Nystagmus series – Part III
(downbeat nystagmus)
"definers of modern neuro-ophthalmology"
William Fletcher Hoyt and Frank Burton Walsh
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/
(downbeat nystagmus)
"definers of modern neuro-ophthalmology"
William Fletcher Hoyt and Frank Burton Walsh
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/

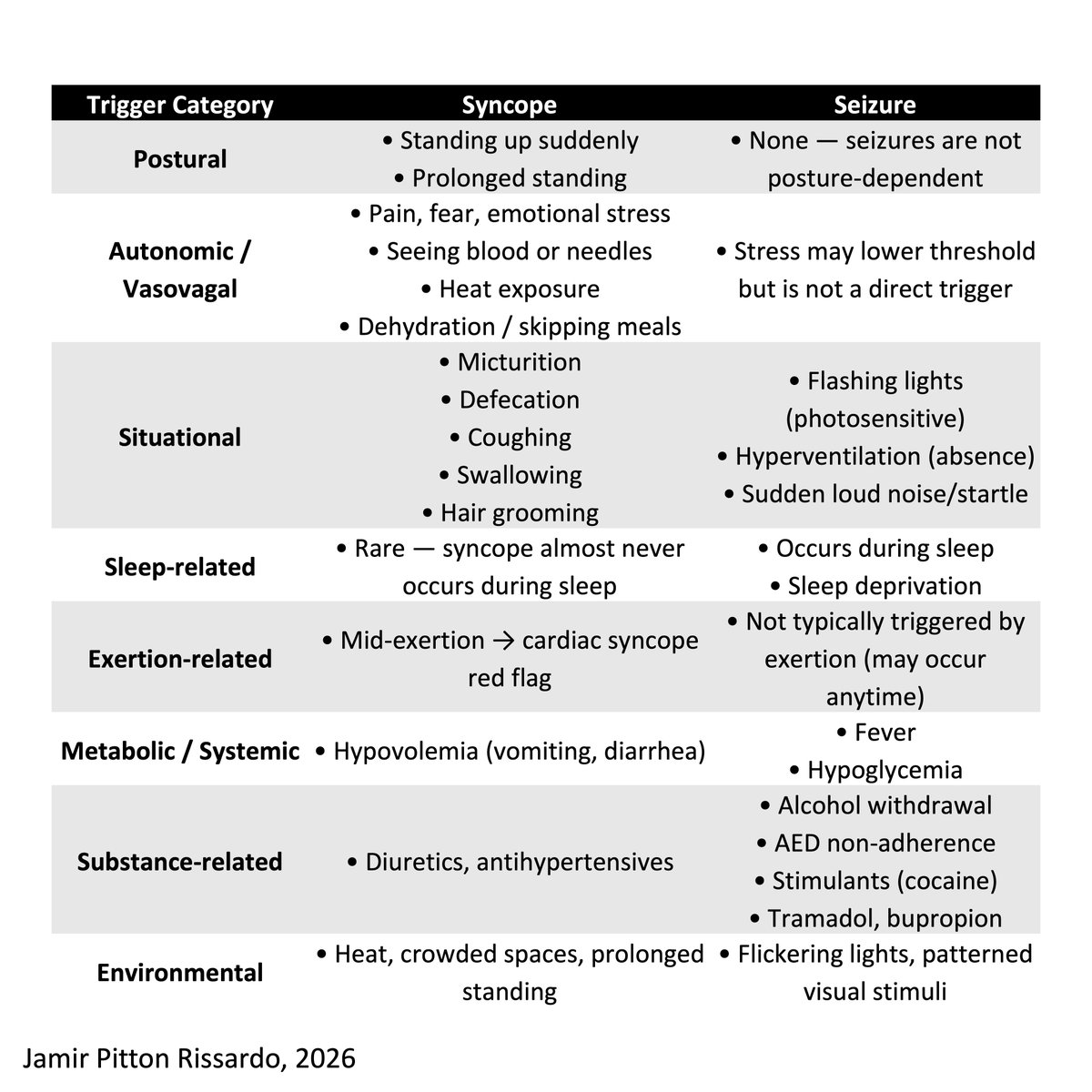
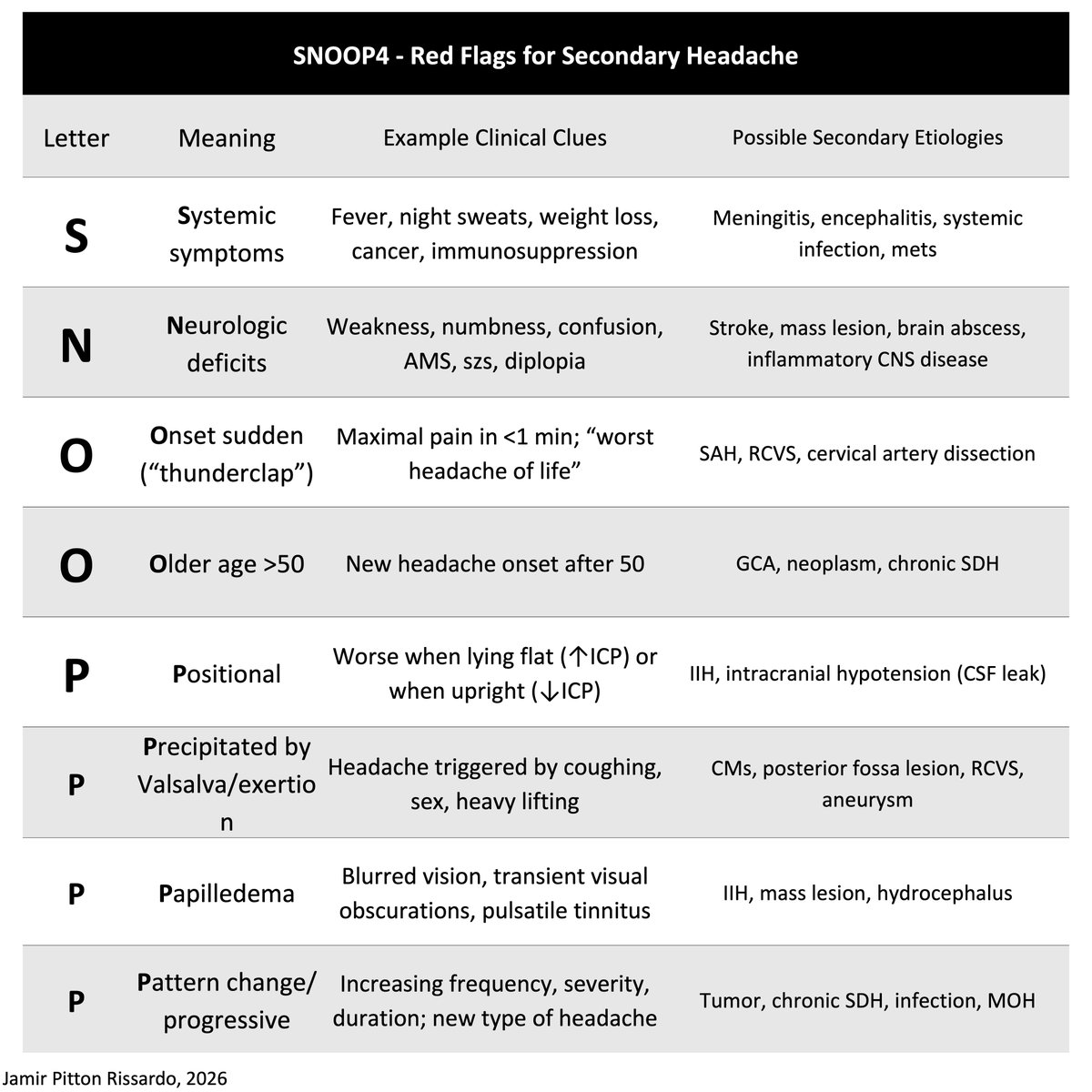
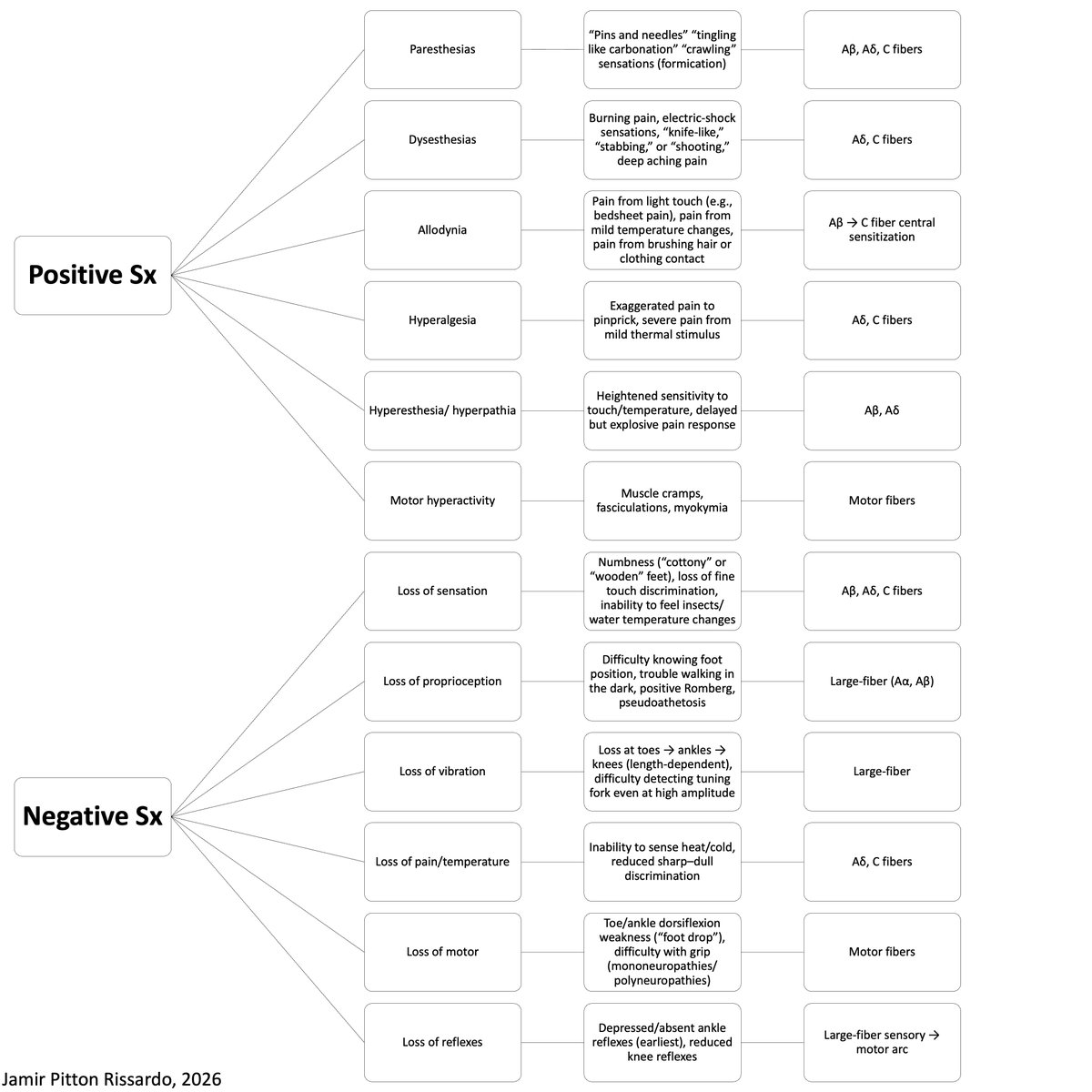
Pathophysiology
“vestibulocerebellum pathway lesion”
- craniocervical junction lesion
- central vestibular imbalance
10.1016/j.jocn.2012.03.017 via: Journal of Clinical Neuroscience
2/
“vestibulocerebellum pathway lesion”
- craniocervical junction lesion
- central vestibular imbalance
10.1016/j.jocn.2012.03.017 via: Journal of Clinical Neuroscience
2/
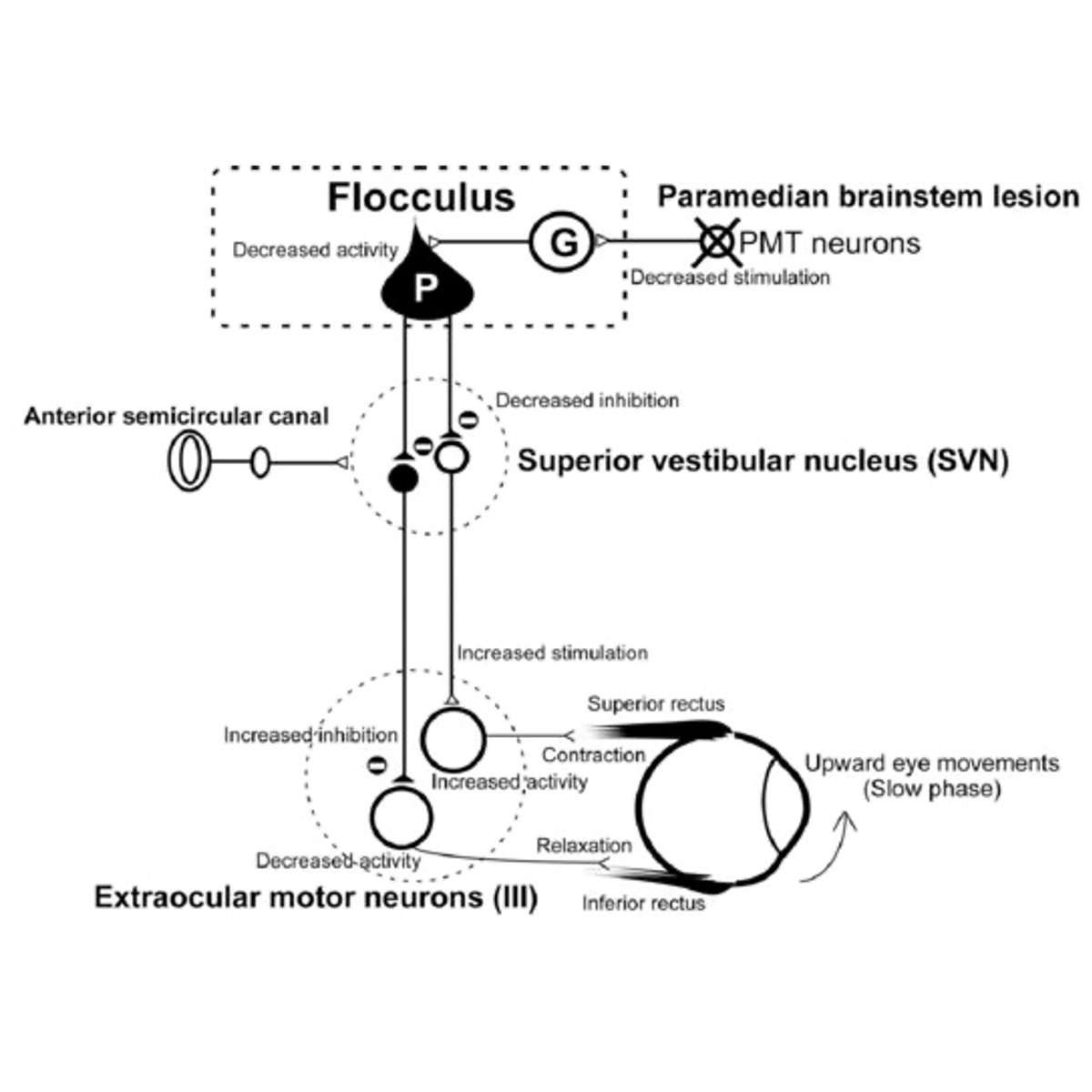
Associated symptoms
cerebellar symptoms
- decomposition of movement
Cerebellum Part I&II
3/
cerebellar symptoms
- decomposition of movement
Cerebellum Part I&II
https://twitter.com/theneurolander/status/1589350801029607424
3/
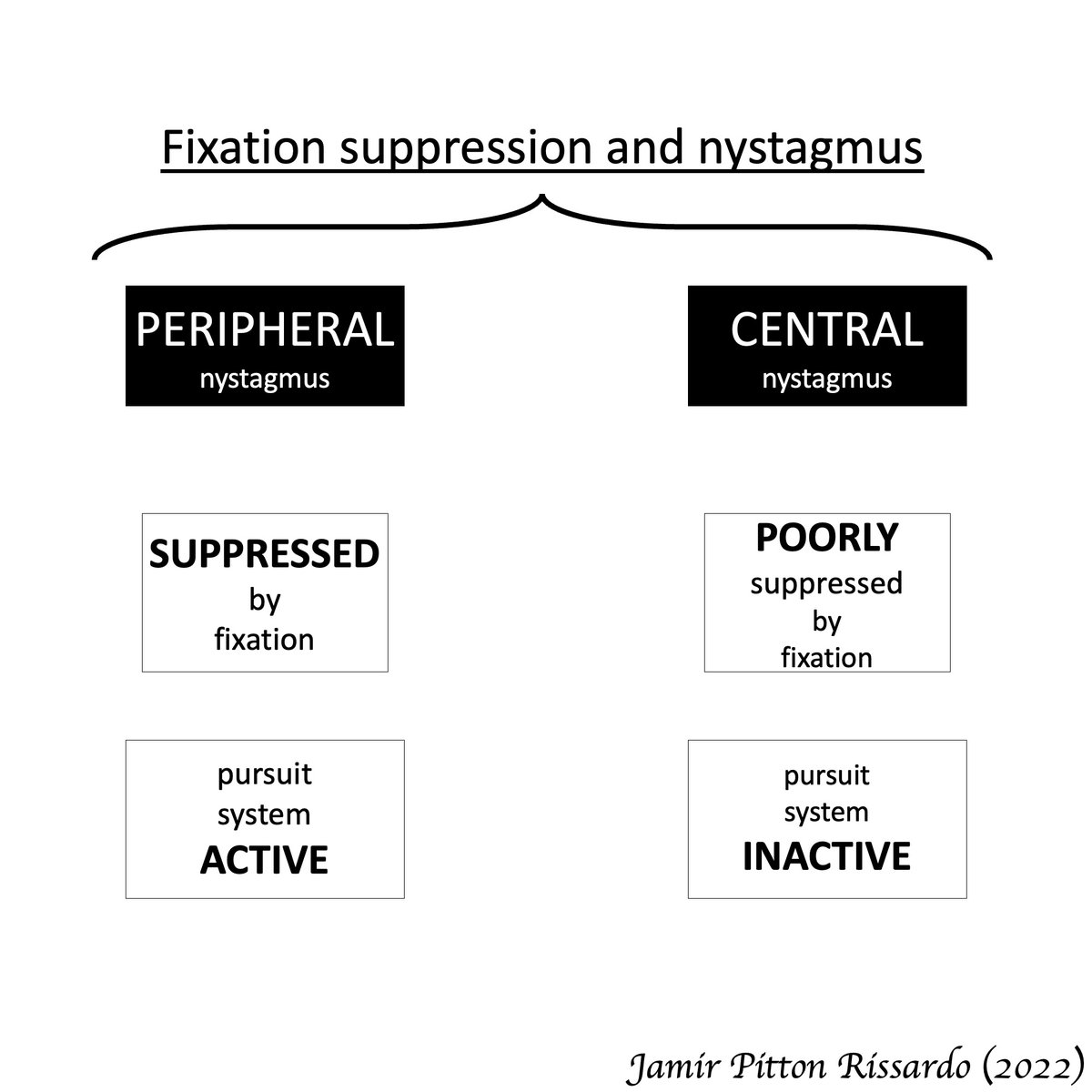
Fixation in central vestibular nystagmus
“poorly suppressed by fixation of a visual target”
- abnormal smooth-pursuit system
4/
“poorly suppressed by fixation of a visual target”
- abnormal smooth-pursuit system
4/
Making downbeat nystagmus more noticeable
Alexander’s law
- looking down and laterally
Bedside maneuvers
- change head position
- vigorous head-shaking
- hyperventilation
- mastoid vibration
5/
Alexander’s law
- looking down and laterally
Bedside maneuvers
- change head position
- vigorous head-shaking
- hyperventilation
- mastoid vibration
https://twitter.com/theneurolander/status/1593278079501303810
5/
Obs
a) often, downbeat nystagmus is associated w/ horizontal gaze-evoked nystagmus
b) slow-phase without specific waveform
c) convergence does not specific change nystagmus features
d) downbeat nystagmus greatest on up gaze; vertical gaze-holding impair
e) rarely disjunctive
6/
a) often, downbeat nystagmus is associated w/ horizontal gaze-evoked nystagmus
b) slow-phase without specific waveform
c) convergence does not specific change nystagmus features
d) downbeat nystagmus greatest on up gaze; vertical gaze-holding impair
e) rarely disjunctive
6/
Downbeat nystagmus - features
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
7/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
7/
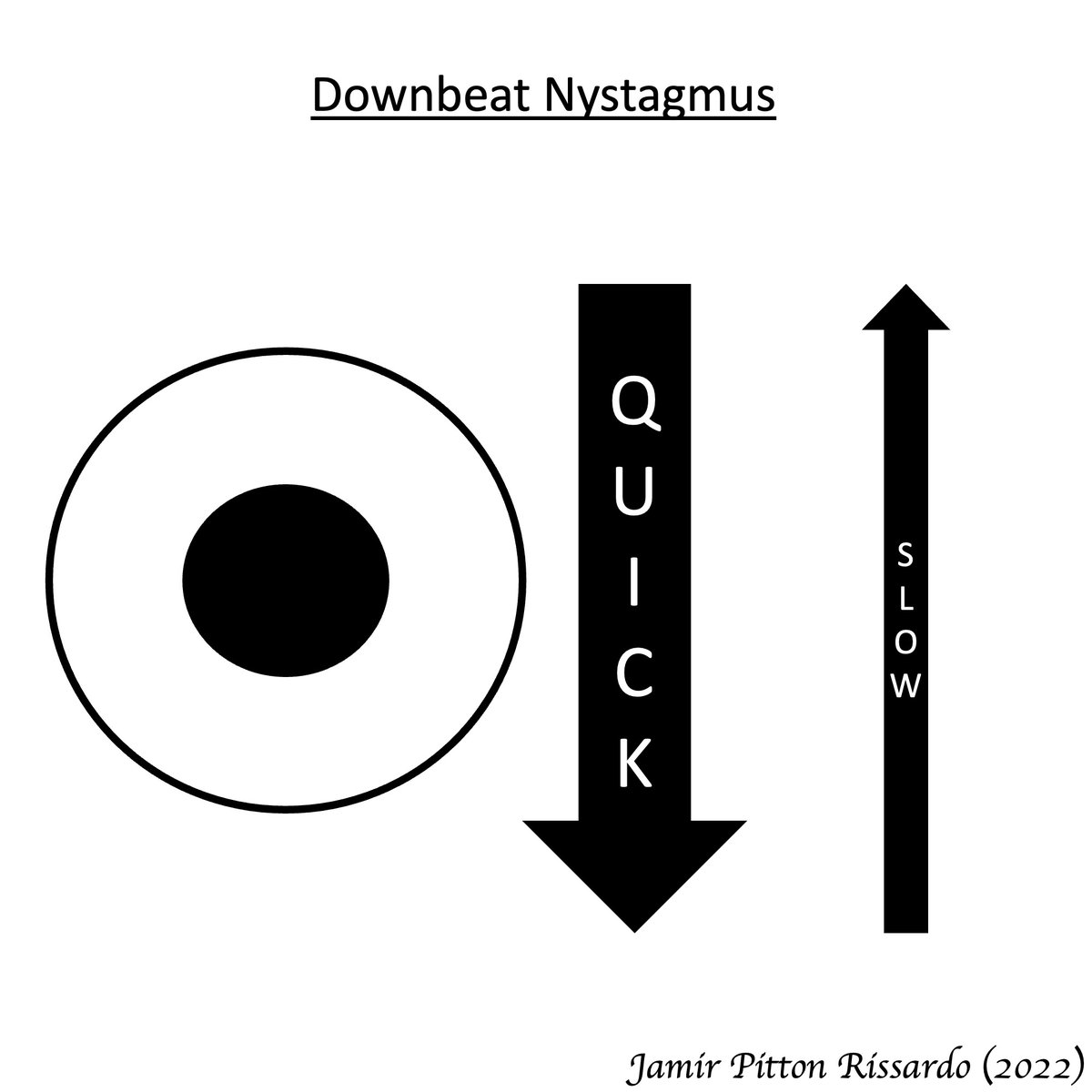
Downbeat nystagmus
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Moran CORE
8/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Moran CORE
8/
Downbeat nystagmus
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Moran CORE
9/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Moran CORE
9/
Downbeat nystagmus
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Moran CORE
10/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Moran CORE
10/
Downbeat nystagmus
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Neuron Bundle
11/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Neuron Bundle
11/
Downbeat nystagmus
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Raed Behbehani
12/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Raed Behbehani
12/
Downbeat nystagmus
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Scott Sanders
13/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Scott Sanders
13/
Downbeat nystagmus
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Neurology Made Interesting
14/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Neurology Made Interesting
14/
Downbeat nystagmus
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Raed Behbehani
15/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Raed Behbehani
15/
Downbeat nystagmus
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Raed Behbehani
16/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Raed Behbehani
16/
Downbeat nystagmus
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Raed Behbehani
17/
i) evoked by looking down and laterally
ii) no suppress by visual fixation
iii) vestibulocerebellar involvement
via: Raed Behbehani
17/
Nystagmus general description
"Nystagmus – Moving eyes!!!"
"Nystagmus – Moving eyes!!!"
https://twitter.com/theneurolander/status/1592278924826140672
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh