Some people have been wondering why Russians have concentrated several brigades near a tiny town called Vuhledar, which approximately occupies only 5 square kilometers, and what makes Russians so obsessed with the idea to take it? 

To understand that, we need to look at the Russian military doctrine. Railroads are a core of Russian logistics and essential to supply entire armies. It allows Russia to move large numbers of supplies and reinforcements within a relatively short period. 

After the destruction of the railroad section in the Crimean bridge, Russians are facing significant logistics issues and frantically looking at possible solutions to reinforce their Southern group.
The railroad pathway highlighted in red color would allow the Russian army to establish an important logistics route between Russia-Luhansk-Donetsk-Mariupol and possibly Crimea. 

The proximity of the railroad to Vuhledar, Novomykhailivka, and Mar'inka makes this endeavor difficult, as the Ukrainian army has fire control over the railroad, making it impossible for Russians to use. I marked that small railroad section with the red line 

This brings us back to the Vuhledar question. Despite the small size, Vuhledar is located at an important strategic point that allows the Ukrainian army to keep under control both the railway and railway stations, more importantly – Volnovakha 

To get closer to the Vuhledar, the enemy made a series of attempts to take over Pavlivka in October and November, which resulted in the total loss of about 2000 people as KIA, MIA, POWs, or seriously crippled on the Russian side.
While the enemy was able to push out Ukrainian troops from Pavlivka, they couldn’t establish control over the settlement, as it’s located much lower than Vuhledar and gives Ukrainian troops great fire control over the area. 

After suffering devastating losses during the Pavlivka offense, the enemy replenishes its forces with manpower and vehicles. It seems like the enemy is planning to utilize additional battalions which just underwent training and rotation.
The same units involved in Pavlivka will be used in Vuhledar – 40th Naval Infantry Brigade, 155th Naval Infantry Brigade, special task unit “Kaskad” and various volunteer battalions such as “Tigr” 
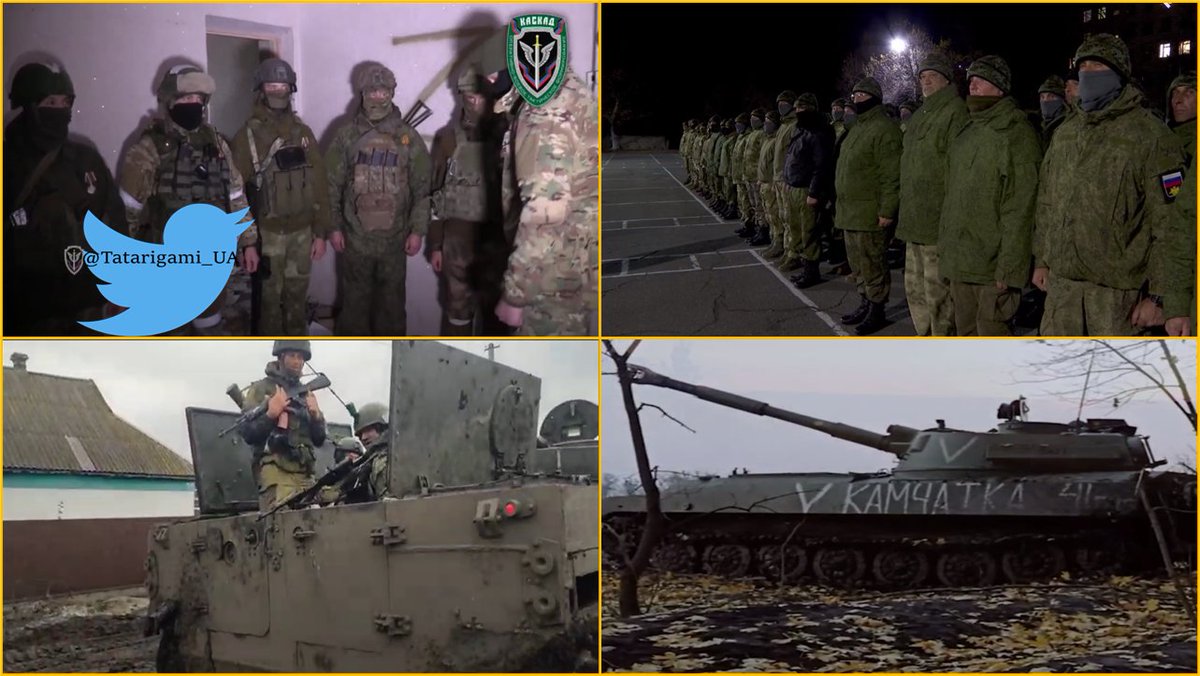

At this moment, the enemy focuses on Vuhledar's defense suppression. To achieve that, the enemy uses regular and rocket artillery, direct and indirect tank fire, and occasional unguided rocket barrages from helicopters and jets. 

The morale remains low, and the regular army units perform fake offensives - they retreat under minimal fire and exaggerate combat reports to justify their retreats. To avoid stalling, the Russian command utilizes brutal tactics:
They use units consisting of BARS(Active Combat Military Reserve), volunteer battalions, and freshly mobilized, supported by armored units to perform assaults and to exhaust available Ukrainian material and human resources 

Another offensive operation will result in much worse losses than during the Pavlivka offense, but the threat to Vuhledar remains real and needs to be taken seriously - the Kremlin wants this task to be done, no matter the cost.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh