Inverted & Perverted Reflexes
The first description of the paradoxical (inverted) triceps reflex
French neurologist Alexandre-Achille Souques (1860–1944)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/
The first description of the paradoxical (inverted) triceps reflex
French neurologist Alexandre-Achille Souques (1860–1944)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/

Definition
“elicitation of the movement opposite to that normally seen when the reflex is elicited”
2/
“elicitation of the movement opposite to that normally seen when the reflex is elicited”
2/
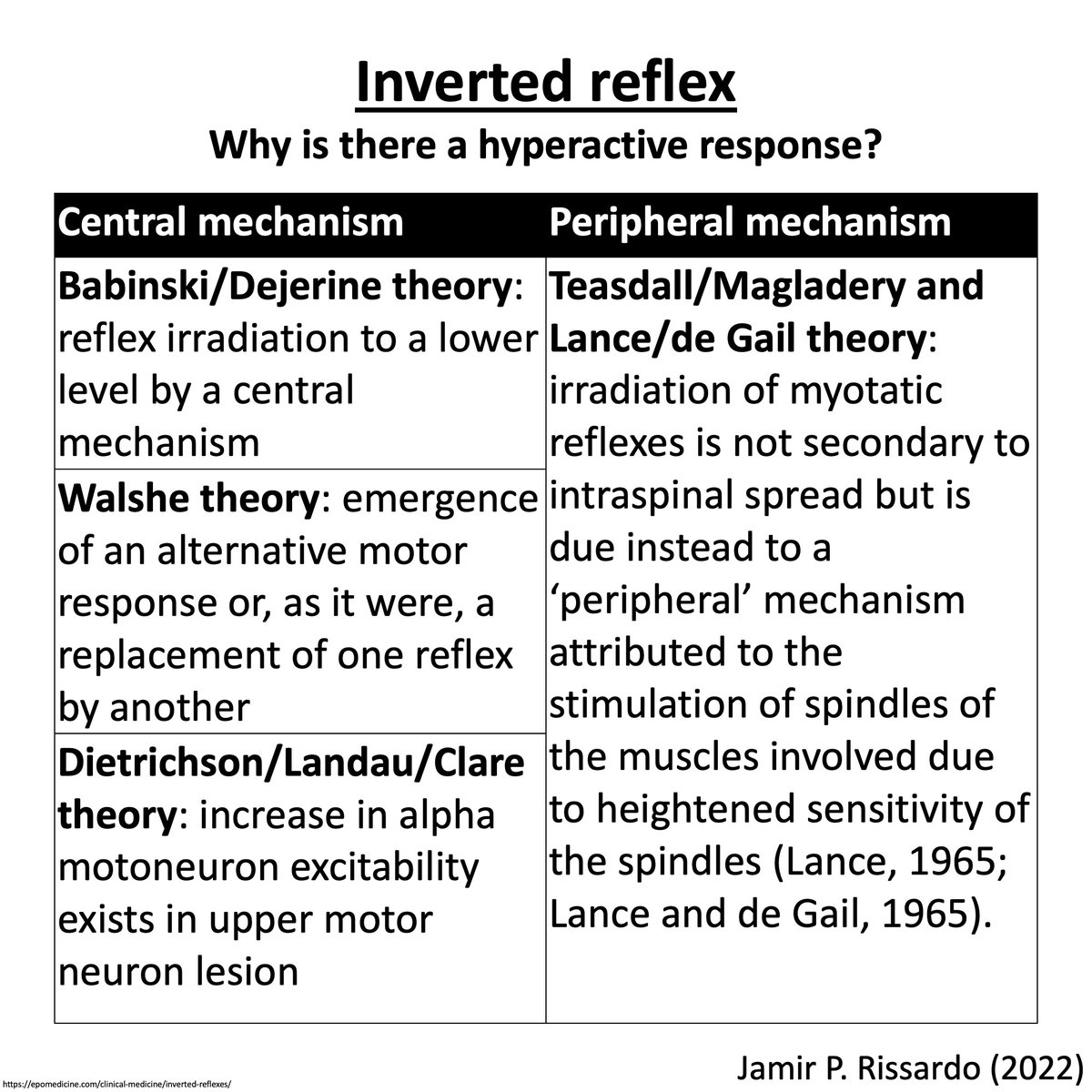
Mechanism
“a lesions simultaneously affecting the roots and spinal cord”
Damaged root
- interrupt local reflex
- absence of contraction
Damaged spinal cord
- interrupt corticospinal tract
- hyperactive response of the lower spinal segment
3/
“a lesions simultaneously affecting the roots and spinal cord”
Damaged root
- interrupt local reflex
- absence of contraction
Damaged spinal cord
- interrupt corticospinal tract
- hyperactive response of the lower spinal segment
3/
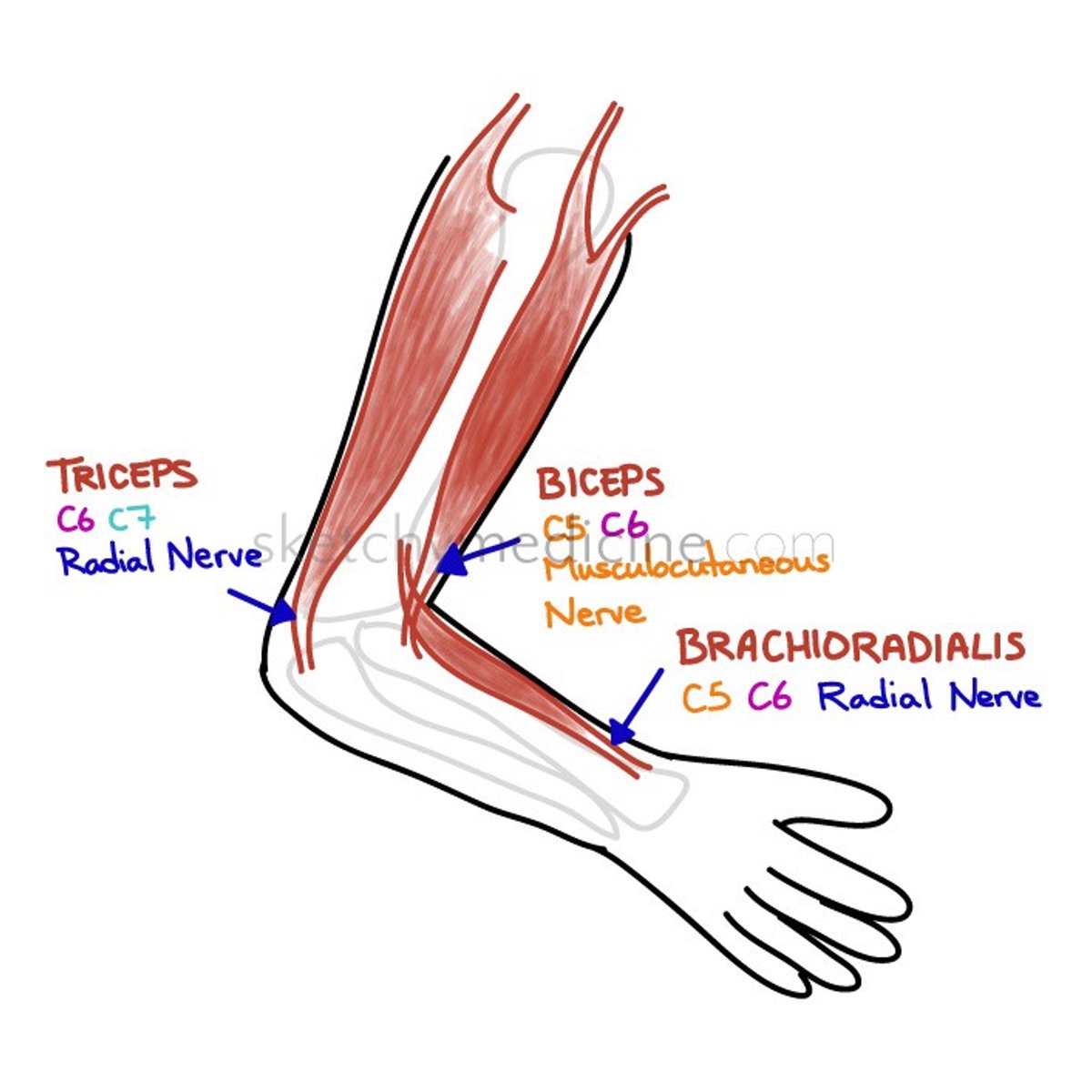
Inverted radial (supinator) reflex
Level of pathology: C5/6
Positive response: Flexion of fingers and extension of elbow rather than elbow flexion when eliciting the supinator (brachioradialis) jerk.
5/
Level of pathology: C5/6
Positive response: Flexion of fingers and extension of elbow rather than elbow flexion when eliciting the supinator (brachioradialis) jerk.
5/

Inverted radial (supinator) reflex
via: Dr Mahyuddin Mohamed
7/
via: Dr Mahyuddin Mohamed
7/
Inverted radial (supinator) reflex
via: Oren Goltzer
8/
via: Oren Goltzer
8/
Paradoxical (inverted) triceps reflex
Level of pathology: C7/8
Positive response: Flexion of elbow rather than extension when eliciting the triceps jerk.
via: MedAruth
9/
Level of pathology: C7/8
Positive response: Flexion of elbow rather than extension when eliciting the triceps jerk.
via: MedAruth
9/
Inverted biceps reflex
Level of pathology: C5/6
Positive response: Extension of elbow rather than flexion when eliciting the biceps jerk.
11/
Level of pathology: C5/6
Positive response: Extension of elbow rather than flexion when eliciting the biceps jerk.
11/
Inverted knee jerk
Level of pathology: L2/3/4
Positive response: Flexion of knee (hamstring contraction) rather than knee extension when eliciting the knee or quadriceps jerk.
12/
Level of pathology: L2/3/4
Positive response: Flexion of knee (hamstring contraction) rather than knee extension when eliciting the knee or quadriceps jerk.
12/
Special
Absent quadriceps reflex with distant toe flexor response
Level of pathology: L3/4
doi.org/10.1016/j.clin… via: Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery
13/
Absent quadriceps reflex with distant toe flexor response
Level of pathology: L3/4
doi.org/10.1016/j.clin… via: Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery
13/
Clinical clues
C5 lesion – inverted biceps
C6 lesion – inverted radial
C7 lesion – inverted triceps
14/
C5 lesion – inverted biceps
C6 lesion – inverted radial
C7 lesion – inverted triceps
14/
NeuroTeach - Content
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh