Nystagmus series – Part VI
(periodic alternating nystagmus, PAN)
“Nystagmus processor for EEG machines”
Italian-American neurologist Joseph Toglia (1927 – 2018)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials @TempleUniv
1/
(periodic alternating nystagmus, PAN)
“Nystagmus processor for EEG machines”
Italian-American neurologist Joseph Toglia (1927 – 2018)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials @TempleUniv
1/

Definition
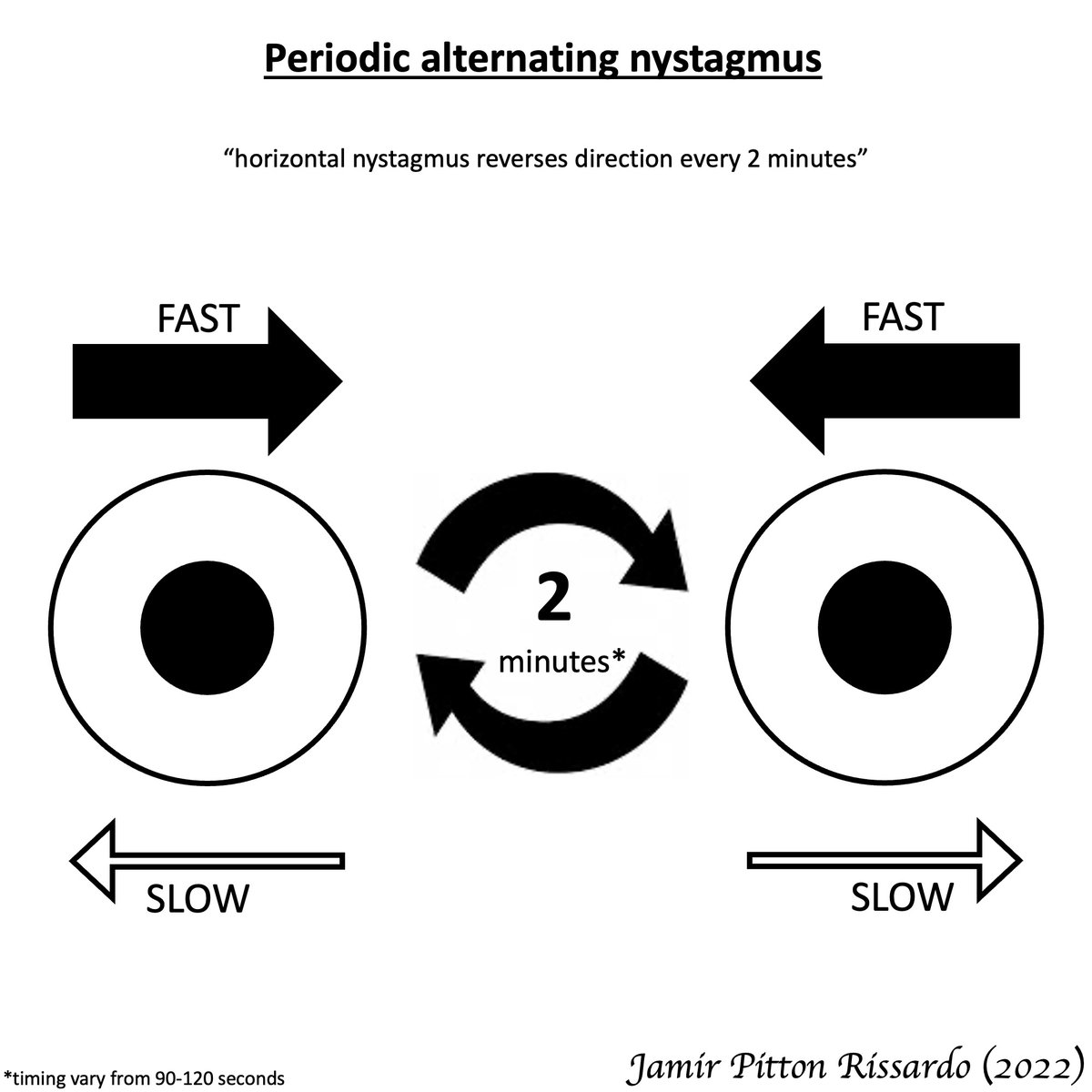
“horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes”
During transition period
-upbeating, downbeating, square-wave jerks can occur
- acquired form is rare, but it is the best understood and the first to have effective treatment
2/
“horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes”
During transition period
-upbeating, downbeating, square-wave jerks can occur
- acquired form is rare, but it is the best understood and the first to have effective treatment
2/
Pathophysiology
“lesion in cerebellum nodulus & uvula”
nodulus & uvula
- responsible for velocity-storage mechanism
- inhibitory control on vestibular rotation using GABA (baclofen-responsive)
vestibular system
- repair mechanism
- reverse direction of nystagmus
3/
“lesion in cerebellum nodulus & uvula”
nodulus & uvula
- responsible for velocity-storage mechanism
- inhibitory control on vestibular rotation using GABA (baclofen-responsive)
vestibular system
- repair mechanism
- reverse direction of nystagmus
3/

Fixation in central vestibular nystagmus
“poorly suppressed by fixation of a visual target”
- abnormal smooth-pursuit system
4/
“poorly suppressed by fixation of a visual target”
- abnormal smooth-pursuit system
https://twitter.com/theneurolander/status/1593997983409995776
4/
Associated symptoms
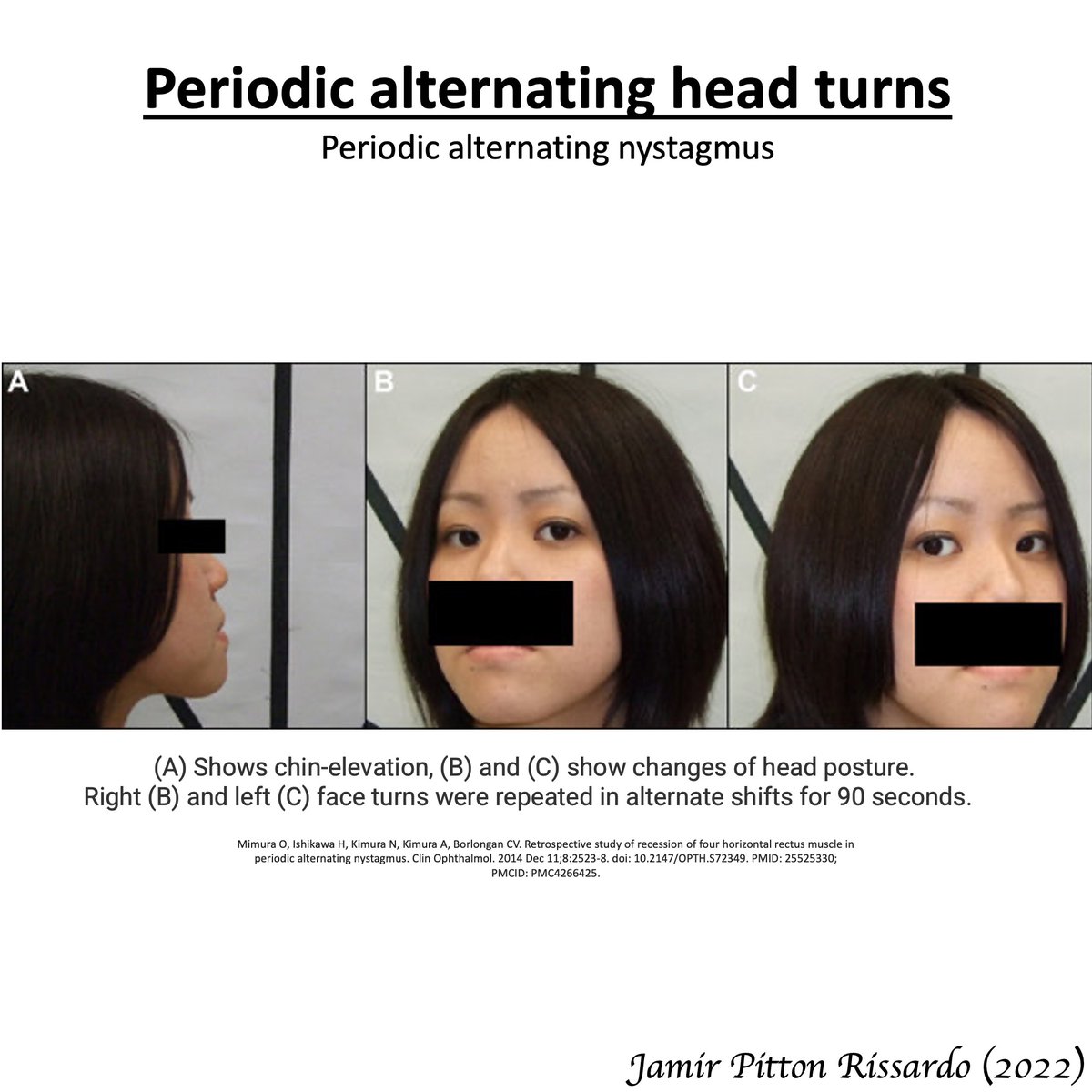
Periodic alternating head turns
- minimizing nystagmus by Alexander’s law
- head turn in the direction of the quick-phase
5/
Periodic alternating head turns
- minimizing nystagmus by Alexander’s law
- head turn in the direction of the quick-phase
5/
Management
Acquire form
- baclofen
Congenital form
- horizontal recti resection
6/
Acquire form
- baclofen
Congenital form
- horizontal recti resection
6/
Obs
a) vestibular stimuli (head rotations) can transiently change nystagmus
b) periodic alternating gaze deviation, if brainstem is affected
c) persist during sleep remaining horizontal in vertical gaze
d) see for 4 minutes every central position horizontal nystagmus
7/
a) vestibular stimuli (head rotations) can transiently change nystagmus
b) periodic alternating gaze deviation, if brainstem is affected
c) persist during sleep remaining horizontal in vertical gaze
d) see for 4 minutes every central position horizontal nystagmus
7/
Differ
a)acquired vs congenital: congenital has congenital features & irregular time
b)ping-pong gaze: ocular deviations reverse after seconds; bihemispheric lesion
c)alternating windmill nystagmus: horizontal&vertical planes
d)paroxysm mixed torsional-horizontal-vertical
8/
a)acquired vs congenital: congenital has congenital features & irregular time
b)ping-pong gaze: ocular deviations reverse after seconds; bihemispheric lesion
c)alternating windmill nystagmus: horizontal&vertical planes
d)paroxysm mixed torsional-horizontal-vertical
8/
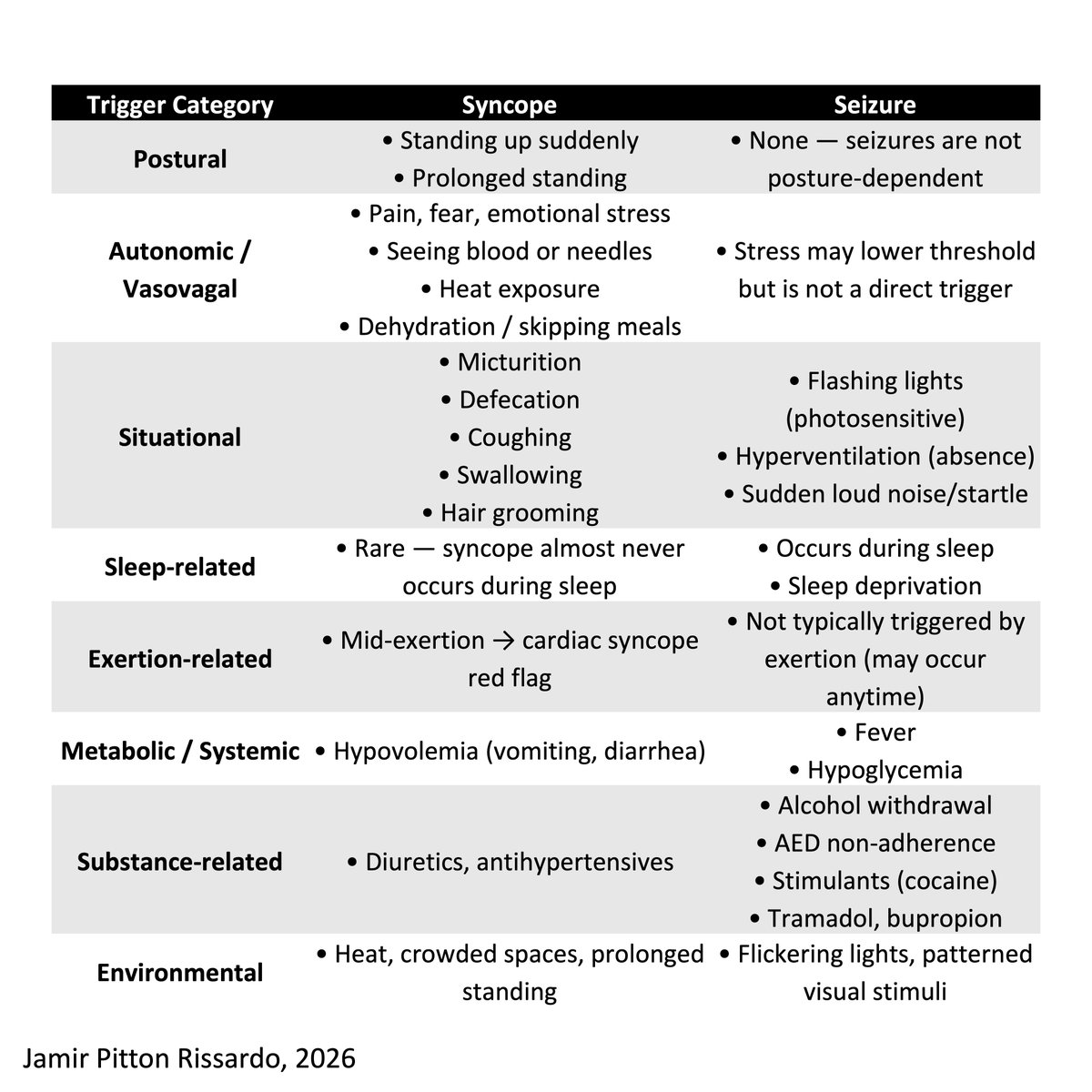
Acquired periodic alternating nystagmus – features
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
9/
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
9/
Acquired periodic alternating nystagmus
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
dizziness-and-balance.com via: Timothy C. Hain
10/
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
dizziness-and-balance.com via: Timothy C. Hain
10/
Acquired periodic alternating nystagmus
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: moran CORE
11/
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: moran CORE
11/
Acquired periodic alternating nystagmus
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: Raed Behbehani
12/
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: Raed Behbehani
12/
Acquired periodic alternating nystagmus
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: Raed Behbehani
13/
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: Raed Behbehani
13/
Acquired periodic alternating nystagmus
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: lmkaud
14/
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: lmkaud
14/
Acquired periodic alternating nystagmus
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: Dr.Aishwarya Anand
15/
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: Dr.Aishwarya Anand
15/
Acquired periodic alternating nystagmus
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: Doc Callan
16/
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: Doc Callan
16/
Acquired periodic alternating nystagmus
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: Alain Thiry
17/
i) horizontal nystagmus reverses direction every 2 minutes
ii) transition phase ⬇️⬆️🔲
iii) no suppress by visual fixation
via: Alain Thiry
17/
Differ
acquired periodic alternating nystagmus vs ping-pong gaze
ping-pong gaze
- ocular deviations reverse after few seconds
- large bihemispheric lesion
- unconscious patients
via: Jama Network
18/
acquired periodic alternating nystagmus vs ping-pong gaze
ping-pong gaze
- ocular deviations reverse after few seconds
- large bihemispheric lesion
- unconscious patients
via: Jama Network
18/
Differ
acquired periodic alternating nystagmus vs ping-pong gaze
ping-pong gaze
- ocular deviations reverse after few seconds
- large bihemispheric lesion
- unconscious patients
via: NEJM
19/
acquired periodic alternating nystagmus vs ping-pong gaze
ping-pong gaze
- ocular deviations reverse after few seconds
- large bihemispheric lesion
- unconscious patients
via: NEJM
19/
Differ
acquired periodic alternating nystagmus vs alternating windmill nystagmus
alternating windmill nystagmus
- horizontal & vertical planes oscillations
- blind patients (most freq)
DOI: doi.org/10.1212/WNL.00… via: Neurology
20/
acquired periodic alternating nystagmus vs alternating windmill nystagmus
alternating windmill nystagmus
- horizontal & vertical planes oscillations
- blind patients (most freq)
DOI: doi.org/10.1212/WNL.00… via: Neurology
20/
Nystagmus general description
"Nystagmus – Moving eyes!!!"
21/
"Nystagmus – Moving eyes!!!"
https://twitter.com/theneurolander/status/1592278924826140672
21/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh