- turning may bring out a stagger
- acute alcohol intoxication
11/
“Wide based, reeling, careening (drunken sailor)”
- inability to walk tandem
- step length varies unpredictably
- turning may bring out a stagger
- acute alcohol intoxication
https://twitter.com/theneurolander/status/1585828189942996994
11/
Tandem gait paradigm
“dysmetria, hypometria, hypermetria, and inappropriate timing of foot placement”
-correlated w/ symptom severity & quantitative balance & gait parameters
-cerebellar, sensory ataxia, vestibulopathy
via: emrcpian
12/
“dysmetria, hypometria, hypermetria, and inappropriate timing of foot placement”
-correlated w/ symptom severity & quantitative balance & gait parameters
-cerebellar, sensory ataxia, vestibulopathy
via: emrcpian
12/
Cerebellar gait observations
Unilateral lesions
- deviation of head&body toward affected side
- when standing, there is an inclination to fall
- when walking a tendency to deviate, toward the side of the lesion
- decrease of the normal pendular movement of the arm
13/
Unilateral lesions
- deviation of head&body toward affected side
- when standing, there is an inclination to fall
- when walking a tendency to deviate, toward the side of the lesion
- decrease of the normal pendular movement of the arm
13/
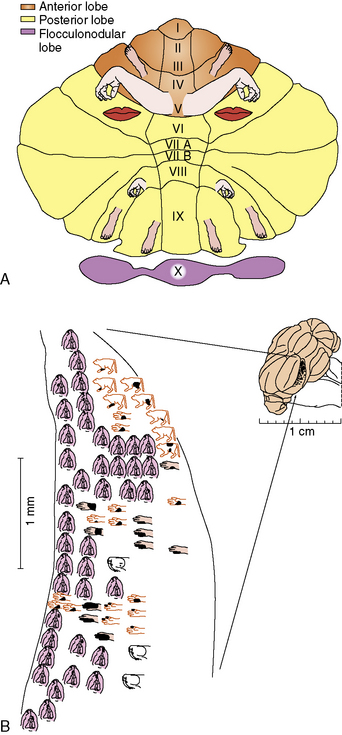
Cerebellar homunculus
vermis lesions
- not able to stand erect and may fall either backward or forward
- gait is staggering, reeling, or lurching in character, without laterality.
neupsykey.com/wp-content/upl…
14/
vermis lesions
- not able to stand erect and may fall either backward or forward
- gait is staggering, reeling, or lurching in character, without laterality.
neupsykey.com/wp-content/upl…
14/
Cerebellar fits
decerebrate rigidity episodes because of brainstem dysfunction due to mass effect from cerebellar lesions
- EEG variable amplitude diffuse asynch slow waves
- noncortical
- misdiagnosis, wrong therapeutic intervention
doi.org/10.1016/j.brai… via: Brain Dev
15/
decerebrate rigidity episodes because of brainstem dysfunction due to mass effect from cerebellar lesions
- EEG variable amplitude diffuse asynch slow waves
- noncortical
- misdiagnosis, wrong therapeutic intervention
doi.org/10.1016/j.brai… via: Brain Dev
15/
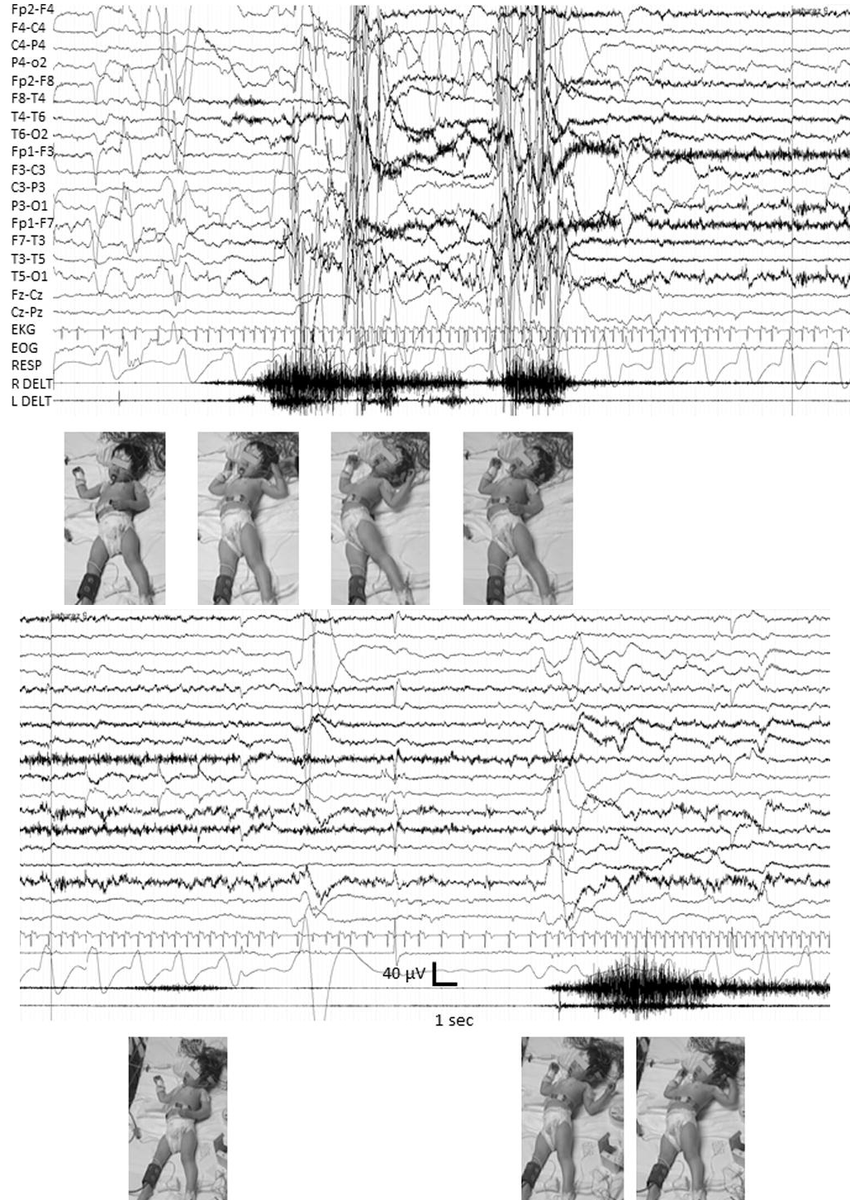
Cerebellar mutism
- complication of posterior fossa surgery, especially in children
- 24% medulloblastoma
- dentate-thalamo-cortical tracts
- neurocognitive outcome is not favorable
posteriorfossa.org
16/
- complication of posterior fossa surgery, especially in children
- 24% medulloblastoma
- dentate-thalamo-cortical tracts
- neurocognitive outcome is not favorable
posteriorfossa.org
16/
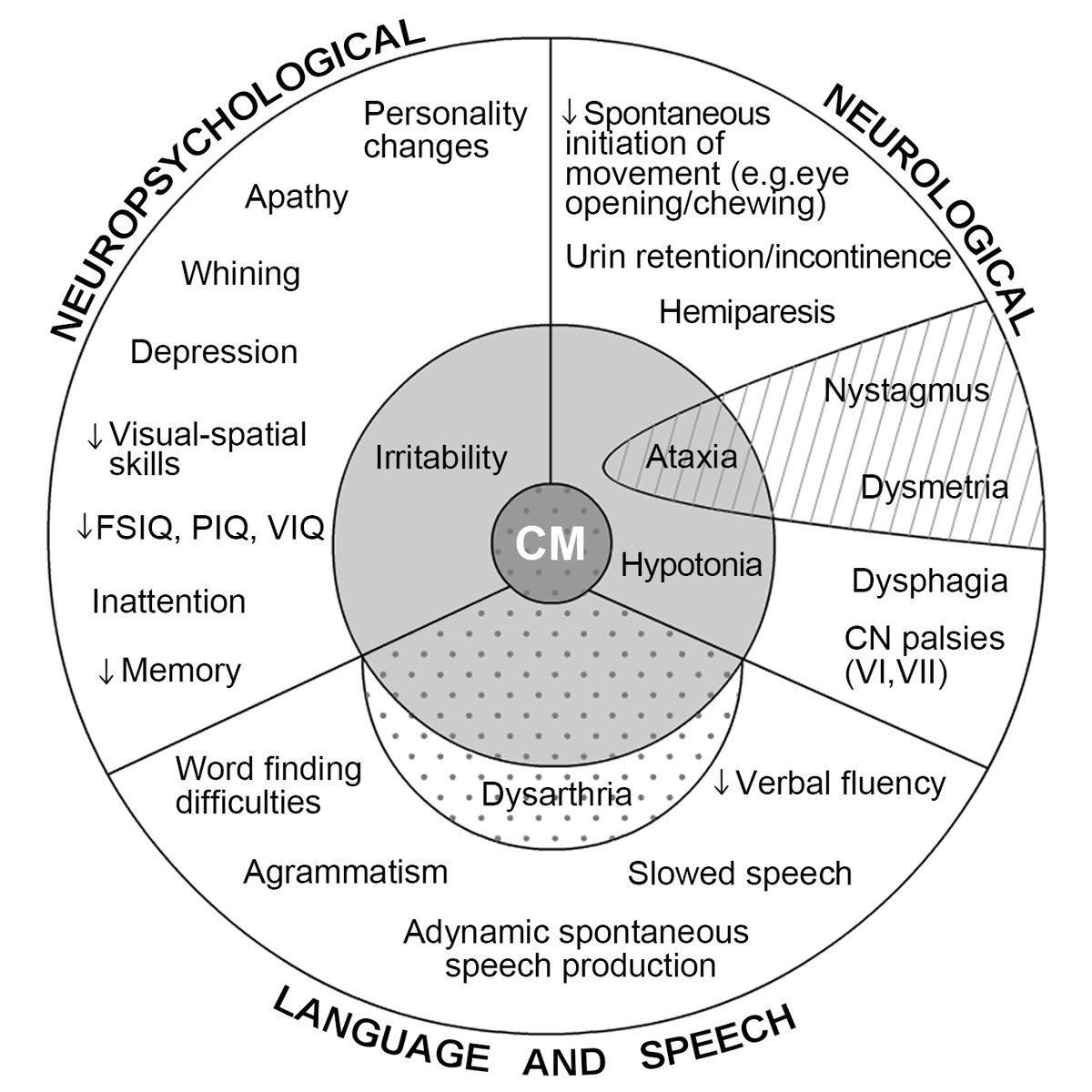
Cerebellar writing
- macrographia, characters become larger
- long writing time
- variable velocity
- deviation&shape pen tip > finger/wrist
doi.org/10.1016/B978-0… via: The Linguistic Cerebellum
17/
- macrographia, characters become larger
- long writing time
- variable velocity
- deviation&shape pen tip > finger/wrist
doi.org/10.1016/B978-0… via: The Linguistic Cerebellum
17/

Cerebellar drift
“drifts mainly outward, either at same level, rising, sinking”
- accentuated by raise&lower arms or tapping wrists
- ipsilateral
3 drifts
cerebellar (out)
pronator (Barre’s sign, ⬇️, pronation)
parietal (contralateral, up&out)
18/
“drifts mainly outward, either at same level, rising, sinking”
- accentuated by raise&lower arms or tapping wrists
- ipsilateral
3 drifts
cerebellar (out)
pronator (Barre’s sign, ⬇️, pronation)
parietal (contralateral, up&out)
18/
Cerebellar drift
“drifts mainly outward, either at same level, rising, sinking”
- accentuated by raise&lower arms or tapping wrists
- ipsilateral
3 drifts
cerebellar (out)
pronator (Barre’s sign, ⬇️, pronation)
parietal (contralateral, up&out)
18/
“drifts mainly outward, either at same level, rising, sinking”
- accentuated by raise&lower arms or tapping wrists
- ipsilateral
3 drifts
cerebellar (out)
pronator (Barre’s sign, ⬇️, pronation)
parietal (contralateral, up&out)
18/
Nystagmus - future thread
- vestibulocerebellar pathways
“often result from involvement of the connections of the cerebellum with other centers rather than actual cerebellar dysfunction”
19/
- vestibulocerebellar pathways
“often result from involvement of the connections of the cerebellum with other centers rather than actual cerebellar dysfunction”
19/
The dysfunctional little brain!!!
Part I
20/
Part I
https://twitter.com/theneurolander/status/1589350801029607424
20/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh