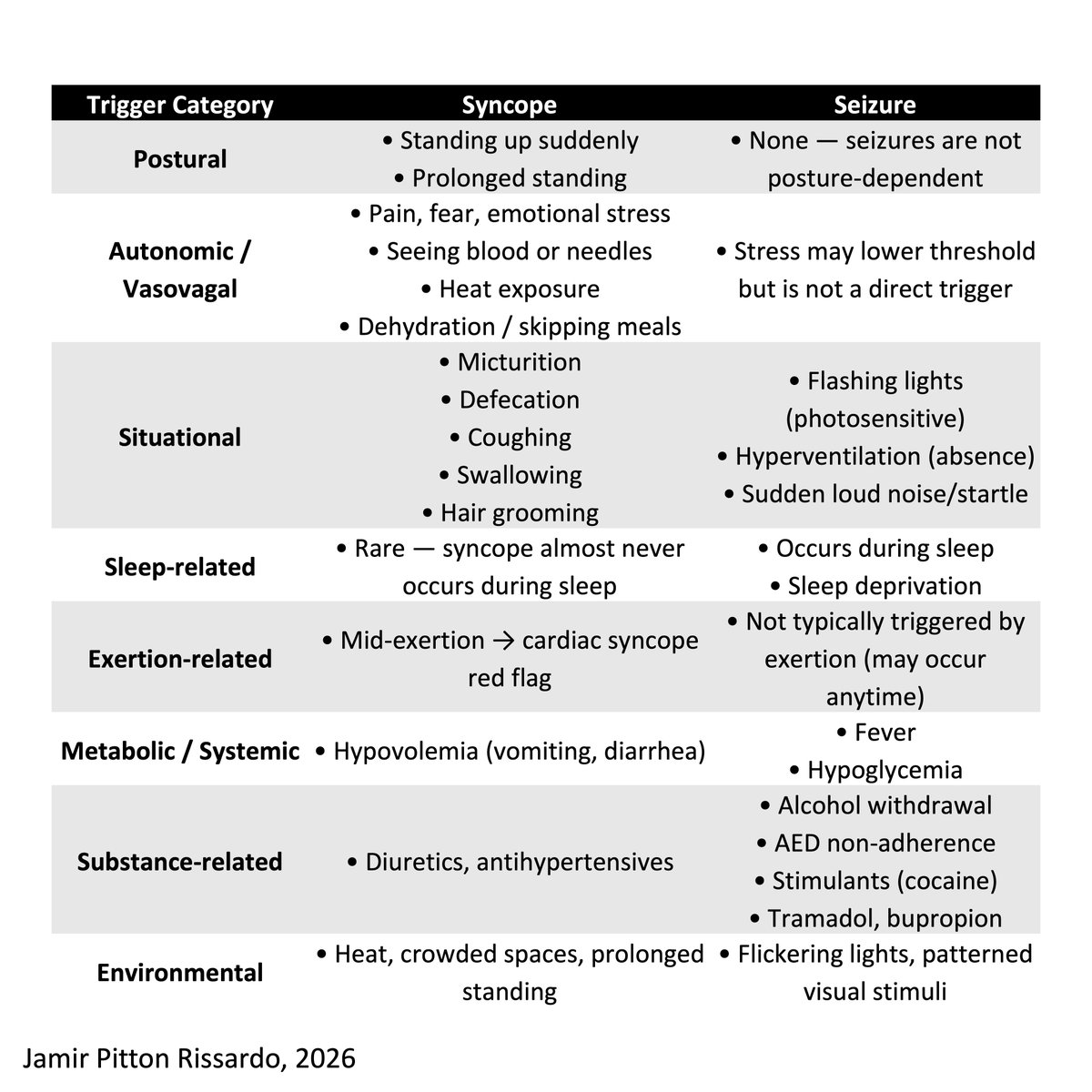
Dermatome!!!
“Dermatomal man, early twentieth century”
University of Edinburgh Image Collections
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/
“Dermatomal man, early twentieth century”
University of Edinburgh Image Collections
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/

History
“dermatomal charts are primarily derived from 3 sources”
Head & Campbell
-herpetic eruptions
Foerster
-rhizotomy in chronic pain
-dermatomal overlap
Keegan & Garrett
-various diseases
-exam & surgical correlate: 53%
American neurosurgeon John Jay Keegan(1889-1978)
2/
“dermatomal charts are primarily derived from 3 sources”
Head & Campbell
-herpetic eruptions
Foerster
-rhizotomy in chronic pain
-dermatomal overlap
Keegan & Garrett
-various diseases
-exam & surgical correlate: 53%
American neurosurgeon John Jay Keegan(1889-1978)
2/

Definition
“area of skin in which sensory nerve derive from a single spinal nerve root”
- 31 spine segments
8C + 12T + 5L + 5S + 1 coccygeal
- dermatomes exist for each spinal nerve, except C1
3/
“area of skin in which sensory nerve derive from a single spinal nerve root”
- 31 spine segments
8C + 12T + 5L + 5S + 1 coccygeal
- dermatomes exist for each spinal nerve, except C1
3/
Clinical significance
“localization”
4/
“localization”
4/
C2 At least one cm lateral to the occipital protuberance at the base of the skull. Alternately, it can be located at least 3 cm behind the ear.
C3 In the supraclavicular fossa, at the midclavicular line.
C4 Over the acromioclavicular joint.
5/
C3 In the supraclavicular fossa, at the midclavicular line.
C4 Over the acromioclavicular joint.
5/

C5 lateral (radial) side of the antecubital fossa just proximal to the elbow (image below)
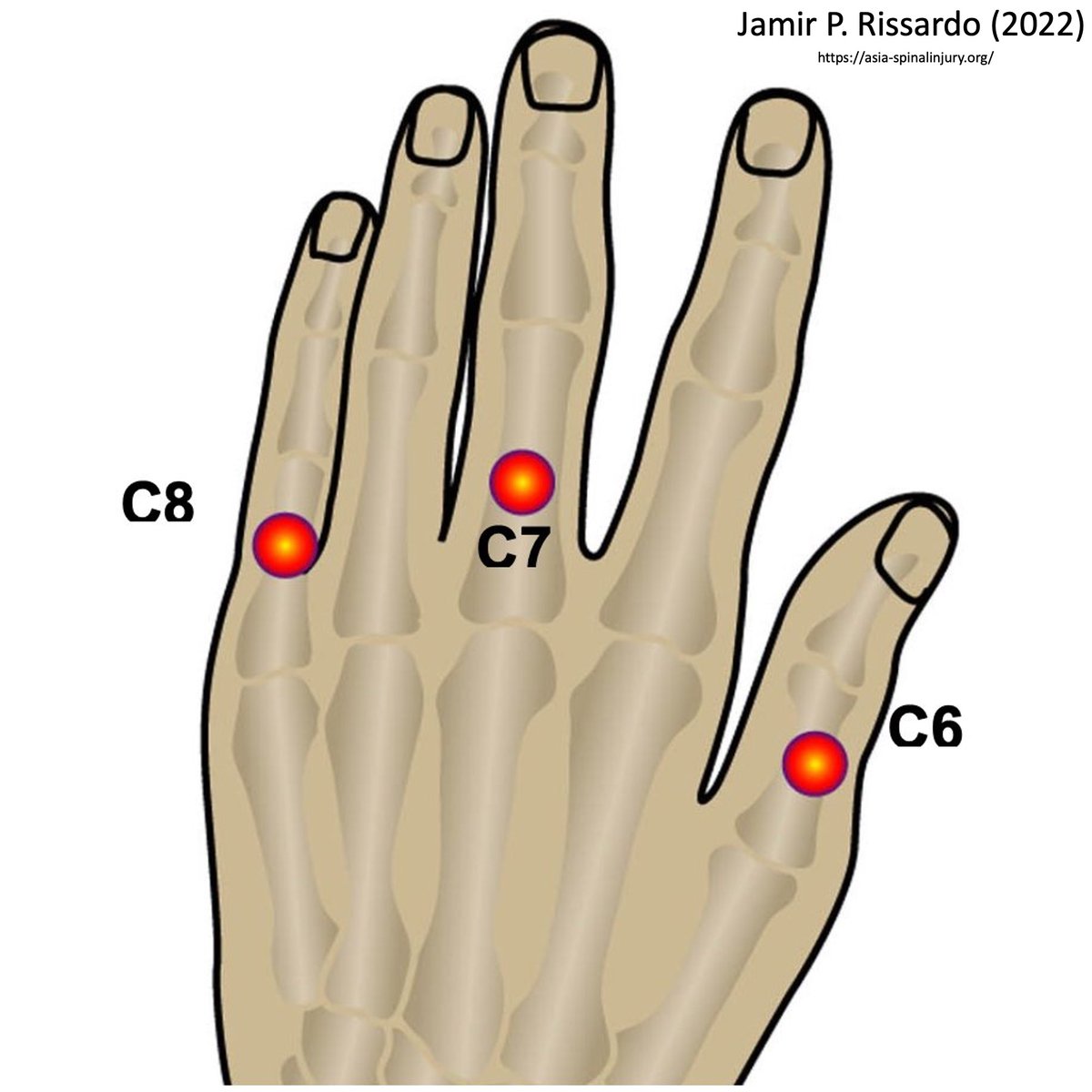
C6 dorsal surface of the proximal phalanx of the thumb
C7 dorsal surface of the proximal phalanx of the middle finger
C8 dorsal surface of the proximal phalanx of the little finger
6/
C6 dorsal surface of the proximal phalanx of the thumb
C7 dorsal surface of the proximal phalanx of the middle finger
C8 dorsal surface of the proximal phalanx of the little finger
6/
T1 On the medial (ulnar) side of the antecubital fossa, just proximal to the medial epicondyle of the humerus.
T2 At the apex of the axilla.
7/
T2 At the apex of the axilla.
7/

T3 Midclavicular line and the third intercostal space, found by palpating the anterior chest to locate the third rib and the corresponding third intercostal space below it.
T4 At the midclavicular line and the fourth intercostal space, located at the level of the nipples.
8/
T4 At the midclavicular line and the fourth intercostal space, located at the level of the nipples.
8/

T5 At the midclavicular line and the fifth intercostal space, located midway between the level of the nipples and the level of the xiphisternum.
T6 At the midclavicular line, located at the level of the xiphisternum.
9/
T6 At the midclavicular line, located at the level of the xiphisternum.
9/

T7 At the midclavicular line, one quarter the distance between the level of the xiphisternum and the level of the umbilicus.
T8 At the midclavicular line, one half the distance between the level of the xiphisternum and the level of the umbilicus.
10/
T8 At the midclavicular line, one half the distance between the level of the xiphisternum and the level of the umbilicus.
10/

T9 Midclavicular line, three quarters of the distance between the level of xiphisternum and level of the umbilicus.
T10 Midclavicular line, located at the level of the umbilicus.
T11 Midclavicular line, midway between the level of the umbilicus and the inguinal ligament.
11/
T10 Midclavicular line, located at the level of the umbilicus.
T11 Midclavicular line, midway between the level of the umbilicus and the inguinal ligament.
11/

L1 Midway between the key sensory points for T12 and L2.
L2 On the anterior-medial thigh, at the midpoint drawn on an imaginary line connecting the midpoint of the inguinal ligament and the medial femoral condyle.
L3 At the medial femoral condyle above the knee.
13/
L2 On the anterior-medial thigh, at the midpoint drawn on an imaginary line connecting the midpoint of the inguinal ligament and the medial femoral condyle.
L3 At the medial femoral condyle above the knee.
13/

L4 Over the medial malleolus.
L5 On the dorsum of the foot at the third metatarsal phalangeal joint.
14/
L5 On the dorsum of the foot at the third metatarsal phalangeal joint.
14/

S3 Over the ischial tuberosity or infragluteal fold (depending on the patient their skin can move up, down or laterally over the ischii).
S4/5 In the perianal area, less than one cm lateral to the mucocutaneous junction.
16/
S4/5 In the perianal area, less than one cm lateral to the mucocutaneous junction.
16/

Mnemonics
4 Rule - 4 of all Segments supplies Areas with 4 words:
C4 - Neck ‘Lace’
T4 - Boob (Nipples)
L4 - Knee
S4 - Anus (Anus is actually S5 but the perianal area is S4)
17/
4 Rule - 4 of all Segments supplies Areas with 4 words:
C4 - Neck ‘Lace’
T4 - Boob (Nipples)
L4 - Knee
S4 - Anus (Anus is actually S5 but the perianal area is S4)
17/
Thoracic
“The entire area supplied by these roots make the letter T. The limbs of T are the topmost, so obviously is supplied by T1”
T4 - Boob (Nipple)
T10 - Belly ButTEN (Umbilicus)
21/
“The entire area supplied by these roots make the letter T. The limbs of T are the topmost, so obviously is supplied by T1”
T4 - Boob (Nipple)
T10 - Belly ButTEN (Umbilicus)
21/

Lumbar
Supplies the Legs and Loin
L1- 1nguinaL Area (Inguinal Area Is L1)
L4- Knee
The Great toe is supplied by L4. (Remember The Great Fire(4) of London)
L5- Middle part of the supply of Sole of the foot is somewhat triangular
Like an inverted V. Roman for 5.
22/
Supplies the Legs and Loin
L1- 1nguinaL Area (Inguinal Area Is L1)
L4- Knee
The Great toe is supplied by L4. (Remember The Great Fire(4) of London)
L5- Middle part of the supply of Sole of the foot is somewhat triangular
Like an inverted V. Roman for 5.
22/

L5 vs S1
L5
Large toe & Lateral Lower Leg
S1
Smal toe & Sole
23/
L5
Large toe & Lateral Lower Leg
S1
Smal toe & Sole
23/
NeuroTeach - Content
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh