Myotonic disorders!
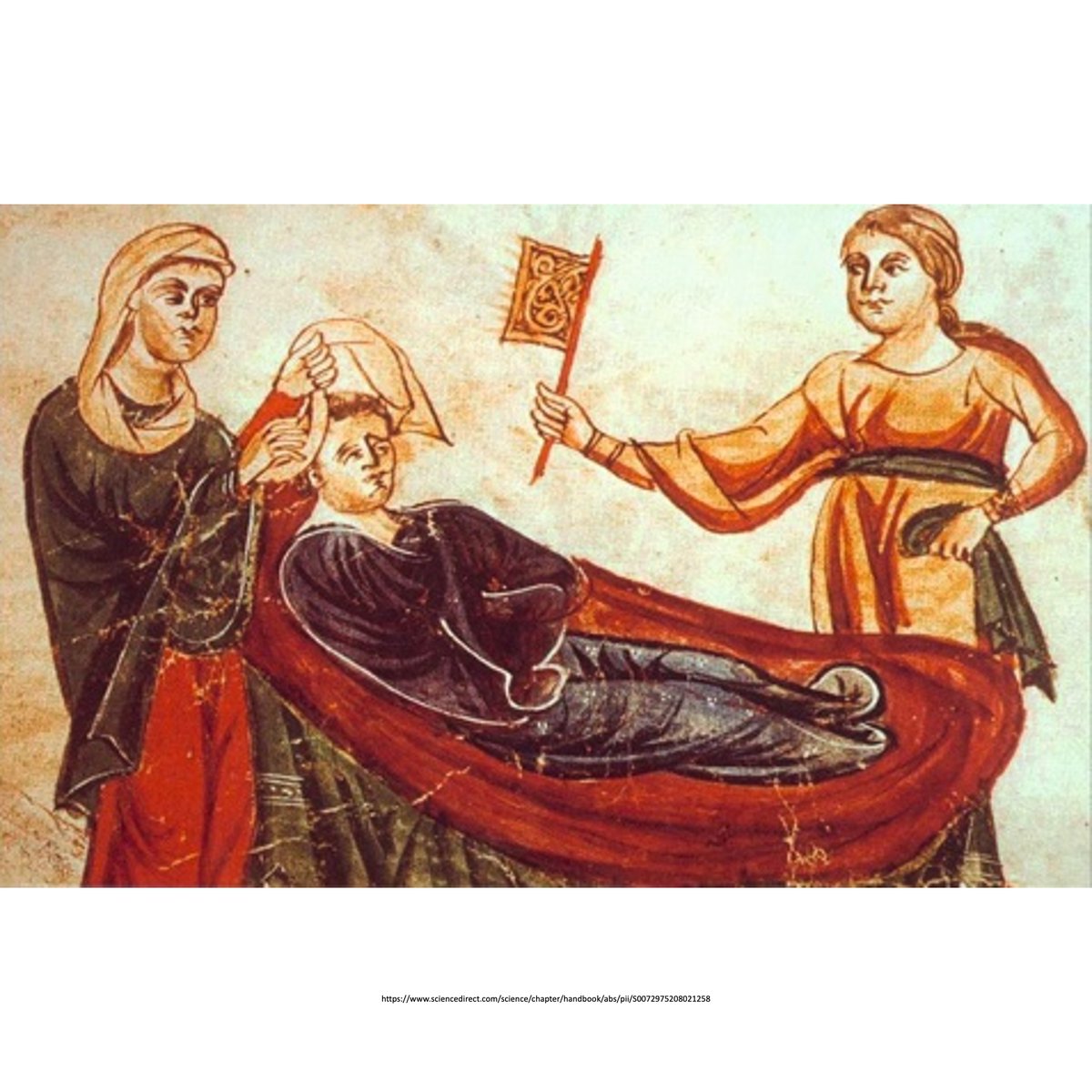
“after a fright, or in an unexpected joyous movement, this convulsive constriction occurs in all limbs…the victim can not stand upright”
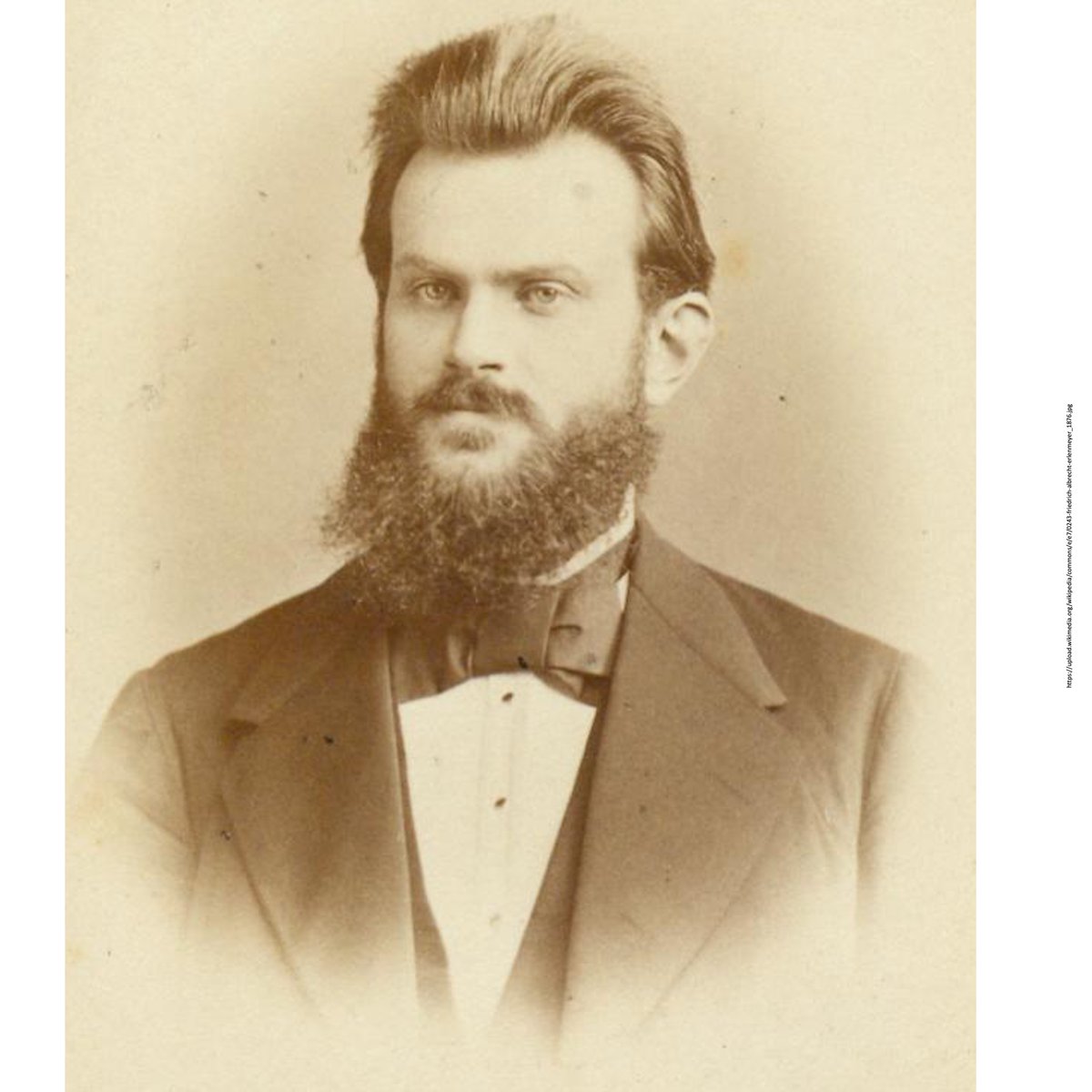
Prussian physician Asmus Julius Thomas Thomsen (1815–1896)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/
“after a fright, or in an unexpected joyous movement, this convulsive constriction occurs in all limbs…the victim can not stand upright”
Prussian physician Asmus Julius Thomas Thomsen (1815–1896)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/

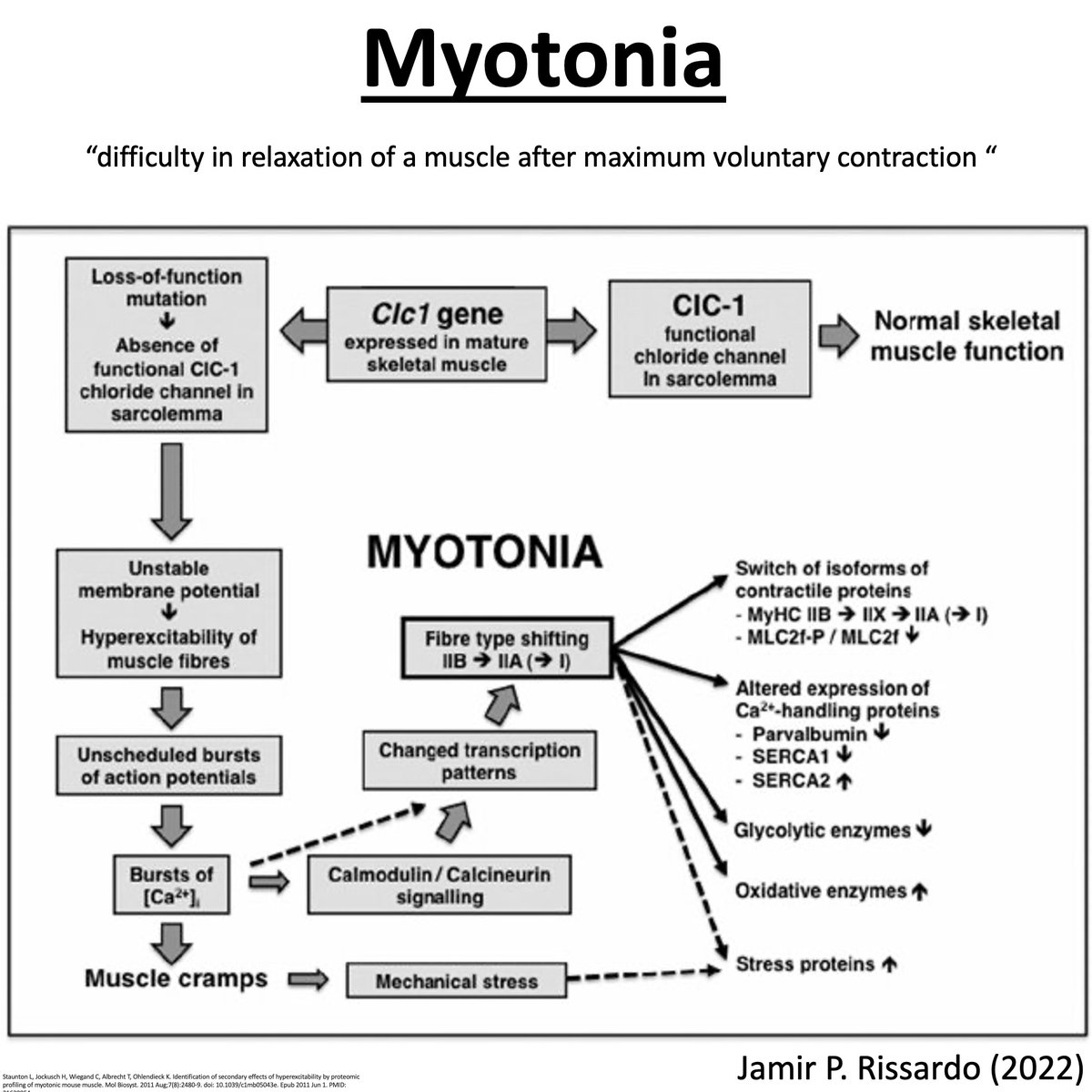
Definition
“difficulty in relaxation of a muscle after maximum voluntary contraction”
It can be specifically
- aggravated by conditions
- affecting regions of the body
- triggered
2/
“difficulty in relaxation of a muscle after maximum voluntary contraction”
It can be specifically
- aggravated by conditions
- affecting regions of the body
- triggered
2/
Myotonic or Tennessee fainting goat
“important in history due to role of chloride channel in muscle excitation”
- 1880s, Marshall County
- CLCN1 gene
via: jimmywan87
3/
“important in history due to role of chloride channel in muscle excitation”
- 1880s, Marshall County
- CLCN1 gene
via: jimmywan87
3/
Electrophysiology
Waxing & wanning of both amplitude & frequency
Potentials
- repetitive discharges
- 2 types: biphasic (<5ms) and positive waves (5-20ms)
5/
Waxing & wanning of both amplitude & frequency
Potentials
- repetitive discharges
- 2 types: biphasic (<5ms) and positive waves (5-20ms)
5/
Dive-bomber
“High frequency discharges in EMG that vary in amplitude & frequency, waxing & waning continuously with firing frequencies ranging from 150/second down to 20/second and producing a sound that has been referred to as a dive bomber sound
*turn sound on
6/
“High frequency discharges in EMG that vary in amplitude & frequency, waxing & waning continuously with firing frequencies ranging from 150/second down to 20/second and producing a sound that has been referred to as a dive bomber sound
*turn sound on
6/
Eyelid myotonia
“tries to open his eyes after having squeezed them tight”
- persist 1-2 minutes
- recruit additional muscles: frontalis
via: neurosigns.org
8/
“tries to open his eyes after having squeezed them tight”
- persist 1-2 minutes
- recruit additional muscles: frontalis
via: neurosigns.org
8/
Tongue myotonia
“tongue protrude, place a depressor on it, hit the tongue depressor with a reflex hammer”
- not clinically visible on inspection
- knot on the side of the tongue after percussion
(Handkerchief knot sign)
doi.org/10.1056/nejmic… VIA: NEJM
9/
“tongue protrude, place a depressor on it, hit the tongue depressor with a reflex hammer”
- not clinically visible on inspection
- knot on the side of the tongue after percussion
(Handkerchief knot sign)
doi.org/10.1056/nejmic… VIA: NEJM
9/
Handgrip myotonia
“make a fist and then fully open the hand”
- open of the fist require other hand
doi.org/10.1056/nejmic… via: NEJM
10/
“make a fist and then fully open the hand”
- open of the fist require other hand
doi.org/10.1056/nejmic… via: NEJM
10/
Handgrip myotonia
can also be noticed
“after a percussion of thenar eminence”
via: Fahad Hossain
11/
can also be noticed
“after a percussion of thenar eminence”
via: Fahad Hossain
11/
Warm-up phenomenon vs paramyotonia
Warm-up phenomenon
-repeated contraction improve myotonia
-usually, after 6 attempts
Paramyotonia (paradoxical myotonia)
-repeated contraction worse myotonia
-usually, in the eyes
-paramyotonia congenita & hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
12/
Warm-up phenomenon
-repeated contraction improve myotonia
-usually, after 6 attempts
Paramyotonia (paradoxical myotonia)
-repeated contraction worse myotonia
-usually, in the eyes
-paramyotonia congenita & hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
12/

Lid lag myotonia
“delay btw eyeball movement and the upper eyelid movement when performing quick vertical eye movements”
-especially, looking up and asked to look rapidly downward, while head still & straight
-staring gaze for 1min
doi.org/10.1212/WNL.00… via: Neurology
13/
“delay btw eyeball movement and the upper eyelid movement when performing quick vertical eye movements”
-especially, looking up and asked to look rapidly downward, while head still & straight
-staring gaze for 1min
doi.org/10.1212/WNL.00… via: Neurology
13/
Tented Mouth
“triangular appearance of the oral aperture with the apex in the midpoint of the upper vermilion and the lower vermilion forming the base”
- congenital myotonic dystrophy
14/
“triangular appearance of the oral aperture with the apex in the midpoint of the upper vermilion and the lower vermilion forming the base”
- congenital myotonic dystrophy
14/

Smooth muscle myotonia
- rare, in nondystrophic types
Can lead to
- dysphagia; esophagus
- abdominal pain & vomiting; GIT
- gallstones; delayed emptying gallbladder
Cesarean delivery recommended due to incoordinate contraction of uterus
17/
- rare, in nondystrophic types
Can lead to
- dysphagia; esophagus
- abdominal pain & vomiting; GIT
- gallstones; delayed emptying gallbladder
Cesarean delivery recommended due to incoordinate contraction of uterus
17/
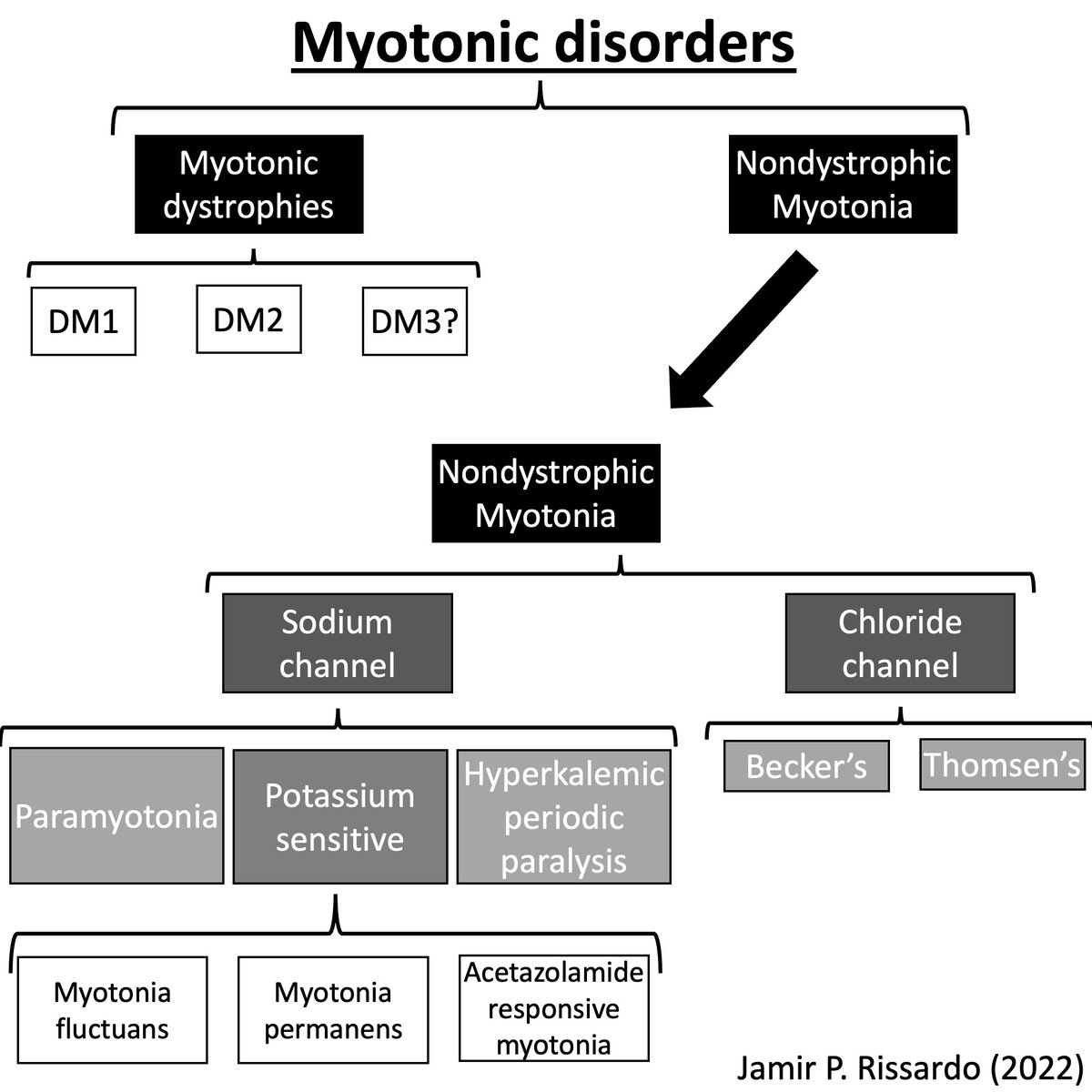
Myotonic dystrophies
DM 1
- CTG trinucleotide repeat on DMPK gene
- most common myotonic disorder
DM 2
- CCTG tetranucleotide repeat on CNBP gene
- rare disorder
18/
DM 1
- CTG trinucleotide repeat on DMPK gene
- most common myotonic disorder
DM 2
- CCTG tetranucleotide repeat on CNBP gene
- rare disorder
18/

Non dystrophic myotonia - chloride channel
•No systemic effects, normal lifespan
Becker
- AR
- severe & progressive
Thomsen
- AD
- mild & nonprogressive
21/
•No systemic effects, normal lifespan
Becker
- AR
- severe & progressive
Thomsen
- AD
- mild & nonprogressive
21/

Non dystrophic myotonia – sodium channel
3 types:
- potassium-sensitive
- paramyotonia
- hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
They are AD & caused by mutation in SCN4A gene
22/
3 types:
- potassium-sensitive
- paramyotonia
- hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
They are AD & caused by mutation in SCN4A gene
22/

Potassium-sensitive myotonia (potassium aggravated myotonia)
Exacerbated by potassium, but not to cold
3 variants
- fluctuans (intermittent related to exercise)
- permanens (constant w/ worsening periods)
- acetazolamide-responsive
23/
Exacerbated by potassium, but not to cold
3 variants
- fluctuans (intermittent related to exercise)
- permanens (constant w/ worsening periods)
- acetazolamide-responsive
23/
Paramyotonia congenita
Paradoxical myotonia
1st signs of stiffness as prolonged eye closure, after
- crying
- sleep near a fan
- washing face w/ cold water
24/
Paradoxical myotonia
1st signs of stiffness as prolonged eye closure, after
- crying
- sleep near a fan
- washing face w/ cold water
24/
Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
“early childhood w/ episodes of periodic weakness”
- attacks in the morning & fasting
- 3 variants: HyperKPP w/o myotonia; w/ myotonia; w/ paramyotnia
25/
“early childhood w/ episodes of periodic weakness”
- attacks in the morning & fasting
- 3 variants: HyperKPP w/o myotonia; w/ myotonia; w/ paramyotnia
25/
Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (chondrodystrophic myotonia)
"prominent and diffuse myotonia that is present at birth"
26/
"prominent and diffuse myotonia that is present at birth"
26/

Electrodiagnostic tests
a.muscle cooling
AD myotonia congenita (MC), burst
PMC, silence➡️contracted
b.short exercise test
AD MC, drop w/ quick recover
AR MC, decremental
PMC, decremental w/ slow recover
c.prolong exercise test
AR, quick recover
HyperKPP, slow recover
27/
a.muscle cooling
AD myotonia congenita (MC), burst
PMC, silence➡️contracted
b.short exercise test
AD MC, drop w/ quick recover
AR MC, decremental
PMC, decremental w/ slow recover
c.prolong exercise test
AR, quick recover
HyperKPP, slow recover
27/
NeuroTeach - Content
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh