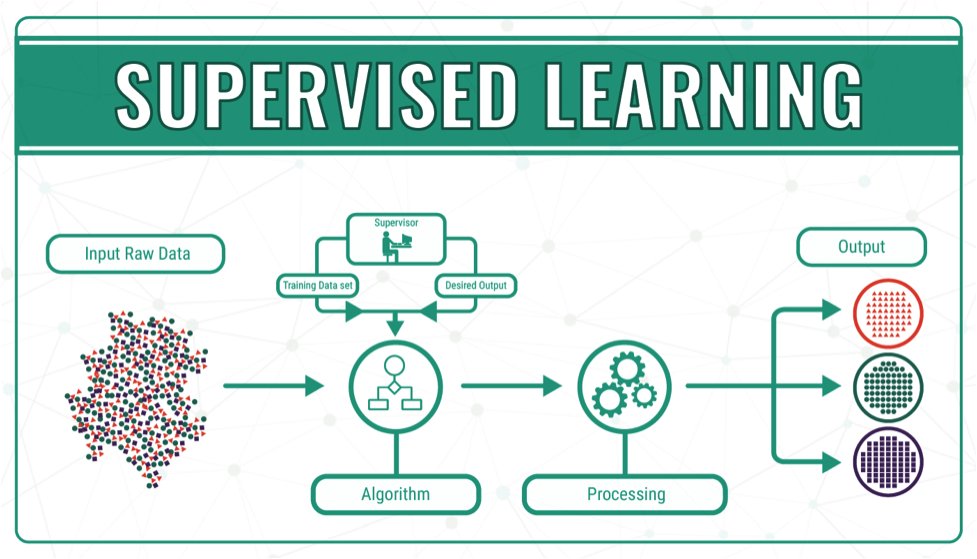
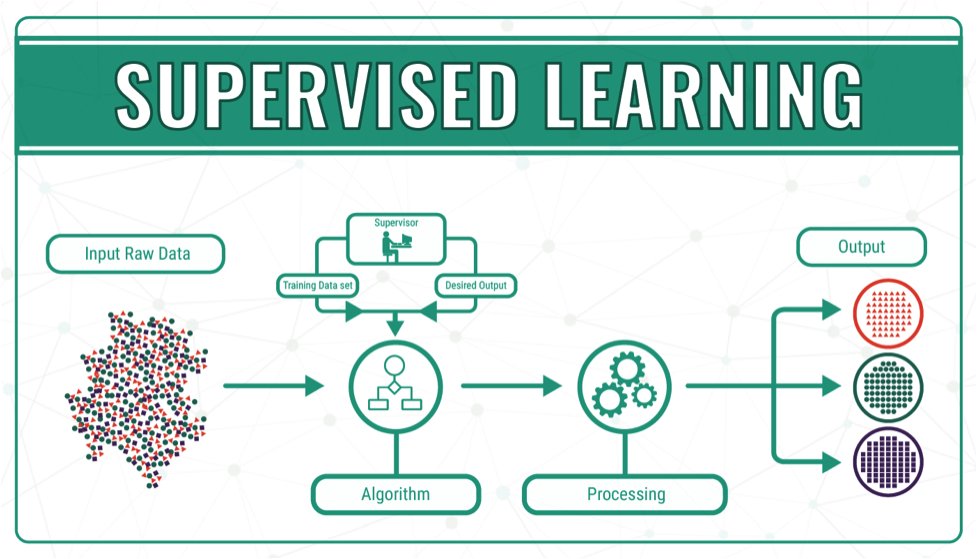
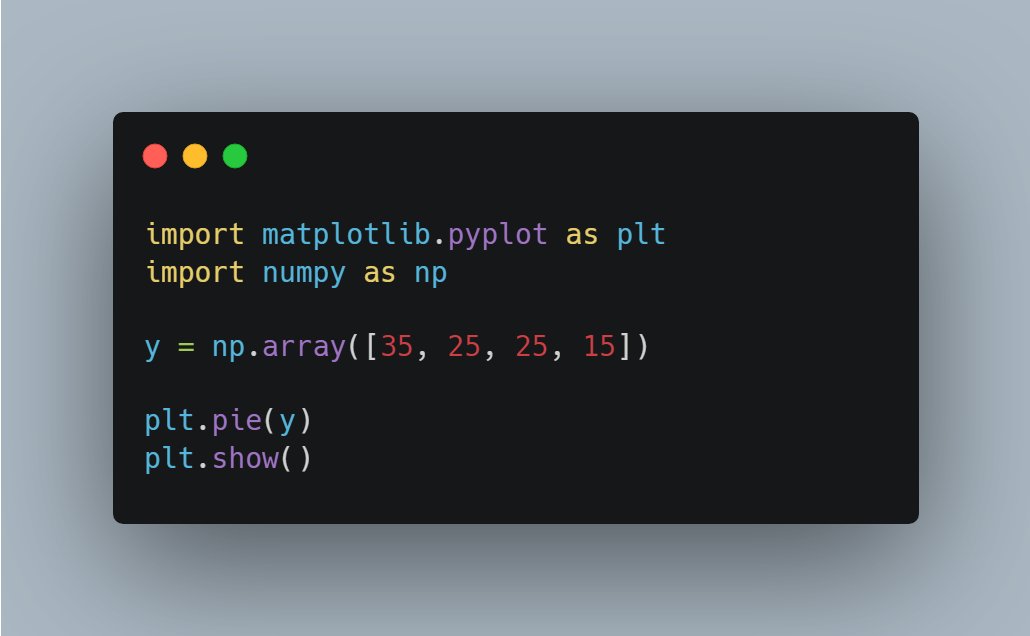
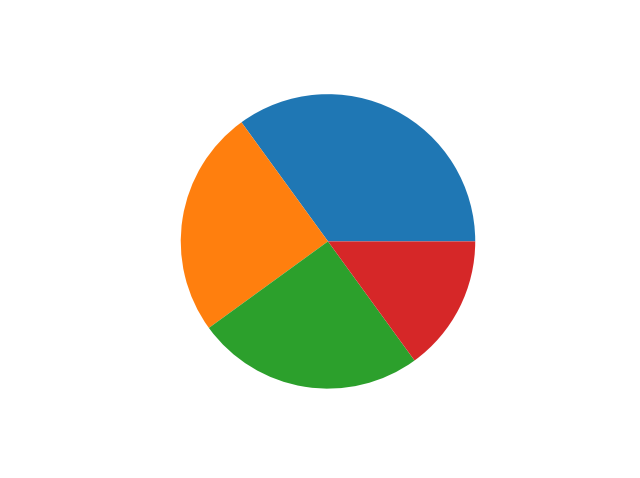
Day 41 of #60daysOfMachineLearning
🔷 Machine Learning 🔷
Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence that involves giving computers the ability to learn from data without being explicitly programmed.
🔷 Machine Learning 🔷
Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence that involves giving computers the ability to learn from data without being explicitly programmed.
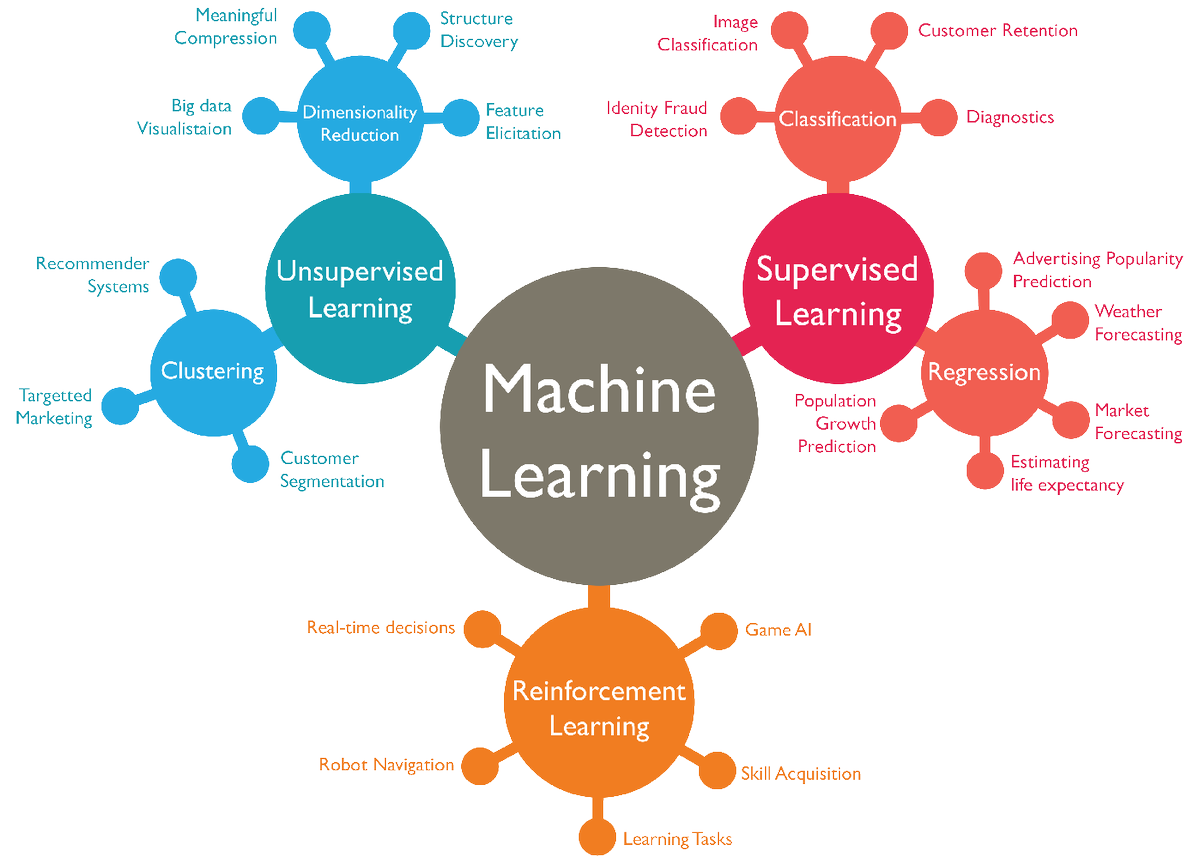
This is achieved by training the computer on a large amount of data, and then allowing it to use what it has learned to make predictions or take actions on new data.
In other words, it is a method of teaching a computer to make decisions or take actions based on the data it has been given, rather than following a set of rules or instructions provided by a human.
This can be a powerful tool for solving complex problems, and it is being used in a wide range of applications, from self-driving cars to medical diagnosis.
Machine learning allows us to make better decisions, faster and more accurately, by harnessing the power of data and algorithms. It is a key part of the future of artificial intelligence, and it is already changing the way we live and work.
If you missed the previous days, don't worry! You can follow along and go back to day 1 by going to this link 👇
twitter.com/i/events/15879…
twitter.com/i/events/15879…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh